Optic Nerve
This nerve of vision is 4 cm long. About 1 million myelinated nerve fibres create it. It comes from the eyeball, 3 or 4 millimeters nasal to the posterior pole of the eyeball. It runs backwards and medially, it joins the optic chiasma when it goes through the optic canal to goes into the cranial cavity. The nerve is originated from the meninges of the brain and is enclosed in 3 meningeal sheaths. The subarachnoid space around the brain, thus, goes around the nerve up to the eyeball.
Connections
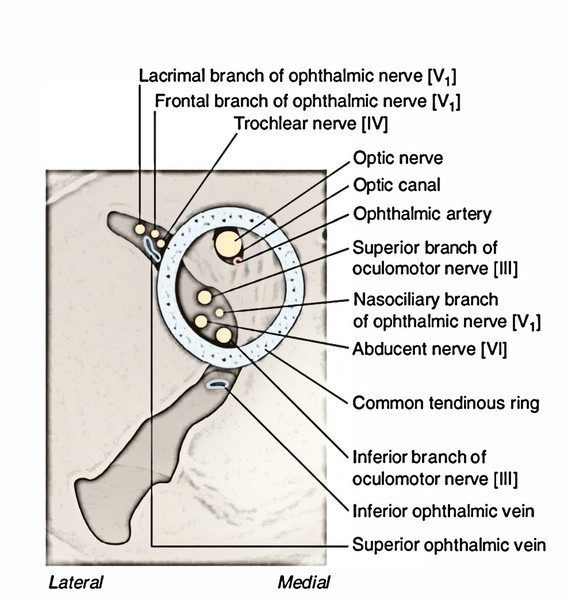
The central artery and vein of the retina pierce the optic nerve infero-medially about 1.25 cm behind the eyeball. The optic nerve is crossed superiorly from before backwards by:
- superior ophthalmic vein
- ophthalmic artery
- nasociliary nerve
- Mnemonic: VAN
Oculomotor Nerve
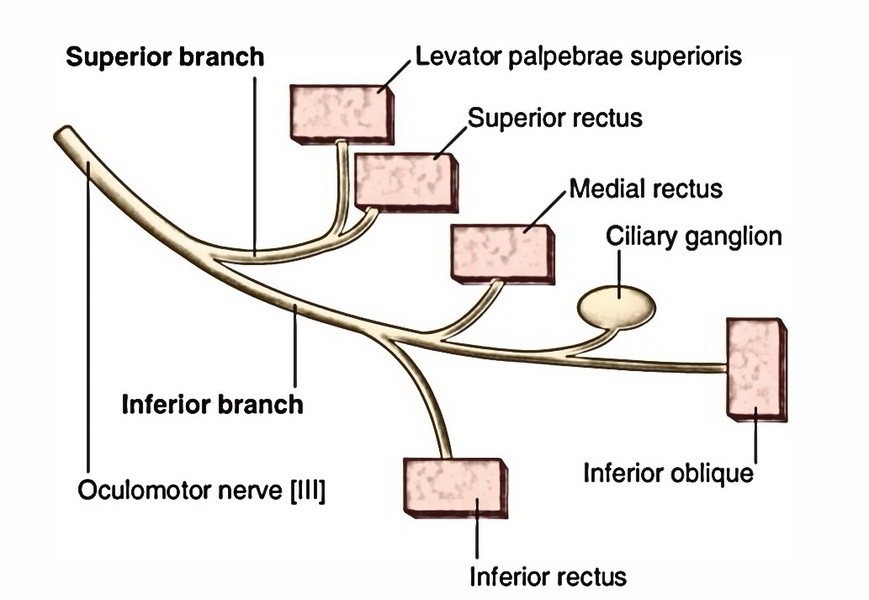
The 2 sections of oculomotor nerve goes into the orbit via superior orbital fissure inside the common tendinous ring. Here the nasociliary nerve is located between the 2 sections.
The smaller superior office runs forwards above the optic nerve and supplies the superior rectus, then pierces it to supply the levator palpebrae superioris.
The bigger inferior division enters below the optic nerve and breaks up into 3 branches to supply medial rectus, inferior rectus and inferior oblique.
The nerve to inferior oblique produces the parasympathetic motor root to the ciliary ganglion.
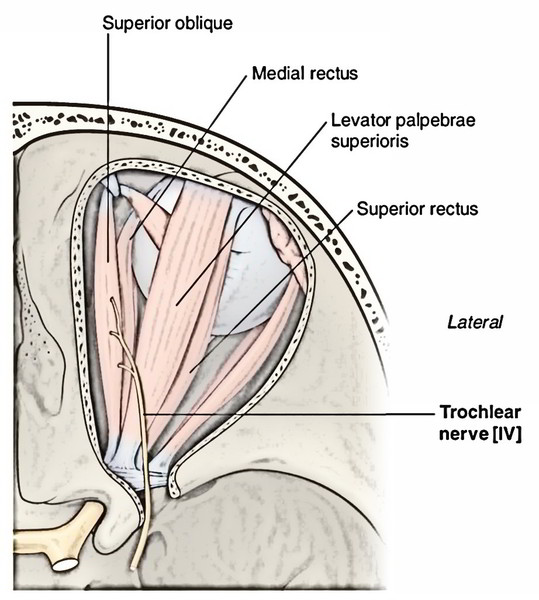
Trochlear Nerve
The trochlear nerve enters the orbit via the superior orbital fissure superolateral to the common tendinous ring and curves medially above the levator palpebrae superioris to reach deep to the posterior part of superior oblique, which it supplies.
Abducent Nerve
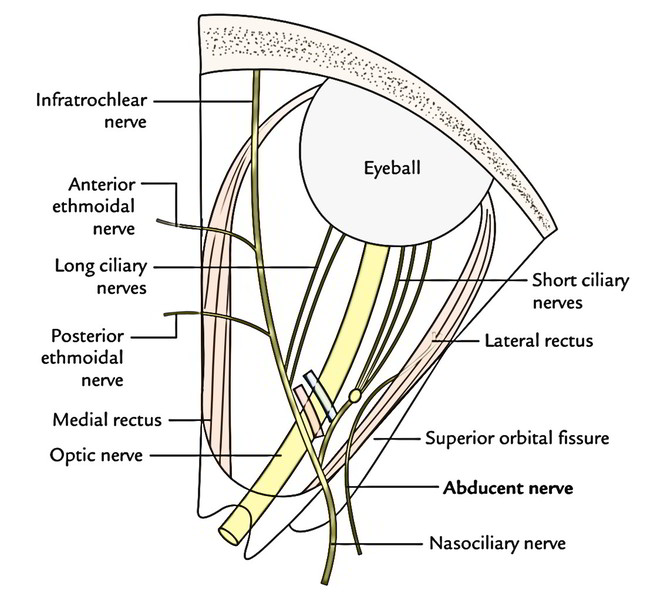
The abducent nerve enters the orbit via superior orbital fissure inside the common tendinous ring lateral to 2 sections of the oculomotor nerve and nasociliary nerve, turns laterally far from optic nerve to go into the posterior part of lateral rectus.
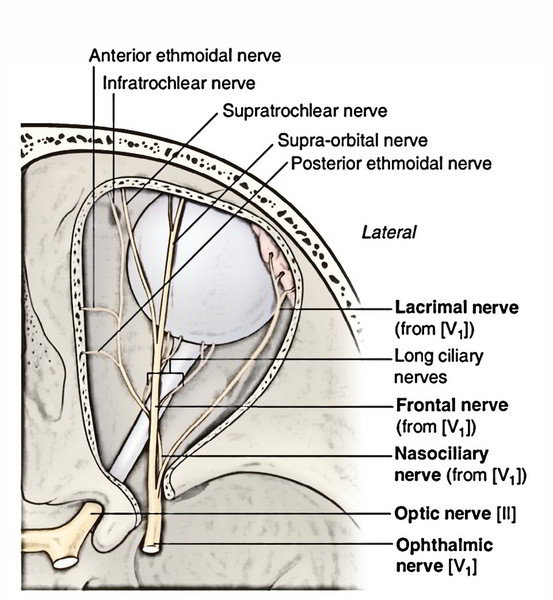
Ophthalmic Nerve
The ophthalmic nerve is the first and the smallest of the 3 sections of trigeminal nerve. It’s only sensory.
Course and Connections
It originates from medial part of the convex anterior border of the trigeminal ganglion. It pierces the dura mater of the trigeminal cavern and enters into the lateral wall of the cavernous sinus where it is located below the trochlear nerve. It enters the orbit via superior orbital fissure by splitting into 3 branches: lacrimal, frontal and nasociliary.
Branches and Distribution
Lacrimal nerve (smallest branch) runs along the lateral wall of the orbit alongside lacrimal artery and ends in the lacrimal gland (for this reason its name). It’s joined by a conveying twig from the zygomaticotemporal branch of the maxillary nerve carrying postganglionic secretomotorfibres to the lacrimal gland The lacrimal Nerve Supplies lacrimal gland and conjunctiva. Afterward it pierces orbital septum to supply the lateral part of the skin of upper eyelid.
Frontal nerve (largest branch) runs forwards between levator palpebrae superioris and periosteum lining the roof of the orbit. In the middle of orbit, it breaks up into large supraorbital and small supratrochlear nerves:
- Supraorbital nerve continues in the line of the frontal nerve to go through supraorbital pass, where it turns upwards into the brow and splits into medial and lateral branches, which supply the scalp as much back as the vertex.
- Supratrochlear nerve runs forwards medial to the supraorbital nerve. It enters above the trochlea for tendon of superior oblique muscle and after that turns upwards along the superior orbital margin and supplies the skin of the lower part of the brow.
- Nasociliary nerve runs forwards and medially, crossing the optic nerve from above and from lateral to medial side behind the ophthalmic artery. On reaching the medial wall of the orbit, it ends by breaking up into anterior ethmoidal and infratrochlear nerves.
It supplies these branches:
- Sensory root to the ciliary ganglion is given just before crossing the optic nerve.
- Long ciliary nerves, 2 or 3, originate from nasociliary nerve as it crosses the optic nerve. They pass forward, goes into theeyeball and supply sensory fibres to the ciliary body, iris and cornea.
- The long ciliary nerves also carry some postganglionic sympathetic fibres to the dilator pupillae.
- Posterior ethmoidal nerve enters the posterior ethmoidal foramen and supplies the ethmoidal and sphenoidal air sinuses.
- Anterior ethmoidal nerve enters the anterior ethmoidal foramen and after that goes through anterior ethmoidal canal to get to the anterior cranial fossa. Now it runs forwards over the cribriform plate of ethmoid and enters the nasal cavity by going through a nasal slit in the side of crista galli. In the nasal cavity, the nerve is located in the groove on the posterior surface of the nasal bone and supplies internal nasal branches to the nasal septum and lateral wall of the nose. At the lower border of the nasal bone, the nerve leaves the nasal cavity and appears on the dorsum of nose as external nasal nerve.
Infratrochlear nerve runs forwards on the medial wall of the orbit just below the trochlea and ends by supplying the skin of upper eyelid.
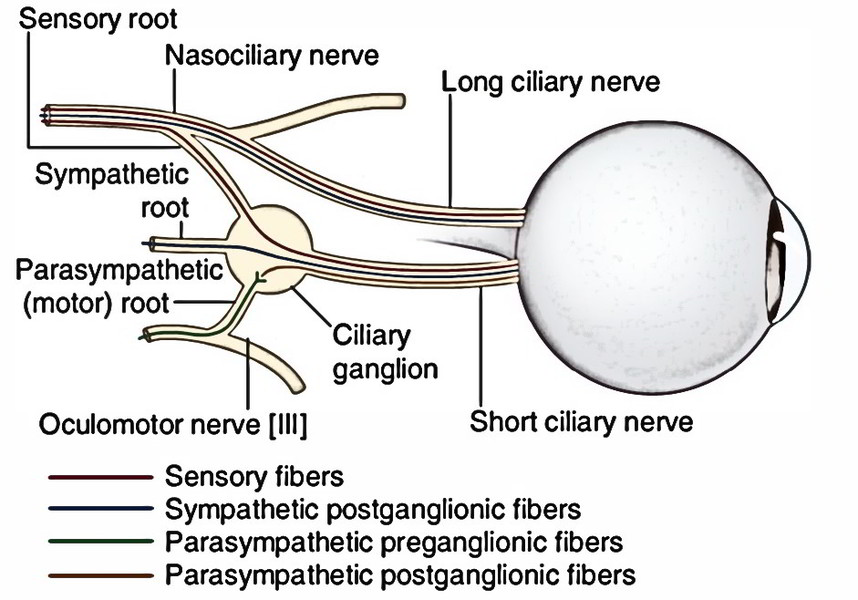
Ciliary Ganglion
It’s a peripheral parasympathetic ganglion, joined with the nasociliary nerve. In spite of the fact that topographically it’s linked to the nasociliary nerve from ophthalmic division of the trigeminal, but functionally it’s linked to the oculomotor nerve.
Location
It’s a tiny body (2 millimeters in diameter) being located near the apex of orbit between the optic nerve and lateral rectus muscle.
Roots
3 roots goes into its posterior end. All these are as follows:
- Motor (parasympathetic) root: It’s originated from nerve to inferior oblique and is composed of preganglionic parasympathetic fibres from EdingerWestphal nucleus. These fibres relay in the ganglion. The postganglionic parasympathetic fibres originate from the cells of the ganglion and go through short ciliary nerves to supply the ciliary muscle and sphincter pupillae.
- Sensory root: It’s originated from nasociliary nerve. It is composed of sensory fibres (for pain, touch and temperature) from eyeball, which go through the ciliary ganglion without relay.
- Sympathetic root: It’s originated from sympathetic plexus around internal carotid artery. It includes post ganglionic sympathetic fibres from superior cervical sympathetic ganglion. The fibres go through the ganglion without relay and additional go through short ciliary nerves to supply the dilator pupillae and blood vessels of the eyeball.
Branches
The branches of ciliary ganglion are short ciliary nerves (8-10). They include fibres from all the 3 roots, run above and below the optic nerve to the eyeball. On reaching the eyeball they pierce the sclera around the connection ofthe optic nerve and pass forwards in the space between the sclera and choroid to reach the target organs.
Clinical Significance
The ciliary ganglion is obstructed to produce dilatation of pupil before cataract extraction.
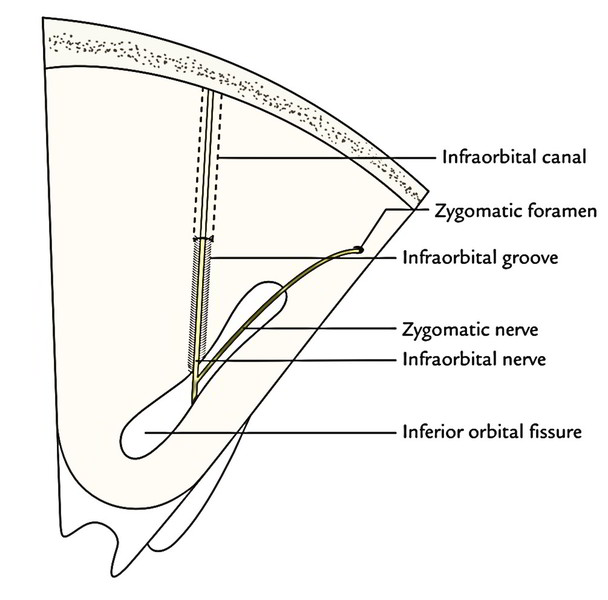
Infra orbital and Zygomatic Nerves
They be located outside the periosteum of the orbit.

 (52 votes, average: 4.52 out of 5)
(52 votes, average: 4.52 out of 5)