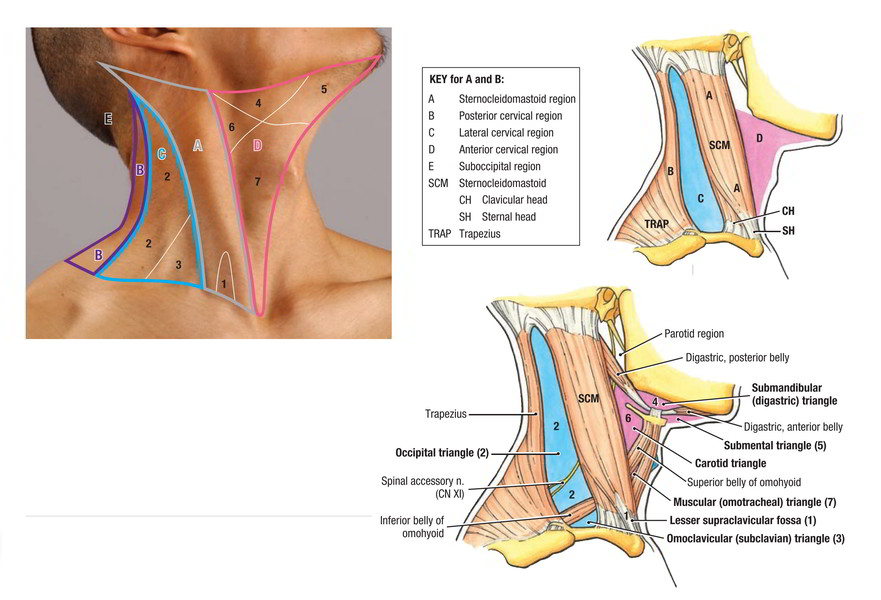
It is about quadrangular in shape. It’s bounded superiorly by the lower border of the body of the mandible, anteriorly by anterior midline of the neck, posteriorly by anterior border of the trapezius and inferiorly by the clavicle and a line stretching from the angle of the mandible to the mastoid process.
Interactive Anatomical Interface
Like lymphadenopathy, cysts, tumors, etc, the side of the neck is the common site for different pathological lesions. For performing different clinical procedures like biopsy, venepuncture, nerve block, etc it is also a regular site.
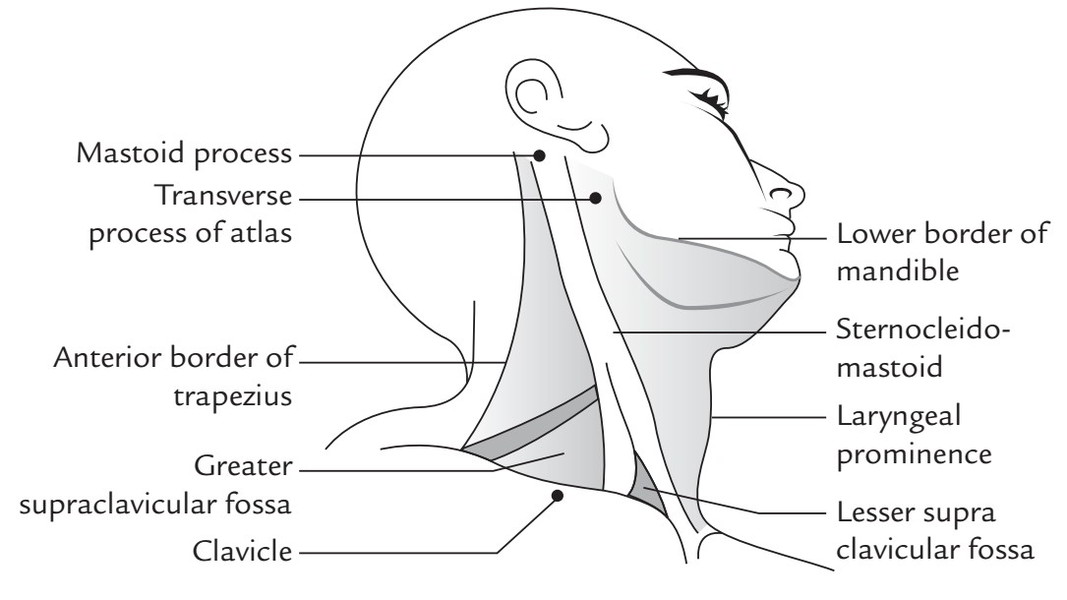
Surface Landmarks on the Side of the Neck
The most significant landmark on the side of the neck is sternocleidomastoid type. It is viewed as a raised ridge extending obliquely from the sternum to the mastoid process and becomes notable when the face is turned to the opposite side.
- Mastoid process is a large bony projection easily felt behind the lower part of the auricle.
- Anterior border of trapezius becomes notable when shoulder is elevated against the resistance.
- Lesser supraclavicular fossa is a small triangular depression above the medial end of the clavicle between the sternal and clavicular heads of sternocleidomastoid. It overlies the internal jugular vein.
- Greater supraclavicular fossa is a depression above the middle one-third of the clavicle. It overlies the cervical part of brachial plexus and the third part of the subclavian artery.
- Transverse process of first cervical vertebra can be felt on deep pressure midway between the angle of the mandible and mastoid process. It’s crossed by spinal accessory nerve.
- Lower border of the mandible can be easily felt by running a finger backwards from chin to the angle of the mandible.
- Clavicle being subcutaneous can be felt along its whole extent in the junction of the neck and chest.

 (51 votes, average: 4.59 out of 5)
(51 votes, average: 4.59 out of 5)