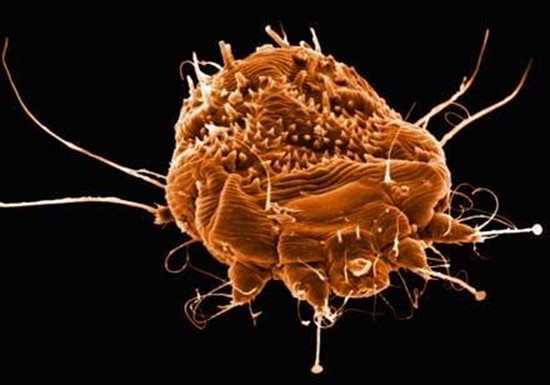
Scabies is an irritating, itchy rash resulting from tiny mite. The burrowing and egg laying of these mites create a rash that almost always changes the hands and fingers, especially the clefts between the fingers.
Scabies is observable as a fine grey line where the mite has burrowed into the skin, finishing in a black dot – the mite. Scabies may additionally change the ankles, feet, toes, elbows and the region around the genitals. When the eggs hatch, they’re readily passed to someone else by direct contact. They’re able to also be picked up from bedding or linen that’s infested with the mites.
What Are The Symptoms?
- Extreme itching.
- Burrows – excellent, short lines on the backs of the hands and the sides of the fingers that end in a black spot the size of a pinhead.
- Scabs on the itchy areas.
Scabies isn’t serious but it’s infectious and could run through a family or maybe even treated quickly. Consult your physician when possible if you imagine scabies or if you’re scraping a lot.
What Is The Treatment?
Your physician will prescribe an anti-parasitic lotion in adequate amount for everyone to be treated. All the skin must be treated for the lotion to be successful.
Self-Help
- Try not to scrape affected regions. This may hinder the physician’s analysis and cause sores to sort that could become infected.
- After thorough washing, you should paint the entire body below the neck with the lotion and leave to dry. Don’t wash it off for 24 hours. To ensure disinfestation, repeat the process a further 24 hours per day or two.
- Carry out the treatment for other members of the family concurrently.
- Launder or atmosphere all bedding and clothes to eradicate the mite. The mite doesn’t live for longer than five or six days after it’s removed from human skin.