Origin
The anterior ethmoidal nerve is a branch of the nasociliary nerve. The anterior ethmoidal nerve goes along with the anterior ethmoidal artery and along with the frontal bone exits the orbit in the middle of the ethmoidal labyrinth via a canal.
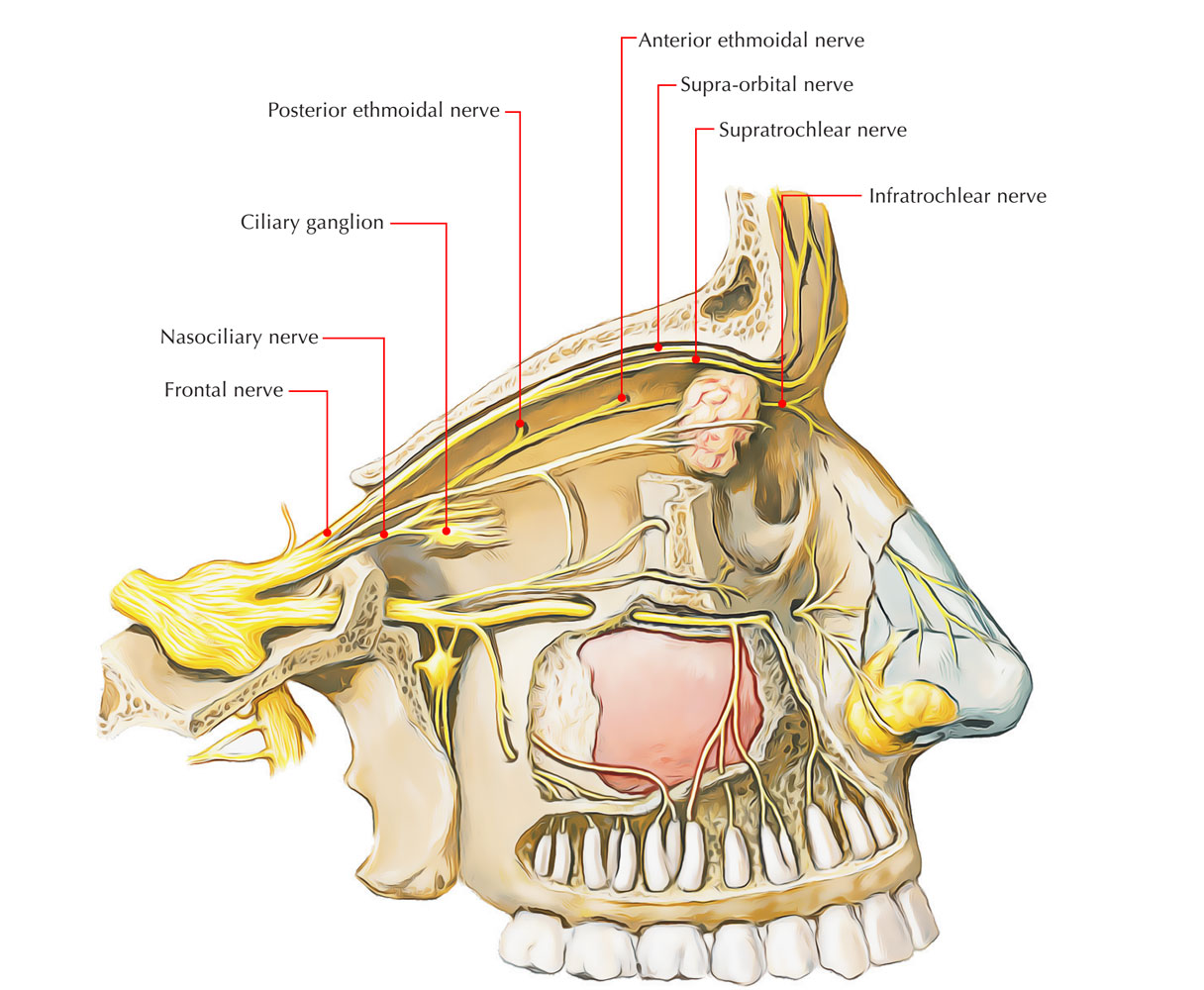
Anterior Ethmoidal Nerves
Insertion
It travels via and innervates the neighboring ethmoidal cells as well as frontal sinus, and afterwards moves directly lateral and superior towards the cribriform plate in the cranial cavity.
- It then travels forward in an indentation on the cribriform plate and also goes in the nasal cavity by directly going laterally towards the crista galli and downwards via a foramen.
- It has branches towards the medial and lateral wall of the nasal cavity and afterwards proceeds forward on the undersurface of the nasal bone.
Before ending as the external nasal nerve, it travels over the external surface of the nose from going in the middle of the nasal bone as well as lateral nasal cartilage.
Innervation
It innervates:
- Adjacent ethmoidal cells
- Frontal sinus
Clinical Significance
Anterior Ethmoidal Nerve Syndrome
Anterior ethmoidal nerve syndrome is referred to a sequence of indications produced from inflammation of the concluding divisions of the anterior ethmoidal nerve. The pain emerges are chiefly of the sinus type but also appear as headache or migraine.


 (92 votes, average: 3.72 out of 5)
(92 votes, average: 3.72 out of 5)