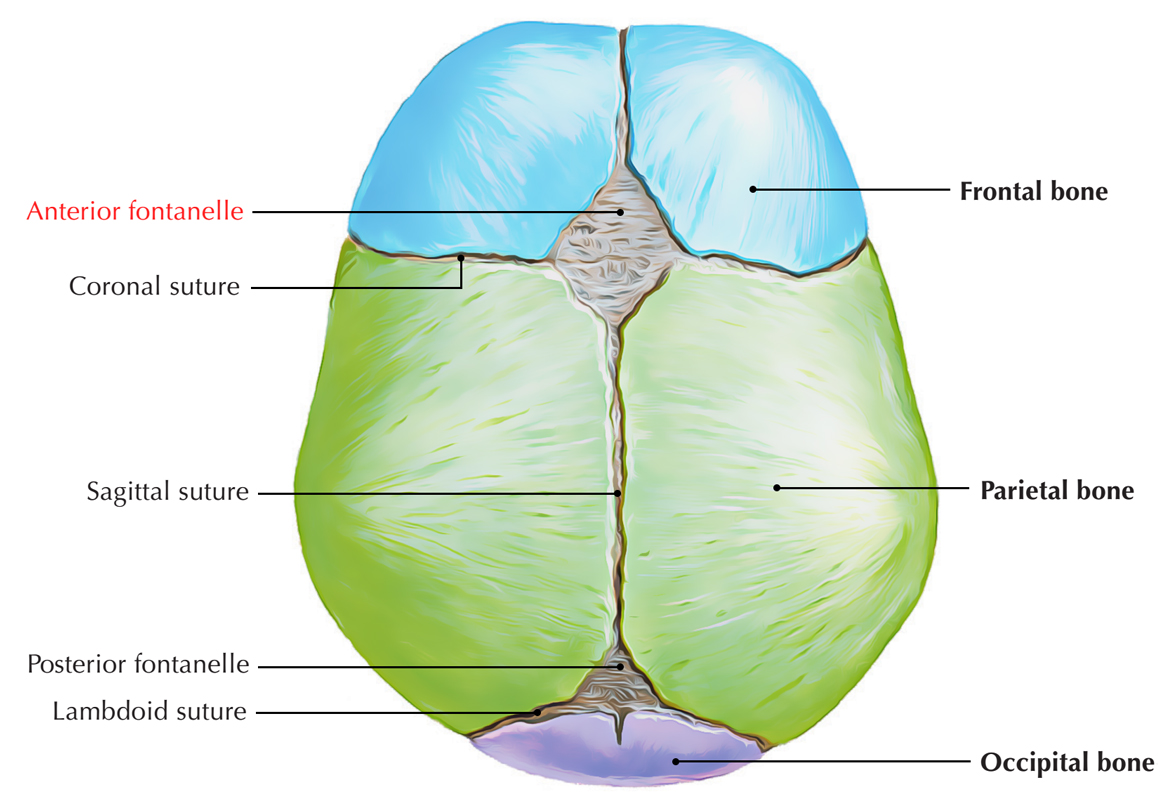
The anterior fontanelle a.k.a. bregmatic fontanelle or frontal fontanelle is the biggest among all the fontanelle and is located at the joint where the sagittal suture, coronal suture, and frontal suture merge.
Anterior Fontanelle
Structure
- Approximately, it is 4 cm in its anteroposterior and 5 cm in its transverse diameter.
- The margins of the two frontal bones and the two parietal bones confine the anterior fontanelle.
- The sutures give it a diamond-shaped outline.
- In sutural zones Islands of cartilage are always found, though in their degree of development, they diverge enormously.
- A deeply depressed fontanelle suggests diminished intracranial pressure similar to in toxic conditions and dehydration, even when the baby is lying flat.
- The anterior fontanelle may seal as early as 6 months or may remain open till the third year.
Functions
The fontanelle enables the skull in order to change its shape at the time of birth for facilitating its passage via the birth canal and also for enlargement of the brain after birth.
Clinical Significance
Congenital Hydrocephalus
- In healthy babies, the alterations created via heart beat and respiration in intracranial pressure are normally visible and detectible at the anterior fontanelle.
- In the neonates, at its greatest width the anterior fontanelle measures approximately 2 cm.
- However, in babies having congenital hydrocephalus is tense and flexible on palpation and it is significantly wider and protrudes outwards.
x

 (69 votes, average: 4.41 out of 5)
(69 votes, average: 4.41 out of 5)