Anterior scalene muscle a.k.a. Scalenus anterior is most superficial among scalene muscles and is located deep towards sternocleidomastoid muscle. It is situated in the middle of the subclavian vein and the subclavian artery. The roots of the brachial plexus travel posterior towards it. The phrenic nerve traverses its anterior surface. Due to its intimate attachments to many structures in this zone, it is the main muscle at the root of neck. It is a vital surgical marker.
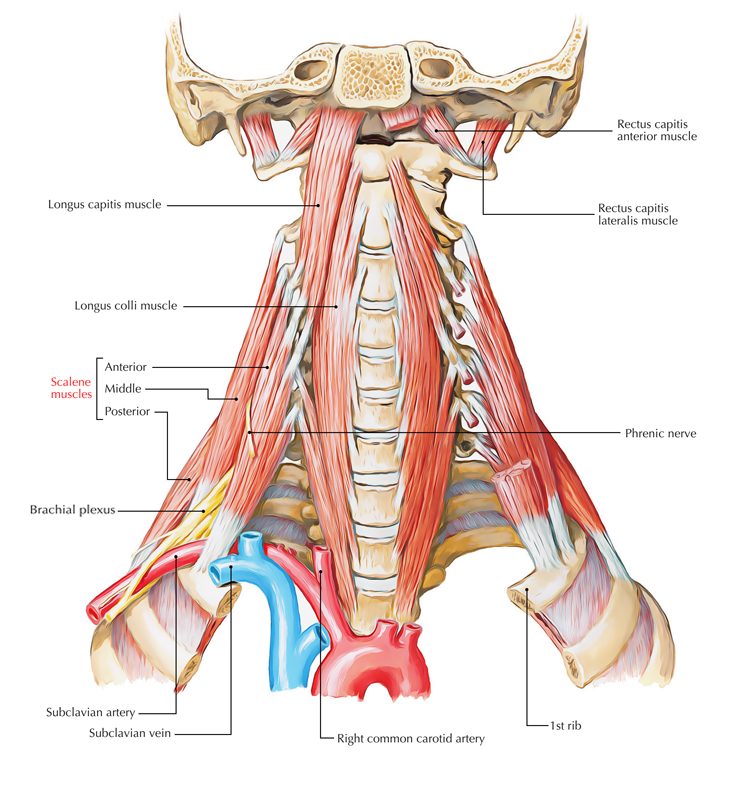
Anterior Scalene Muscle
Origin
It originates from anterior tubercles of transverse processes of vertebrae C3, C4, C5, and C6.
Insertion
The fibres join and move downwards almost vertically in order to be inserted by:
- A narrow, flat tendon towards the scalene tubercle on the inner rim of the 1st rib.
- Towards the ridge on the upper surface of the rib anterior to the groove for the subclavian artery.
Nerve Supply
Anterior scalene muscles are innervated by ventral rami of C4, C5, and C6 spinal nerves.
Actions
- Acting inferiorly, it bends the neck forwards and laterally.
- Rotates neck to the opposite side.
- It acts as a contributing muscle of respiration as it assists in order to lift up the 1st rib by functioning superiorly.
Relations
At the root of the neck, the scalenus anterior muscle creates a vital landmark due to:
- Phrenic nerve goes superficial towards it.
- Subclavian artery travels deep towards it.
- Brachial plexus is located at its lateral margin.
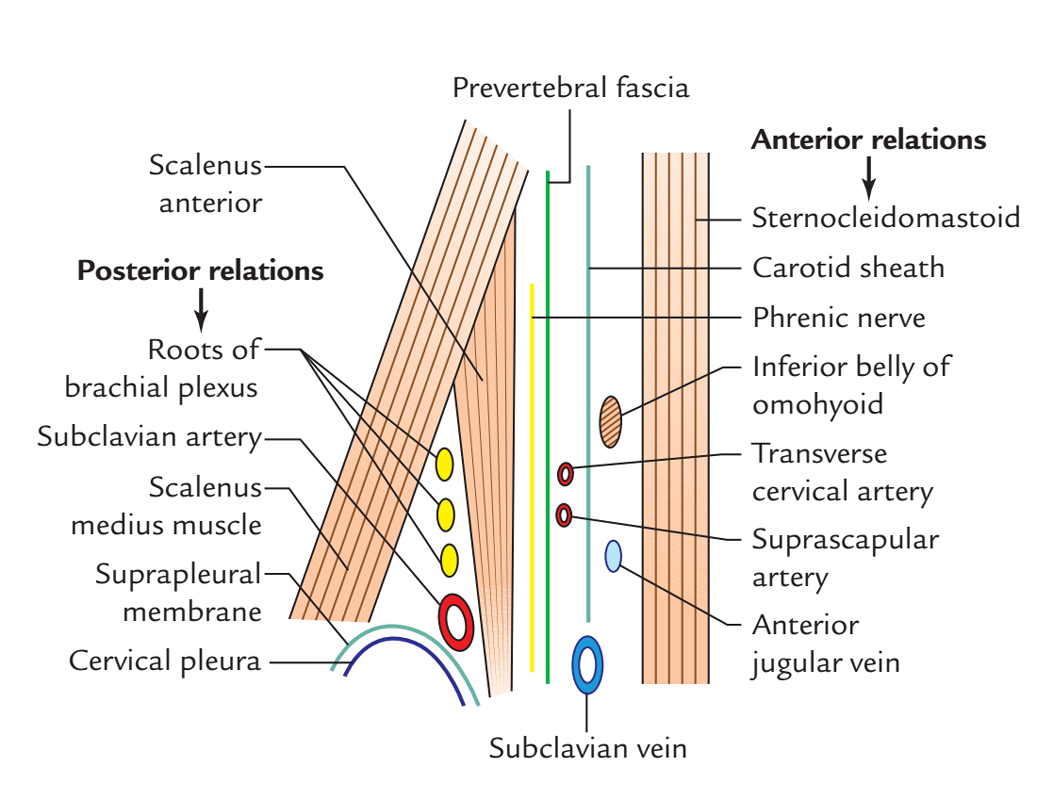
Anterior Scalene Muscle: Relations
Anterior Relations:
- Phrenic nerve
- Arteries:
- Transverse cervical
- Suprascapular
- Veins
- Anterior jugular Vein.
- Subclavian vein
- Two muscles
- Inferior belly of omohyoid muscle.
- Sternocleidomastoid (clavicular head).
- Carotid sheath is located perpendicularly opposite to the muscle.
- Clavicle Bone.
Posterior Relations:
- Roots of brachial plexus.
- Subclavian artery.
- Scalenus medius muscle (medial portion).
- Cervical pleura.
- Suprapleural membrane.
Other
- The lateral margin of the scalenovertebral triangle or triangle of the vertebral artery is created by the medial margin of scalenus anterior.
- The lateral margin of the scalenus anterior and trunks of brachial plexus are related to each other.
- The ascending cervical artery separates the upper part of scalenus anterior and longus capitis.
Clinical Significance
Scalene Syndrome
It includes complications that are created in the scalene triangle because of constriction of lower trunk of brachial plexus (C8 and T1) and subclavian artery:
- Lifting its base by the cervical rib.
- Due to spasm of scalene muscles.
Symptoms
- Stinging sensation and lack of sensation alongside the inner rim of forearm and hand.
- Gradual paresis and intrinsic muscles of the hand begin to waste.
- Due to constriction of subclavian artery, ischemic pain and deficiency of radial pulse.

 (55 votes, average: 4.33 out of 5)
(55 votes, average: 4.33 out of 5)