The Arterial Supply of the Heart is mostly provided by 2 coronary arteries, which originate from the ascending aorta immediately above the aortic valve.
The coronary arteries and their branches run on the surface of heart being located inside the subpericardial fibro fatty tissue.
A. Coronary arteries are vasa vasorum of the ascending aorta.
B. Anatomically coronary arteries aren’t end-arteries but functionally they behave like end-arteries.
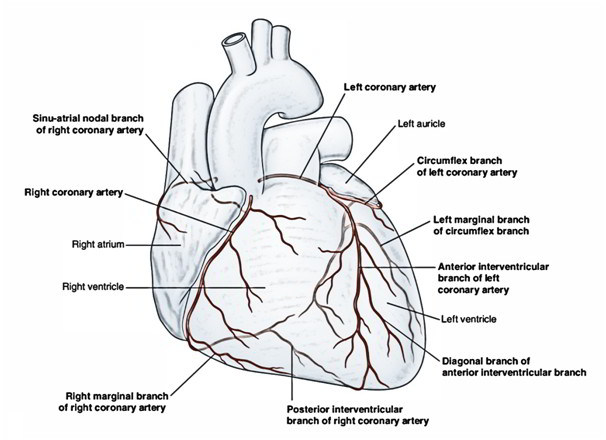
Right Coronary Artery
Origin
The right coronary artery originates from the anterior aortic sinus of the ascending aorta, immediately above the aortic valve.
Course
After arising from the ascending aorta, the right coronary artery first runs forwards between the pulmonary trunk and the right auricle, and after that it descends just about vertically in the right atrioventricular groove (right anterior coronary sulcus) up to the junction of the right and the inferior borders of the heart. At the inferior border of the heart, it turns posteriorly and runs in the groove where it ends by anastomosing with the left coronary artery.
Branches And Distribution
Right Conus Artery
It supply the anterior surface of the pulmonary conus (infundibulum of the right ventricle).
Atrial Branches
They supply the atria. One of the atrial branches – the artery of sinuatrial node (also referred to as sinuatrial nodal artery) provides the SA node in 60% cases. In 40% of individuals it originates from the left coronary artery.
Anterior Ventricular Branches
They’re 2 or 3 and supply the anterior surface of the right ventricle.
The marginal branch is the largest and runs along the lower margin of the sternocostal surface to make it to the apex.
Posterior Ventricular Branches
They may be generally 2 and supply the diaphragmatic surface of the right ventricle.
Posterior Interventricular Artery
It runs in the posterior interventricular groove up to the apex. It supplies the posterior part of the interventricular septum, atrioventricular node (AV node) in 60% of the cases, and right and left ventricles.
In 10% individuals, the posterior interventricular artery originates from the left coronary artery.
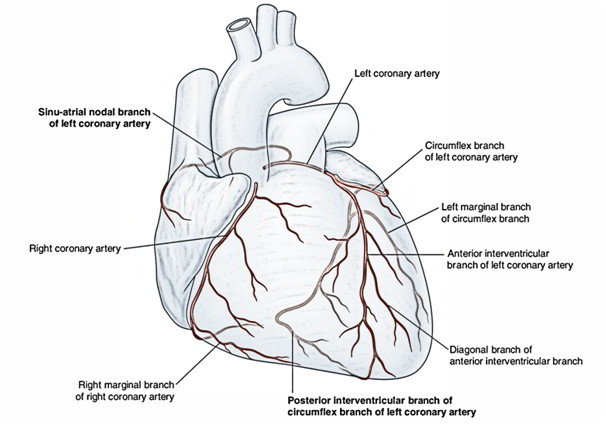
Left Coronary Artery
Origin
The left coronary artery originates from the left posterior aortic sinus of the ascending aorta, immediately above the aortic valve.
Course
After arising from ascending aorta, the left coronary artery runs forwards and to the left between the pulmonary trunk and the left auricle. It then divides into an anterior interventricular and circumflex artery. The anterior interventricular artery (left anterior descending/LAD) runs downwards in the anterior interventricular groove to the apex of the heart. It then enters posteriorly around the apex of the heart to go into the posterior interventricular groove to terminate by anastomosing with the posterior interventricular artery- a branch of the right coronary artery.
The circumflex artery winds around the left margin of the heart and continues in the left posterior coronary sulcus up to the posterior interventricular groove where it ends by anastomosing with the right coronary artery.
Branches And Distribution
1) Anterior interventricular artery/left anterior descending (LAD) artery: It provides (a) anterior part of interventricular septum, (b) greater part of the left ventricle and part of right ventricle, and (c) a part of left bundle branch (of His) posterior atrioventricular groove (right posterior coronary sulcus) up to the posterior interventricular.
2) Circumflex artery: It supplies a left marginal artery that provides the left margin of the left ventricle up to the apex of the heart.
3) Diagonal artery: It may originate directly from the trunk of the left coronary artery.
4) Conus artery: It supplies the pulmonary conus.
5) Atrial branches: They supply the left atrium.
Major Branches Of The Left And Right Coronary Arteries
Right coronary artery | Left coronary artery |
|---|---|
| Right marginal artery | Anterior interventricular artery |
| Posterior interventricular artery | Circumflex artery |
| Sinuatrial nodal artery | Diagonal artery |

 (53 votes, average: 4.53 out of 5)
(53 votes, average: 4.53 out of 5)