The carotid canal is a V-shaped recession on the floor of which and the orifice of the aqueduct of the cochlea is near the posterior margin, inhabiting the gap posteriorly as well as medially in the middle of the jugular fossa.
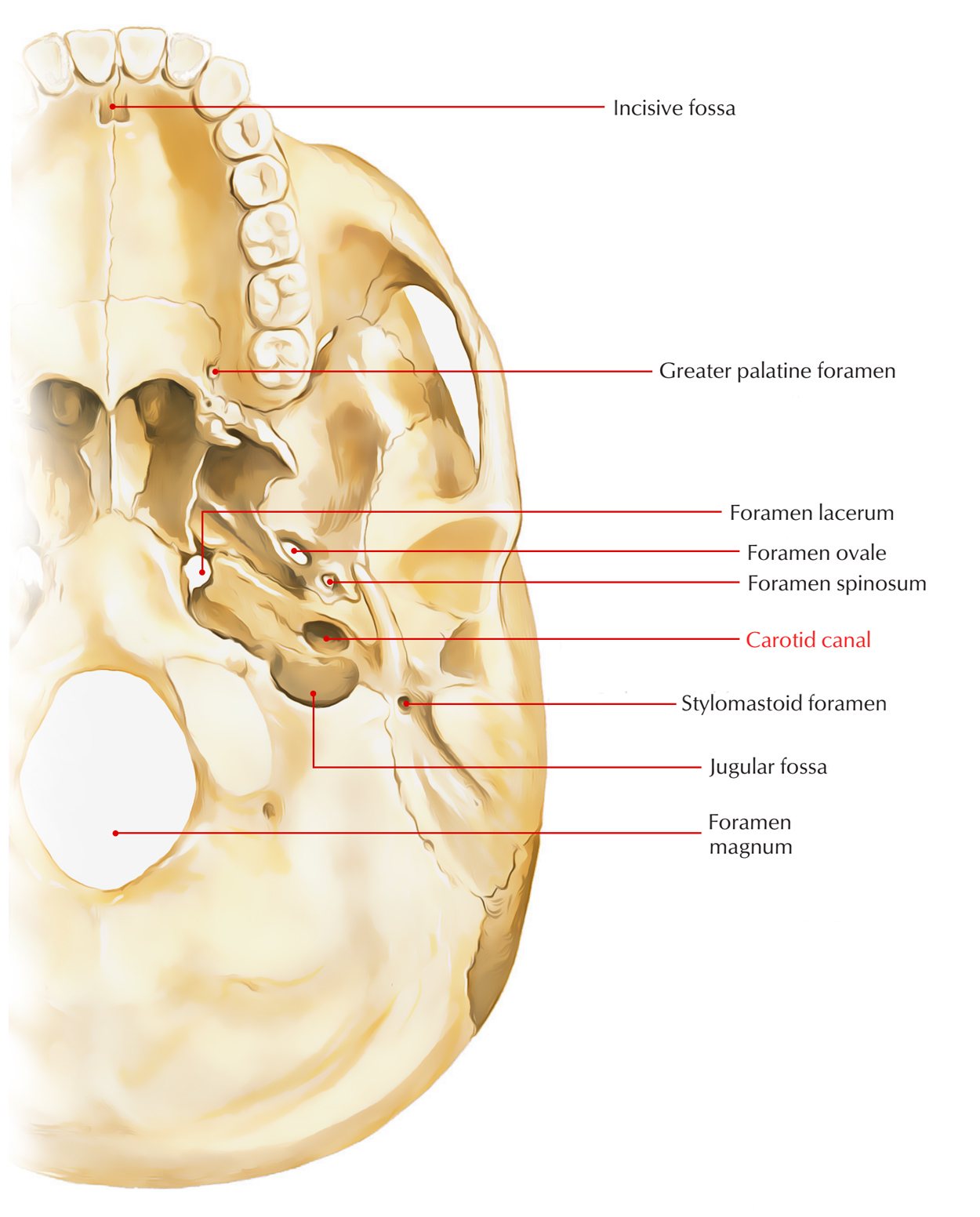
Carotid Canal
Structure
The circular opening of the inferior opening of the carotid canal is located opposite the jugular fossa and a little medial towards the tympanic plate divided from it by a sharp crest.
- This canal is located parallel towards the anterior angle, pointed upwards at first, then curves perpendicularly and turns forwards and medially; getting towards the anterior part of the apex of the bone, it unseals in front by an oblique irregular orifice.
- It travels into the cranium, together with a plexus of sympathetic nerves via the canal the internal carotid artery.
- From the carotid canal is the opening of the canaliculus tympanicus on the rim of bone dividing the jugular fossa, via which the tympanic branch of the glossopharyngeal nerve travels in order to reach the tympanum.
Within the orifice of the carotid canal other small openings referred to as canaliculi carotici tympanici may be observed which give route to the tympanic branches of the internal carotid artery along with carotid sympathetic plexus.
Relations
1. Structures located in this fossa are the petrous ganglion of the glossopharyngeal nerve as well as the aqueduct transmits a tubular prolongation of the dura mater, which creates a channel of communication in the middle of the perilymph of the cochlea as well as the subarachnoid space.
2. Anterior and medial towards the orifice of the carotid canal is the inferior surface of the apex of the bone resembles a rough quadrilateral surface which:
- Creates the floor of the carotid canal.
- Functions for the attachment of the cartilaginous portion of the auditory tube.
- The origin of the levator veli palatini muscle.
3. It has the dense fibrous tissue connected to it which fills up the petro-basilar fissure in the middle of it along with the basilar portion of the occipital bone.
4. It is found on inferior surface of the petrous temporal bone. It transmits:
- Internal carotid artery with sympathetic plexus all around it.
- Internal carotid venous plexus connecting cavernous sinus along with internal jugular vein.
- Emissary vein joining pharyngeal venous plexus as well as cavernous sinus.

 (49 votes, average: 4.47 out of 5)
(49 votes, average: 4.47 out of 5)