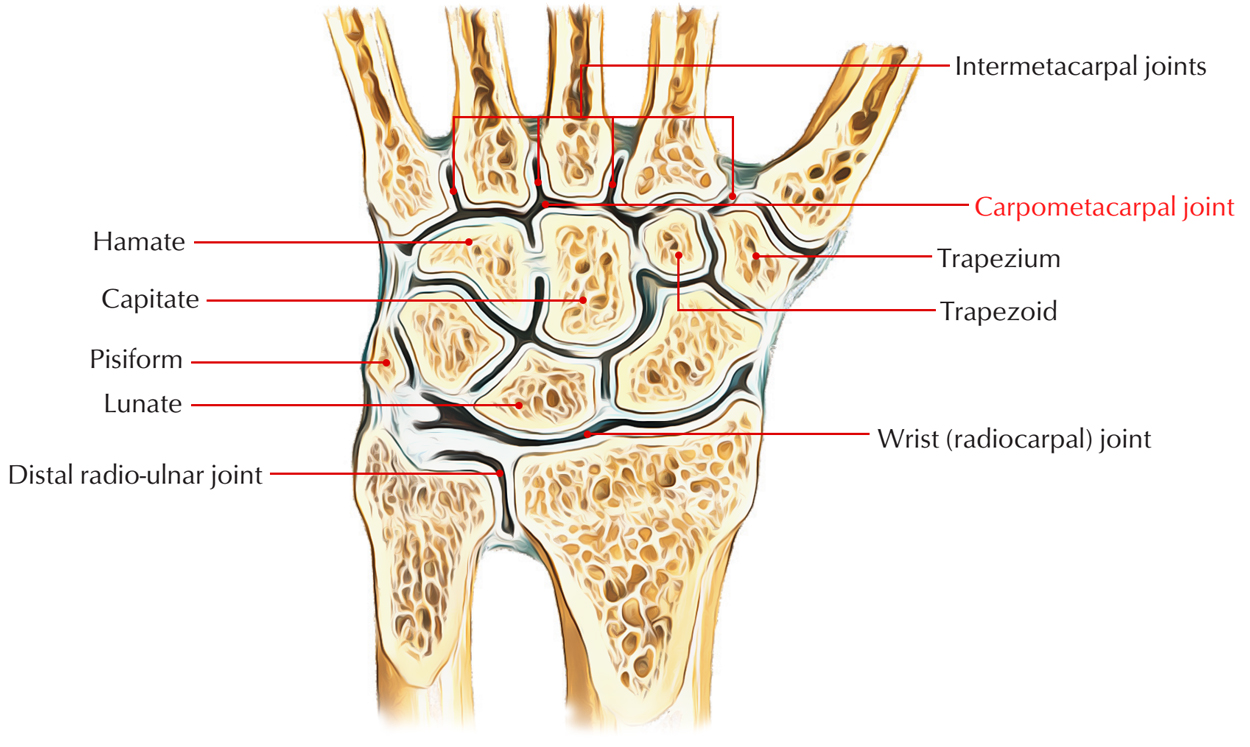
The carpometacarpal joints with the exception of the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb, which is a saddle joint, are type of plane synovial joints. Functionally as well as medically, the most important joint is the first carpometacarpal joint. The distal side of the carpals of distal row articulates with the base of metacarpals. There are five carpometacarpal joints among the metacarpals and also the associated distal row of carpal bones. The saddle joint, among metacarpal I along with the trapezium, gives a variety of movements to the thumb, which is not a function of the other digits.
Carpometacarpal Joint
Structure
The carpometacarpal joints among metacarpals II to V as well as the carpal bones are much less movable compared to the carpometacarpal joint of the thumb, enabling only restricted gliding actions. Motion of the joints enhances medially, and then metacarpal V glides to the greatest degree. This may be noticed best on the dorsal side of the hand when it makes a fist.
Articular Surfaces
Both proximal along with distal articular surfaces are reciprocally concavo-convex and therefore enable large variety of actions on this joint.
Ligaments
- Capsular ligament (joint capsule) covers the joint cavity and is a thick loose fibrous sac. It is connected distally towards the boundary of the bottom side of first metacarpal bone and proximally towards the margins of articular side of the trapezium. The inner surface of the capsule is lined with synovial membrane.
- Lateral ligament is a wide fibrous band extending through lateral side of the trapezium towards the lateral aspect of the base of 1st metacarpal bone.
- Anterior (palmar) ligament – via palmar surface of trapezium it expands obliquely towards the ulnar side of the base of 1st metacarpal.
- Posterior (dorsal) ligament – through dorsal surface of trapezium it expands obliquely also towards the ulnar aspect of the base of 1st metacarpal.
Relations
The joints are outlined by different muscles as well as tendons of the thumb. Anteriorly by muscles of thenar eminence and posteriorly by long and short extensos of thumb. Laterally by tendon of abductor pollicis longus.
Furthermore, it relates to:
- Radial artery on its posteromedial aspects.
- First dorsal interosseous muscle on its medial aspect.
Blood Supply
Nerve Supply
By median nerve
Movements
The various movements, which occur at the first carpometacarpal joint, are as follows:
- Flexion and extension.
- Abduction and adduction.
- Opposition.
- Medial and lateral rotation.
- Circumduction.

 (53 votes, average: 4.66 out of 5)
(53 votes, average: 4.66 out of 5)