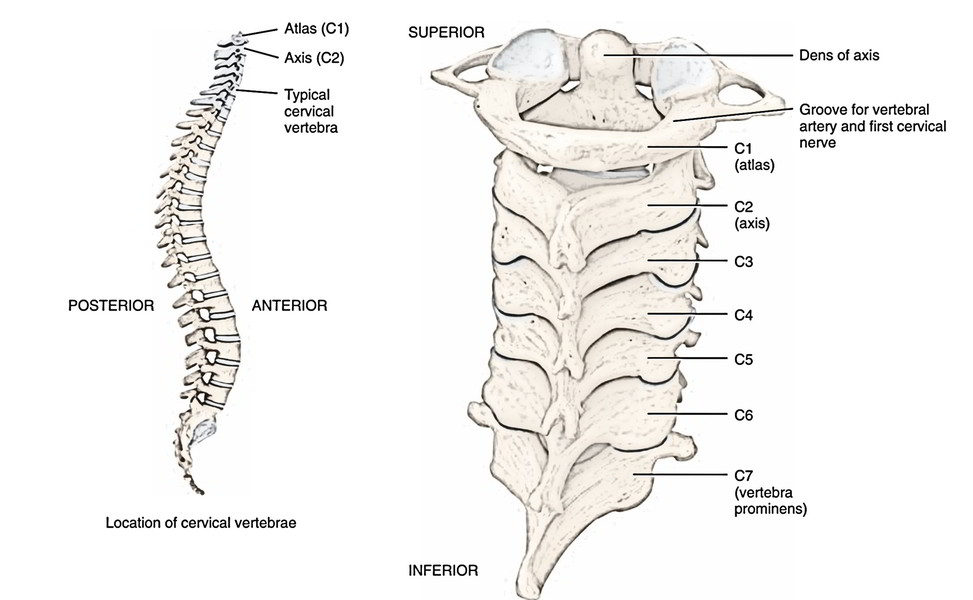
There are 7 cervical vertebrae, numbered 1 to 7 from above to downwards. As they need to hold less weight, they may be small in size when compared with thoracic and lumbar vertebrae. The presence of foramen in their own transverse processes termed foramen transversarium – the cardinal attribute of cervical vertebrae identifies them. The third to 6th are typical since they have common features. For individual identification, the first, second and 7th possess special features.
Atypical Features of first, second and seventh Cervical Vertebrae
| First cervical (atlas) | Absence of body. Absence of spine. Long transverse processes. Superior articular facets are concave and elongated. They are kidney-shaped. The inferior articular facets are more or less circular |
|---|---|
| Second cervical (axis) | Presence of odontoid process. Transverse processes are small and lack the anterior tubercle. Anterior margin of the inferior surface of the body projects downwards to a considerable extent. Foramen transversarium is directed superolaterally (cf. in typical vertebrae it is directed vertically). Inferior surface presents a deep and wide inferior vertebral notch placed in front of the inferior articular process. The superior vertebral notch is shallow and is present behind the superior articular process |
| Seventh cervical (vertebra prominens) | Spine is strong, long and not bifid. Transverse process is relatively long and lacks the anterior tubercle. Foramen transversarium is relatively small |
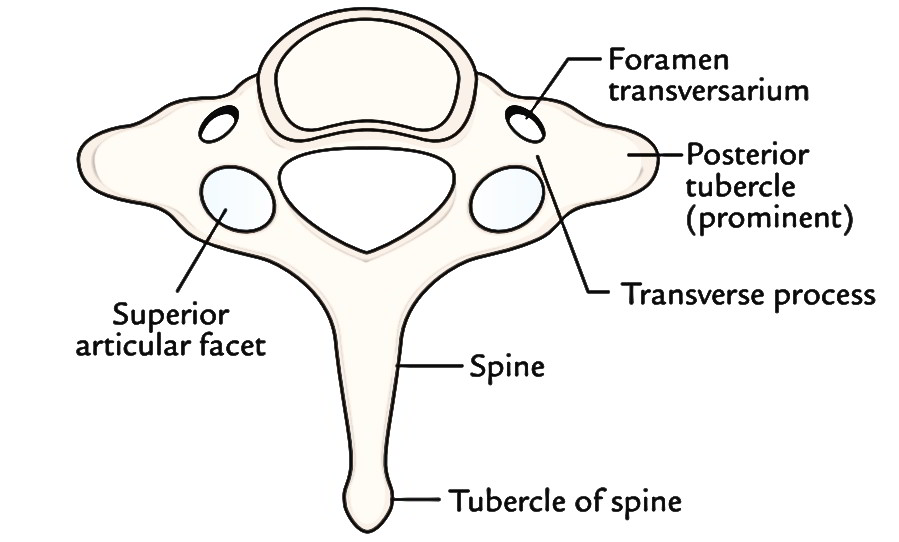
Features of Typical Cervical Vertebrae
The features of typical cervical vertebrae are as follows:
1. The body:
- It’s small.
- It’s wider from side to side than from before back-wards.
- Its superior surface is concave transversely with upward projecting lips on every side.
- The inferior surface on the anterior margin of the body projects downwards in front of the intervertebral disc while the lateral margins are beveled laterally to create the synovial joints with projecting lips of the vertebra below. All these are referred to as uncovertebral joints (joints of Luschka).
2. The vertebral foramen is triangular and bigger compared to the body.
3. The superior and inferior articular facets are flat:
- Superior facets are pointed backwards and upwards.
- Inferior facets are pointed forwards and downwards.
4. The transverse processes are small and pierced by foramen transversarium. Every process has anterior and posterior roots, which finish in tubercles named anterior and posterior tubercles. They can be joined together by costotransverse tavern. The costal component is composed of anterior root, anterior tubercle costotransverse pub and posterior tubercle. The posterior root represents the transverse component of the growing vertebra.
5. The spine is short and bifid.
Features of Atypical Cervical Vertebrae
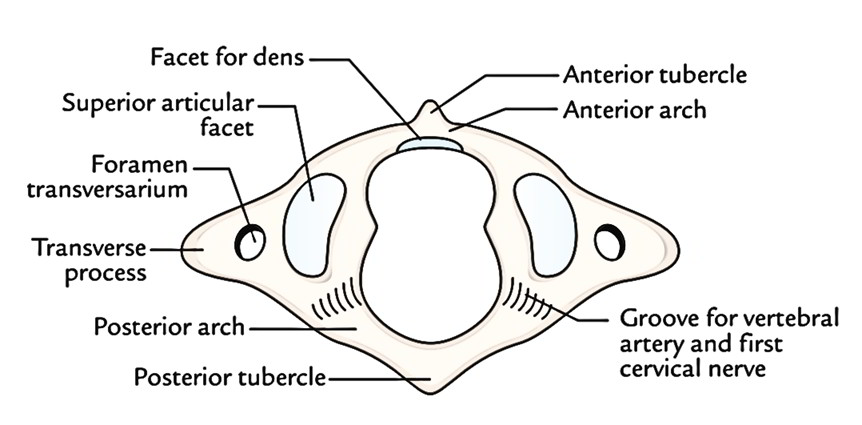
First Cervical Vertebra
The first cervical vertebra is named atlas for the reason that it supports the world of the head on its shoulders. Based on Greek mythology, the Atlas is the God who supported the world of world on his shoulders.
It’s following features:
- It is ring-shaped and does not have any body and no spine.
- It is composed of: Left and right lateral masses joined by a short anterior arch and a long curved posterior arch and Left and right transverse processes.
- The anterior arch is indicated in the median plane by the anterior tubercle on its anterior aspect and an oval facet on its posterior aspect for articulation with the lairs of the second cervical vertebra to create atlantoaxial joint.
- The posterior arch forms 2-fifth of the ring and its posterior aspect is marked by a median posterior tubercle. The upper surface of the posterior arch behind the lateral mass is marked by a groove which lodges the vertebral artery and the first cervical nerve.
The lateral mass presents these features:
- Its upper and lower surfaces carry superior and inferior articular facets, respectively.
a) The superior articular facet is concave and elongated. It’s pointed upwards and medially to articulate with the corresponding condyle of the occipital bone to create the atlanto-occipital joint.
b) The inferior articular facet is flat and circular. It’s pointed downwards, medially and backwards to articulate together with the corresponding facet on the axis vertebra to create the atlantoaxial joint. - The medial surface of the lateral mass is marked by a small roughened tubercle to give connection to the transverse ligament of the atlas.
- The transverse processes project laterally from the lateral masses. They’re powerful and bigger than that of other cervical vertebrae. The elongated transverse processes serve as efficient levers for the rotation of the atlas vertebra.
- The most significant attribute of atlas vertebra is the absence of its body. The body is absent because during development the centrum of first cervical vertebra gets fused with the centrum of axis to create the lairs. Hence holes of axis vertebra compose the body of the atlas vertebra.
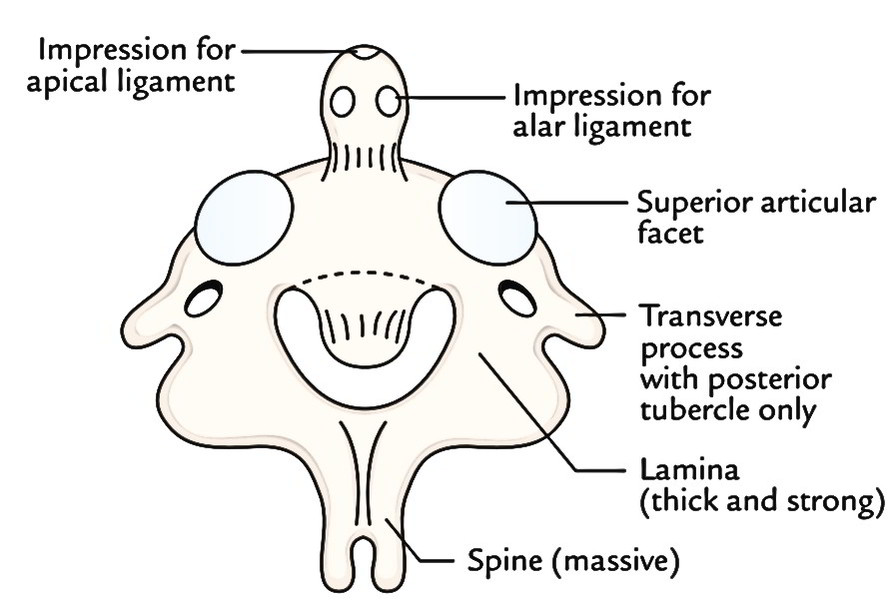
Second Cervical Vertebra
The second cervical vertebra is termed axis as the atlas rotates like a wheel around the pivot supplied by the odontoid process (or lairs) of second cervical vertebra.
It’s the following features:
- It possesses a powerful toothlike process projecting upwards from the body termed odontoid process. The odontoid process composes the centrum (body) of the atlas, which has fused with the centrum of the axis vertebra.
The holes articulate anteriorly with the anterior arch of the atlas and posteriorly with the transverse ligament of the atlas. It gives connection to the apical ligament at its apex and on every side below the apex to the alar ligaments. - The notable anterior margin of the inferior outermost layer of the body projects downwards to a substantial extent.
- The spine is substantial, i.e., it’s large, thick and quite powerful and deeply grooved inferiorly. Its tip is bifid.
- The transverse processes are extremely small and lack the anterior tubercles. The foramen transversarium is directed upwards and laterally.
- The laminae are thick and powerful.
- The superior articular facets on the upper surface of the body go onto the pedicles. The gigantic pedicle overhangs the foramen transversarium laterally.
- The superior articular facet is large, flat and circular. They’re weight bearing and encroach on the side of the body. It’s directed upwards and laterally to joint with the corre-sponding facet of the atlas.
- The inferior articular facet is located posterior to the transverse process and is directed downwards and forwards to joint with the third cervical vertebra.
- The old name of the axis was the OS Cheloni as a result of its similarity to the head of a tortoise.
Seventh Cervical Vertebra
The 7th cervical vertebra is referred to as vertebra prominens because its spine is extremely long and creates a notable felt projection in the lower part of the nuchal furrow.
The features of the 7th vertebra are as follows:
- Its spine is thick, long and almost horizontal. It’s not bifid and finishes in a tubercle.
- The transverse processes are relatively long and large and lack the anterior tubercles.
- The foramen transversarium is comparatively small and doesn’t carry the vertebral artery. It carries only accessory vertebral vein.
Clinical Significance
Carotid tubercle: The anterior tubercle of the transverse process of 6th cervical vertebra is large and termed carotid tubercle of Chassaignac because the common carotid artery can be compressed against it, medial to the anterior border of sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Hangman’s fracture
Luschka’s joints are commonest sites of osteophyte formation.
Klippel-Feil syndrome is a clinical state where cervical vertebrae are fused and deformed congenitally.
The congenital fusion of ring of atlas vertebra to the base of the occiput is termed occipitalization of atlas. It’s 1 of the very typical abnormalities of the upper cervical vertebrae.

 (52 votes, average: 4.67 out of 5)
(52 votes, average: 4.67 out of 5)