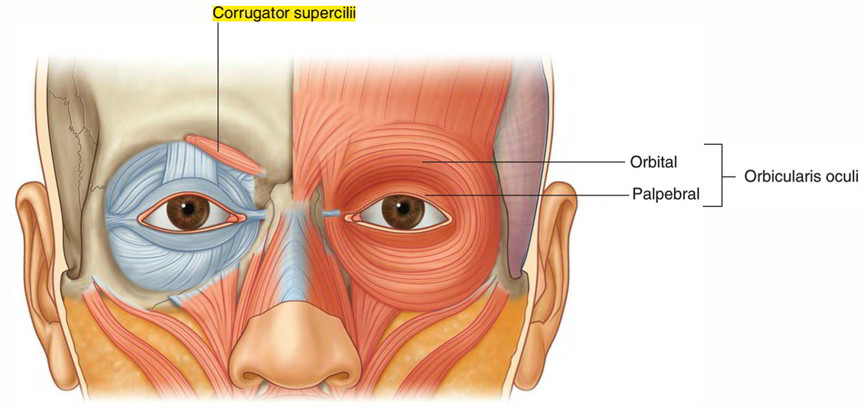
The second muscle in the orbital group is the much smaller corrugator supercilii. which is deep to the eyebrows and the orbicularis oculi muscle and is active when frowning. It arises from the medial end of the superciliary arch, passing upward and laterally to insert into the skin of the medial half of the eyebrow. It draws the eyebrows toward the midline, causing vertical wrinkles above the nose.
The corrugator supercilii typically creates strong vertical or slightly oblique wrinkles and vertical bulges on the glabella between the medial ends of the eyebrows. It also swells the skin at the medial end of the eyebrow into a wide, thick, crescent-shaped bulge. This action pulls the brows shelflike over the eyes, shading them from strong light.
A depression forms in the skin above the middle of the eyebrow (actually closer to the medial end) as the corrugator contracts. It often gives the eyebrow an S-shaped curve – the eyebrow develops a central downward dip (usually close to the medial end) as the muscle pulls the middle portion of the eyebrow downward and inward. This is especially noticeable if the medial portion of the frontalis is also lifting the medial end of the eyebrow. The corrugator may also create a long, oblique, shallow furrow on the lateral side of the front of the forehead.
This furrow is directed upward and outward from the medial end of the eyebrow or from the skin depression located above the middle of the eyebrow.
The lowering of the brow by the corrugator narrows the eye opening by pushing the skin below the eyebrow and upper eyelid downward.
Origin
The bone at the medial end of the superciliary arch, near the upper inner corner of the orbit.
Insertions
The skin of the middle portion of the eyebrow, and the skin of the forehead immediately above it. The fibers interlace with fibers of the frontalis and orbicularis oculi.
Actions
Draws the eyebrow medially. It forms vertical furrows on the eyebrow. This causes the expression of frowning.
The corrugator supercilii attaches to the region of the frontal bone next to the nasal bone. From there, its fibers run superiorly and laterally to attach into the skin superior to the eyebrow. Because the frontal bone attachment is more fixed, when the corrugator supercilii contracts, it pulls the skin deep to the eyebrow inferomedially toward the frontal bone attachment (towards the other eyebrow). When both corrugator supercilii muscles contract, both eyebrows are pulled inferomedially towards each other.
Structure
The corrugator supercilii muscles are anatomical structures isolated from the frontal and eyelid orbicular muscles. Their innervation comes from a temporal fillet branch, without zygomatic branch association. The medial distance from the motor point to the midfrontal line is 13 mm. The fillet branch that enrich corrugator muscles proceed in a parallel line to the supraorbital edge, keeping a distance of between 3 mm below and 13 mm above the edge. There are many fillet connections with the trigeminus nerve branches, after the supraorbital foramen. The nerve penetration point in the muscle was predominant in its medium and superior third, being larger in the medium and rare in the inferior third.
Test Your Knowledge
Corrugator Supercilii

 (59 votes, average: 4.53 out of 5)
(59 votes, average: 4.53 out of 5)