Fascia is a band or sheet of connective tissue, beneath the skin.
Pectoral Fascia
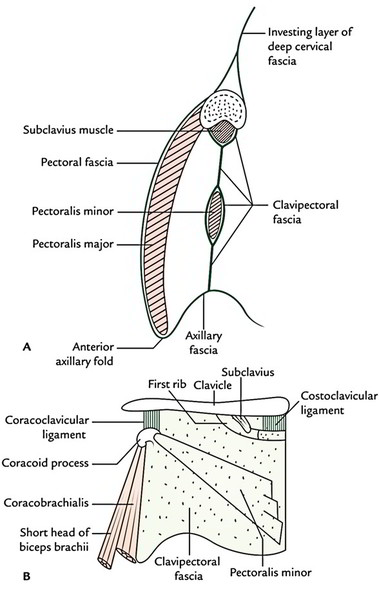
It’s the deep fascia covering the anterior aspect of the pectoralis major muscle. It’s thin and anchored firmly to the muscle by numerous fasciculi.
Extent
- Superiorly, it’s connected to the clavicle. Inferiorly, it’s continuous with the fascia of anterior abdominal wall.
- Superolaterally, it enters over the deltopectoral groove to become continuous with the fascia covering the deltoid muscle.
- Inferolaterally, it curves round the inferolateral border of the pectoralis major to become continuous with the axillary fascia. The axillary fascia is a dense fibrous sheet that extends across the base of the axilla.
Clavipectoral Fascia
The clavipectoral fascia is a strong fascial sheet deep to the clavicular head of the pectoralis major muscle, filling the space between the clavicle and the pectoralis minor muscle.
A as observed in sagittal section of anterior axillary wall; B as viewed from front.
Extent
- Vertically, it extends from clavicle above to the axillary fascia below. Its upper part splits into 2 laminae to enclose the subclavius muscle. The posterior lamina becomes continuous with the investing layer of deep cervical fascia and gets fused with the axillary sheath. The anterior lamina gets connected to the clavicle. Its lower part splits to enclose the pectoralis minor muscle. Below this muscle it extends downwards as the suspensory ligament of axilla, that is connected to the dome of the axillary fascia. The suspensory ligament keeps the dome of axillary fascia pulled up, thus maintaining the concavity of the axilla.
- Medially, clavipectoral fascia is connected to the first rib and costoclavicular ligament and blends with external intercostal membrane of the upper 2 intercostal spaces.
- Laterally, it’s connected to the coracoid process and blends with the coracoclavicular ligament. The thick upper part of the fascia extending from first rib near costochondral junction to the coracoid process is termed costocoracoid ligament.
- The clavipectoral fascia encloses 2 muscles—subclavius and pectoralis minor.
Structures piercing the Clavipectoral Fascia
All these are as follows:
- Lateral pectoral nerve.
- Thoraco-acromial artery.
- Lymphatics from the breast to the apical group of axillary group of lymph nodes.
- Cephalic vein. The first 2 structures pass outwards, on the other hand the lower 2 structures pass inwards.
x

 (48 votes, average: 4.65 out of 5)
(48 votes, average: 4.65 out of 5)