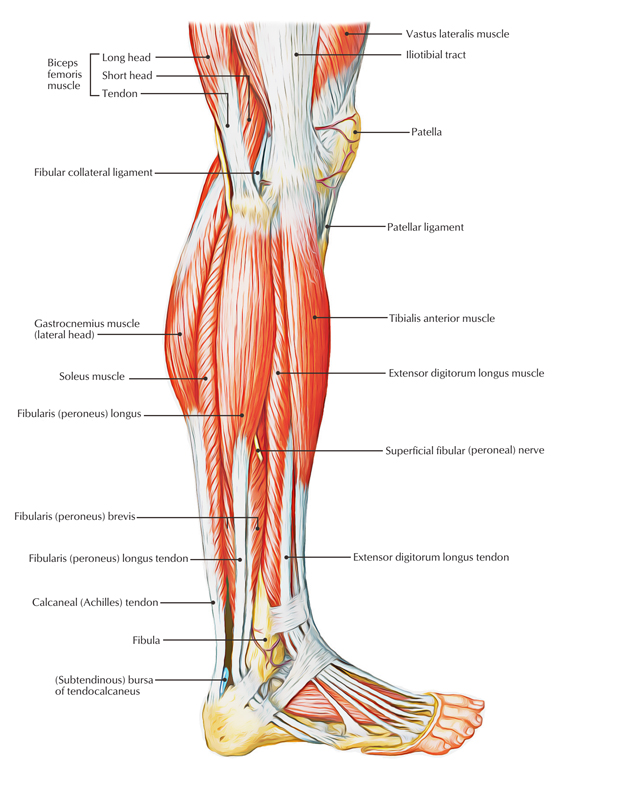
The fibularis brevis is also called the peroneus brevis, it is a short peroneal muscle that lies simply below the peroneus longus muscle. The peroneal muscles extend along the external part of the lower leg and foot.
Fibularis (Peroneus) Longus
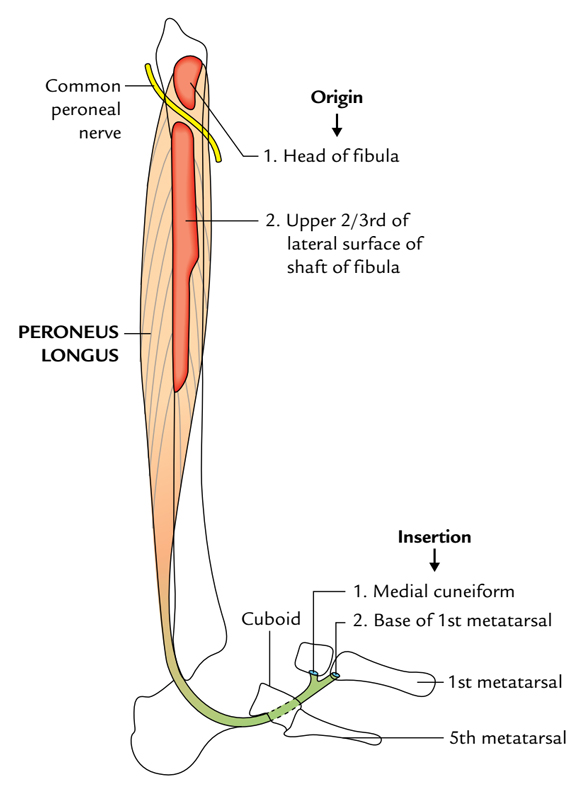
Origin
The fibularis brevis emerges via the intermuscular septa differentiating it out of the surrounding muscles at the front as well as back of the leg and also via the lower two-thirds of the lateral side of the body of the fibula, medial towards the peroneus longus. It is the shorter as well as smaller among the peroneus muscles group and also is located below the layer of the peroneus longus. The fibularis brevis can possess superficial along with deep bellies.
Fibularis (Peroneus) Longus: Origin and Insertion
Insertion
The fibers move down top to bottom, however in front of the preceding muscle and also terminate in a tendon that goes at the back of the lateral malleolus alongside, the two tendons that are lubricated via a common mucous sheath as well as wrapped inside the exact same compartment.
The tendon of the peroneus brevis generally enter inside the base of the fifth metatarsal close to its protrusion, but variants may connect to the flexor digiti minimi brevis or diverge to enter at the dorsum of the fifth metatarsal, inside the fourth dorsal interosseous muscle.
Its tendon can possibly divide with one section connecting the fibularis tertius tendon or maybe giving rise to the abductor digiti minimi muscle. The fibularis brevis tendon generally gives a tendinous band towards the extensor expansion
(dorsal aponeurosis) of the little toe or maybe the base of the fifth proximal phalanx, as well as its fibularis quartus variation, fibularis (peroneus) digiti minimi.
Nerve Supply
The primary supply is by superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve (root value L5 and S1). The skin covering up the muscle is stimulated through roots L5, S1 and S2.
Action
Fibularis (peroneus) brevis is an evertor of the foot. The pull of its tendon operates in such a direction in order to produce plantar flexion of the ankle simultaneously, due to its path and attachments.
Functional Activity
- When standing on one leg, it helps to stop the body from dropping to the other side, thus operating along with a reversed origin as well as attachment.
- This muscle is even well positioned to avoid mediolateral sway while standing.
- In walking as well as running, particularly above rough ground, it plays a vital part in managing the position of the foot and also should stop the foot from getting too inverted.
- Even so, this particular process does not consistently seem to work properly, and the foot over-inverts, making the weight to go down on the lateral side of the foot pressing the foot in further inversion, in a lot of cases. This may significantly injure as well as rupture the tendon of the muscle and oftentimes the anterior talofibular ligament of the ankle joint.
Palpation
- With the fingers positioned on the belly of fibularis longus going down towards the lower half of the fibula within the very same vertical line, while the foot is everted as well as plantarflexed the belly of fibularis brevis could be examined.
- Its tendon can easily be marked out towards the groove simply over the fibular tubercle and after that ahead to its attachment in the tubercle of the fifth metatarsal.

 (58 votes, average: 4.53 out of 5)
(58 votes, average: 4.53 out of 5)