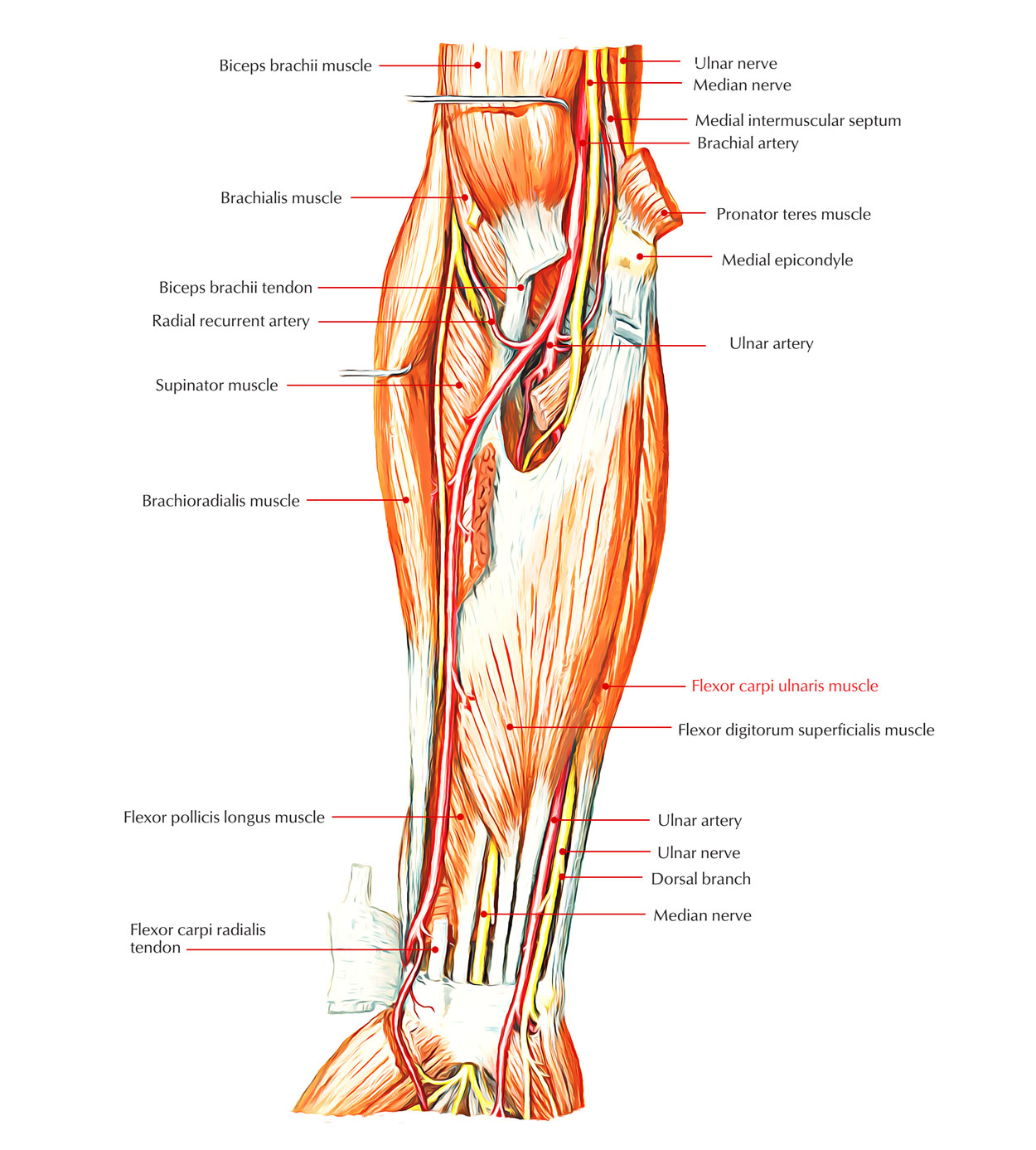
The flexor carpi ulnaris muscle is a muscle of the forearm that works to flex and adduct (medial deviation) the hand.
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
Origin
The common flexor belly/tendon is the common proximal connection of five muscles:
- Pronator teres
- Flexor carpi radialis
- Palmaris longus
- Flexor carpi ulnaris
- Flexor digitorum superficialis
The flexor carpi ulnaris emerges proximally via the medial epicondyle of the humerus through the common flexor belly tendon.
It emerges from two heads: a small humeral head along with a large ulnar head.
- Humeral head starting with the medial epicondyle of the humerus through a common flexor origin, and
- Ulnar head via an aponeurosis through the upper two-third of the posterior border of the ulna as well as through the medial margin of the olecranon process.
Insertions
The flexor carpi ulnaris muscle is certainly the most medial of the muscles within the superficial level of flexors, possessing a long linear origin via the olecranon as well as posterior boundary of the ulna, along with an origin through the medial epicondyle of the humerus. Into
- Pisiform bone
- Hook of hamate along with the base of fifth metacarpal bone, specifically together with pisohamate and pisometacarpal ligaments.
The muscle fibers merge on a tendon that goes distally and also connects to the pisiform bone of the wrist. Beyond this point, force is transmitted towards the hamate bone of the wrist and towards the bottom of metacarpal V by pisohamate and pisometacarpal ligaments. The latter is real attachment due to sesamoid bone (pisiform) forms within its tendon. The ulnar nerve goes into the anterior chamber of the forearm by travelling through the triangular gap among the humeral and ulnar heads of the flexor carpi ulnaris.
Actions
- It adducts the wrist joint together with the extensor carpi ulnaris.
- It flexes the wrist joint together with the flexor carpi radialis.
Normal Activity
- The flexor carpi ulnaris in order to connect over the hand along with its fibers going vertically within the sagittal plane goes across the wrist joint on the anterior side, as a result it flexes the hand over at the wrist joint.
- The flexor carpi ulnaris along with its fibers going vertically inside the frontal plane goes across the wrist joint on the ulnar side, hence it ulnar adducts the hand on the wrist joint.
- Activity at the wrist joint takes place at the radiocarpal as well as midcarpal joints.
- Flexor carpi radialis, palmaris longus, and flexor carpi ulnaris along with their fibers going on vertically within the sagittal plane can flex the forearm at the elbow joint due to the fact that they go across it anteriorly.
Reverse Activity
- The flexor carpi ulnaris’ sagittal plane inverse activity is flexion of the forearm in the wrist joint. Its frontal plane inverse activity is ulnar deflection of the forearm over at the wrist joint. Reverse activities at the wrist joint take place whenever the hand is set by keeping an immovable object but the forearm moves corresponding to the fixed hand.
- The reverse activity of flexion of the arm on the elbow joint is incredibly essential and takes place when.
- A person grips a stationary object and draws his or her body toward it examples consist of making use of a handicap bar or making use of a handrail whenever climbing stairs.
Nerve Supply
The flexor carpi ulnaris muscle is a strong flexor as well as adductor of the wrist and is stimulated by the ulnar nerve.

 (59 votes, average: 4.82 out of 5)
(59 votes, average: 4.82 out of 5)