Flexor Hallucis Longus is a multipennate muscle whose fibers emerge through the flexor side of the fibula and also through the adjacent aponeurosis of the flexor digitorum longus. Flexor digitorum longus is the bulkiest as well as most powerful of the three deep muscles of the calf. Under this the muscle emerges in connection through the entire flexor side of the fibula along with the lower portion of the interosseous membrane.
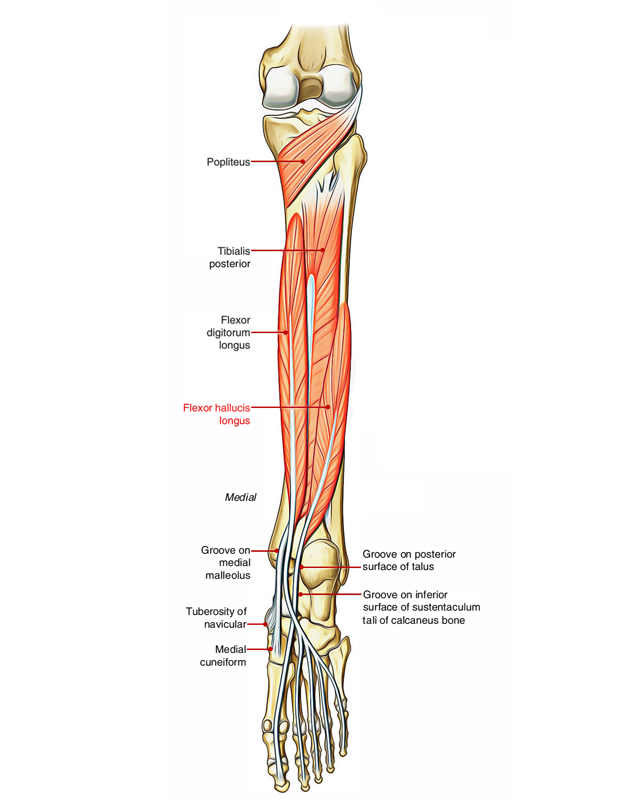
Flexor Hallucis Longus
Attachment
The fibers spiral in order to be placed inside a central tendon which leaves through the muscle just at the lower end of the tibia. The tendon grooves the posterior process of the talus and the below the surface of the sustentaculum tali, through which it move straight ahead like a bowstring, below the arched medial border of the foot to be inserted in the base of the distal phalanx of the great toe.
It is crossed in the sole by the tendons of flexor digitorum longus and provides a strong strip towards the medial two of these for the second and the third toes. The peroneal artery descends deep towards it on the fibular aponeurosis of flexor digitorum longus. A fibrous roof on the deep side of flexor hallucis longus covers the artery.
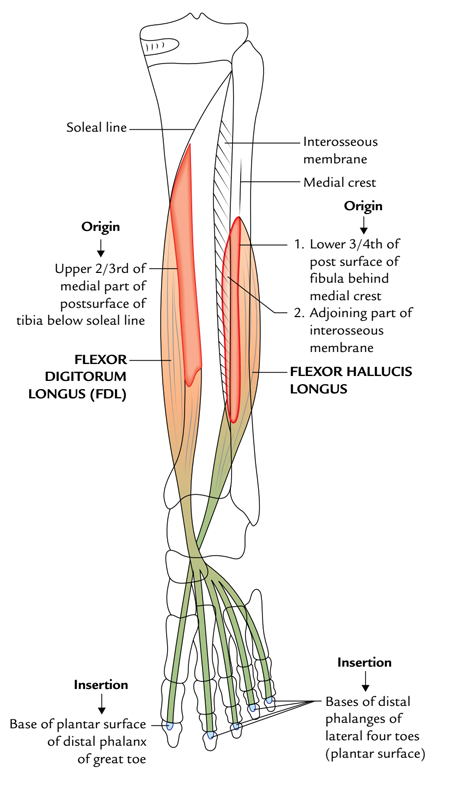
Flexor Hallucis Longus: Origin and Insertion
Innervation
The flexor hallucis longus is innervated by a branch of the tibial nerve which contains fibers via the L5, S1, and S2 spinal nerves.
Function
- The flexor hallucis longus muscles work during walking in order to support the foot and ankle in mid-stance to lateral position, contributing in medio-lateral balance.
- They assist in the maintaining the stability whenever weight is on the forefoot and it helps other plantar flexors in allowing it specifically in order to move weight towards the forefoot.
- The flexor hallucis longus bends the distal phalanx of the great toe. It assists in plantar flexion along with inversion of the foot whenever the foot is about to move.
Activities
- The flexor digitorum longus and the flexor hallucis longus act mainly as flexors of the distal phalanges of their particular toes having crucial extra functions of helping plantar flexion and inversion of the foot.
- Activation of the flexor hallucis longus muscle creates powerful flexion of the distal phalanx and reasonably weak flexion of the proximal phalanx of the great toe.
Clinical Significance
Flexor hallucis longus produces the last thrust through the foot in the toe-off stage of the gait cycle. At this moment in the cycle, triceps surae have currently contracted and flexor digitorum longus is finishing its constriction. For that reason great toe flexion is the last action before the foot is raised through the floor before swing stage. The muscle contributes in order to preserve the medial longitudinal arch.
Fractures of the sustentaculum tali can trigger entrapment of the flexor hallucis longus or flexor digitorum longus tendons along with other problems that might show reconstructive surgery.
Post-operative management consists of using a lower leg splint for 5-7 days, partial weight-bearing having 20 kg for 6-8 weeks in the patient’s own shoes, early series of motion workouts of the ankle, subtalar and mid-tarsal joints.
Flexor Hallucis Longus Rupture
- Avulsion fracture through the hallux distal phalanx is triggered by great resistance to flexion on the distal phalanx as the foot is by force plantarflexed. Total rupture of the flexor hallucis longus is unusual however can take place in a number of locations.
- Tear of the tendon at its attachment without having a bony piece allows the tendon to pull back proximally, enabling the great toe to dorsiflex. If the avulsed tendon includes a piece of bone, anatomic open decrease is recommended.
- The tendon sheath is revealed at or simply proximal towards the metatarsophalangeal joint having a direct repair work of the tendon to the distal phalanx. Surgical repair work is carried out via a medial incision with the proximal phalanx of the hallux over the neurocirculatory bundle.
Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendonitis
If this stress is extreme due to excessive force or repeating, injury to the flexor hallucis longus tendon might occur. Appears whenever the flexor hallucis longus muscle contracts or is extended, stress is positioned via the flexor hallucis longus tendon.
Causes
Flexor hallucis longus tendonitis might take place traumatically due to a high force passing through the tendon past what exactly it can endure or more frequently due to continuous wear and tear connected with excessive use.
Symptoms and Signs
- Patients experience pain in the region of the inner ankle which might travel down in the first toe.
- In less serious cases, patients might just experience pain having rest following tasks needing strong or recurring constriction of the flexor hallucis longus.
- They might also experience pain along with tightness after waking the following early morning
- The pain connected with this condition has the tendency to be of continuous creation which gradually gets worse over weeks to months having extension of irritating tasks
Treatment for Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendonitis
- Many patients having flexor hallucis longus tendonitis recover well having a suitable physiotherapy program.
- Among the essential parts of treatment is that the patient rests adequately through any task that increases their pain till they are signs and symptom totally free, crutches might be needed.
- This enables the body to start the recovery procedure in the absence of additional tissue injury. When the patient can carry out these tasks pain complimentary, a continuous go back to these tasks is shown supplied there is no increase in signs and symptoms.
- Disregarding signs and symptoms will probably result in the condition ending up being chronic.
- When chronic, recovery slows considerably leading to considerably increased healing times along with an increased probability of future reoccurrence.
- Immediate suitable treatment in every one of patients having flexor hallucis longus tendonitis is important to guarantee an ideal result.
- The R.I.C.E (rest, icing, compression, elevation) strategy especially having consistent icing and anti-inflammatory medication might assist to substantially decrease swelling in the preliminary stage of this condition.
- To make sure an ideal result a finished versatility, strength and balance routine under directions through a physio therapist is essential.
- A continuous go back to task or sports need to take place under assistance through the dealing with professional and offered there are no increase in signs and symptoms in the lasts of recovery.
Contributing Elements to the Development of Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendonitis
- Bad foot biomechanics (specifically flat feet).
- Bad versatility.
- Improper training or shoes (specifically using shoes which are too huge).
- Insufficient heat up.
- Muscle weak point.
- Inaccurate method (specifically in ballet dancers).
- Insufficient recovery following previous injury.
Physiotherapy for Flexor Hallucis Longus Tendonitis
- Soft tissue massage therapy.
- Electrotherapy (e.g. ultrasound).
- Anti-inflammatory recommendations.
- Stretches.
- Joint mobilization.
- Ice or heat therapy.
- Using crutches.
- Workouts to enhance strength, versatility as well as balance.
- Task adjustment recommendations.
- Biomechanical adjustment.
- Proper footwear recommendations.
- A continuous return to activity program.

 (59 votes, average: 4.75 out of 5)
(59 votes, average: 4.75 out of 5)