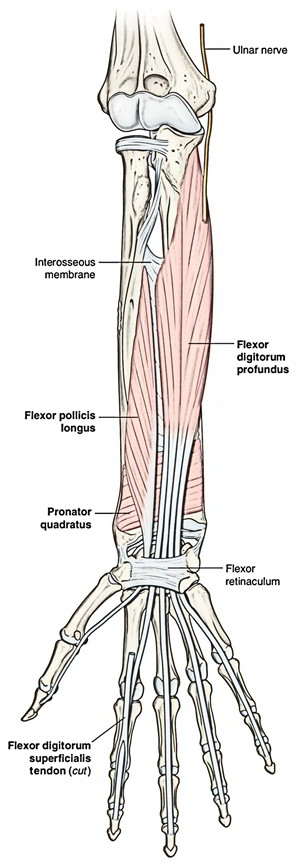
The flexor pollicis longus muscle starts from the surrounding half of the anterior side of the interosseous membrane along with the anterior side of the radius. Through upper two-third of the anterior side of the radius under the anterior oblique line and attaching part of the interosseous membrane.
Flexor Pollicis Longus
Where does the Insertion
The flexor pollicis longus is located laterally to the FDP and covers the anterior aspect of the radius distal to the attachment of supinator muscle. It attaches within the anterior surface of the base of distal phalanx of the thumb. It is a potent muscle and creates a single large tendon, which travels via the carpal tunnel, lateral towards the tendons of the flexor digitorum superficialis as well as flexor digitorum profundus muscles, and then within the thumb where it attaches to the base of the distal phalanx.
Innervation
The flexor pollicis longus is innervated by the anterior interosseous nerve which is a division of the median nerve.
Actions
- The flexor pollicis longus is the only muscle that flexes the interphalangeal joints of the thumb.
- It also flexes proximal phalanx and first metacarpal at the metacarpophalangeal (MP) along with carpometacarpal (CM) joints but it mainly flexes the distal phalanx of the thumb.
- The anterior interosseous nerve and blood vessels move down upon interosseous membrane among flexor pollicis longus and flexor digitorum profundus.
The flexor pollicis longus traverses the CMC joint of the thumb medially in order to attach over the distal phalanx of the thumb with its fibers going vertically within the frontal plane on the ulnar side. It pulls the thumb medially in the direction of ulna towards the index finger in the plane of the palm of the hand. This activity is referred to as flexion of the thumb.
The flexor pollicis longus crosses the wrist joint on the radial/lateral side to attach onto the hand, it radially abducts the hand at the wrist joint with its fibers running vertically in the frontal plane. The actions of elbow joint flexion and pronation of the radioulnar joints are weak or absent because the humeroulnar head of the flexor pollicis longus is small or even absent. Pronation of the forearm at the RU joints usually involves motion of the radius around a fixed ulna.
- So at the first CMC joint by flexing the metacarpal of the thumb the flexor pollicis longus flexes the thumb. The flexor pollicis longus does supports to opposition since thumb flexion is a component of thumb opposition.
- In order to attach over the distal phalanx of the thumb, on the ulnar side the flexor pollicis longus also overlaps the MCP and the IP joints of the thumb medially. As a result the flexor pollicis longus also flexes the proximal and distal phalanges of the thumb at these joints as well.
- The flexor pollicis longus is the only muscle that can flex the thumb at the IP joint. Motion at the wrist joint occurs at the radiocarpal and midcarpal joints.
- The flexor pollicis longus crosses the wrist joint anteriorly it flexes the hand at the wrist joint with its fibers running vertically in the sagittal plane.

 (51 votes, average: 4.56 out of 5)
(51 votes, average: 4.56 out of 5)