The glabella is the skin in the middle of the eyebrows and superior to the nose. It also stands for the underlying bone which is somewhat indented, and connects the two superciliary ridges. It is just superior towards the nasion and is a cephalometric marker (For study of the dental and skeletal relationships of a human skull). The pineal gland is located about 7 cm posterior towards the glabella.
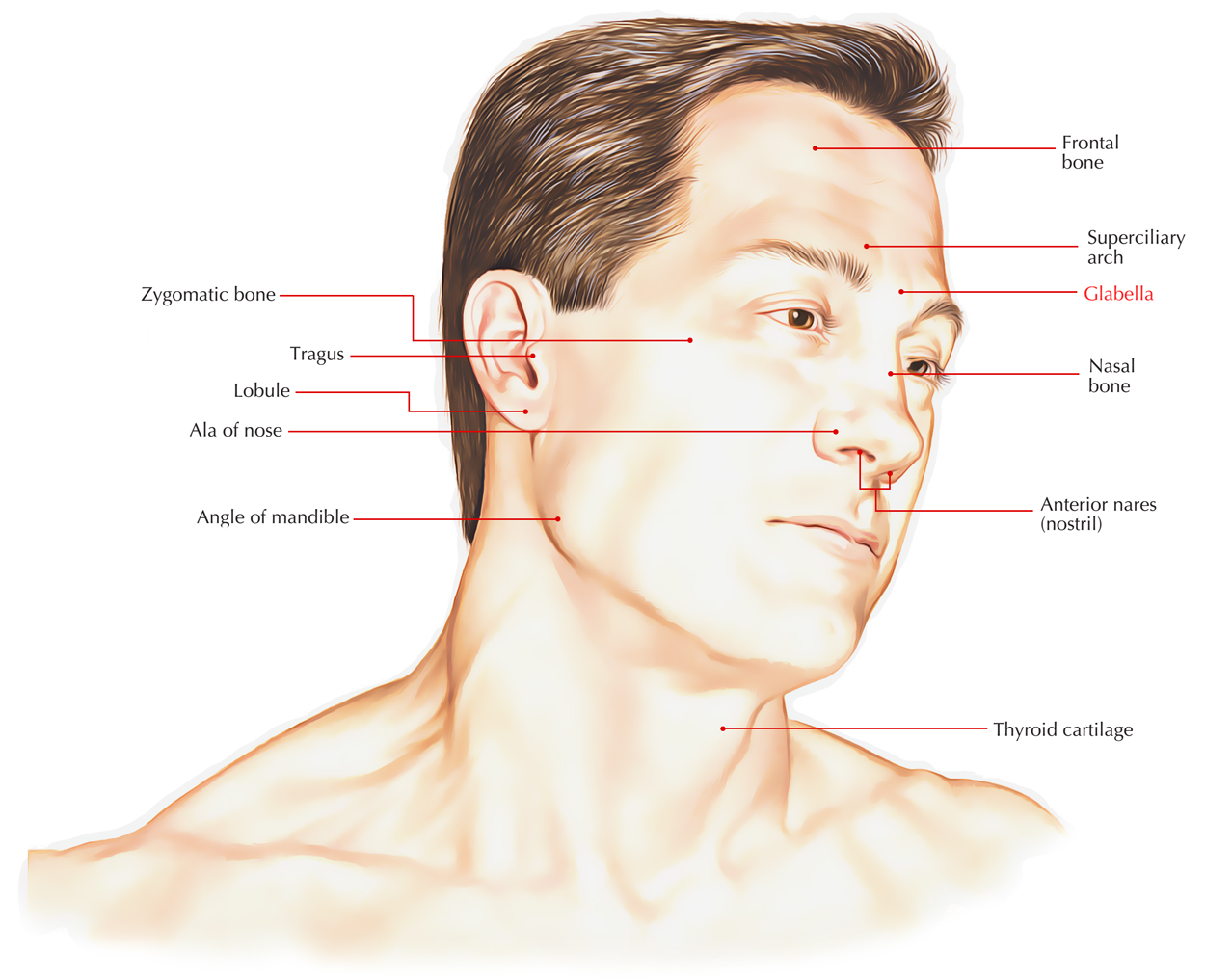
Glabella
Variation
Functional
There is a large amount of variation in functional anatomy of glabella. Example: When most people frown, they primarily bring their brows together as well as depress them. However, this is not done by everyone. Some people predominantly frown in a vertical form, intensely depressing their brows. When others frown, they may elevate their medial brows at the same time as moving them medially, giving a questioning expression.
Structural
- Glabella creates a rounded protrusion in adult males and is generally flat in children as well as adult females.
- The prominence of forehead, on either side, the frontal eminence is evident above the eyebrow.
- The frontal prominence is typically more pronounced in children and adult females.
Clinical Significance
Cosmetic Surgery/ Cosmetology
The first area that was cosmetically treated with BoNT-A injections was the glabella. This use of BoNT-A was according to long-standing surgical procedures, same as other areas of the upper face. It was common to decrease the mass of the glabellar musculature during a bicoronal browlift, to facilitate glabellar furrowing and decrease downward draw on the brow.
[su_spoiler title=”References”] [/su_spoiler]
 (61 votes, average: 4.49 out of 5)
(61 votes, average: 4.49 out of 5)