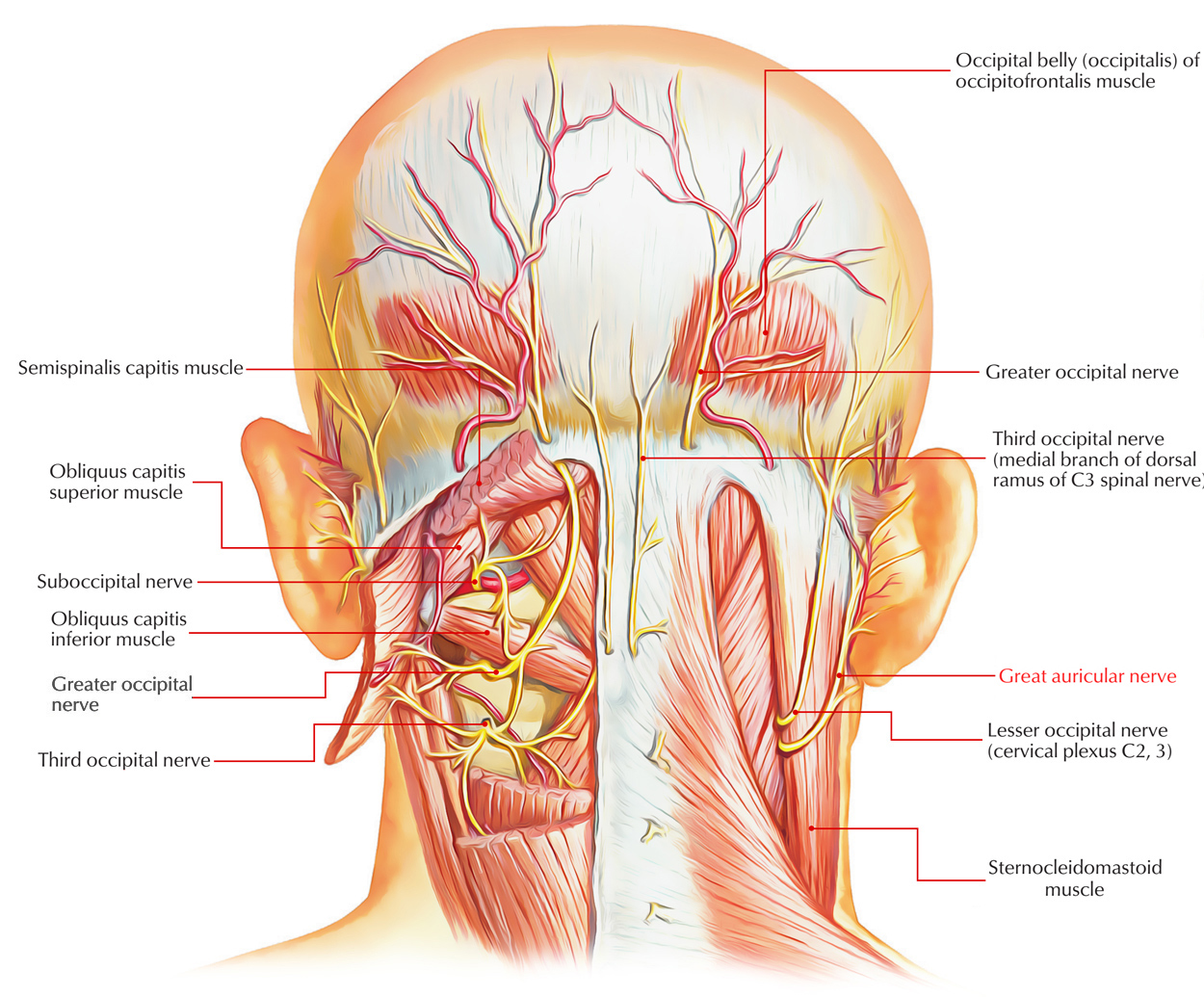
The great auricular nerve is a branch of the cervical plexus. It originates from the anterior rami of the C2 as well as C3 spinal nerves rises upwards on the surface of the sternocleidomastoid muscle.
Great Auricular Nerve
Insertion
From the posterior margin of the sternomastoid the great auricular nerve turns and on the surface of the muscle travels nearly vertically then crosses towards the ramus in order to supply the lower third of the ear, the lower posterior auricular skin, the angle of the jaw and the submandibular area.
Interactions
It interconnects with:
- Transverse cervical nerve
- Cervical branch of the facial nerve
- Marginal mandibular nerve
The great auricular nerve may send a mastoid branch which connects with the lesser occipital nerve.
Function
1. The great auricular nerve supplies:
- The skin over the parotid gland, mastoid process and pinna.
- The lobule and antitragus.
- The skin overlying the angle of the mandible.
2. It sometimes alone supplies sensation towards the tragus, other times it shares this function with the auriculotemporal nerve.
3. The great auricular nerve generally innervates the tail of the helix and the scapha.

 (55 votes, average: 4.65 out of 5)
(55 votes, average: 4.65 out of 5)