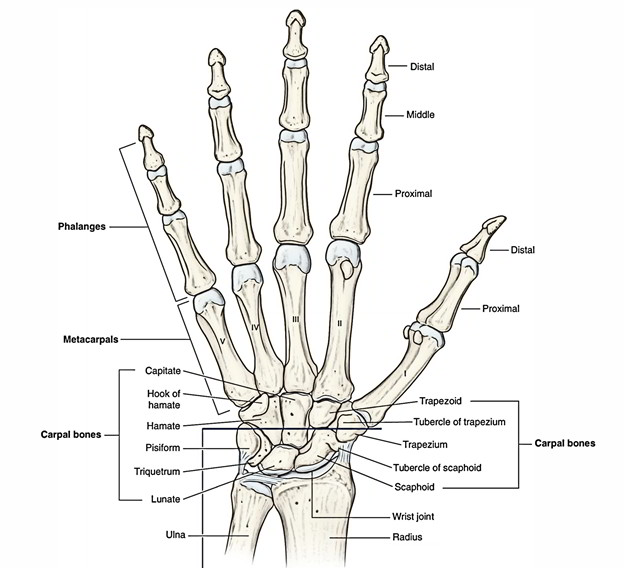
The hamate is triangular in shape, the apex of the triangle being steered proximally. The hamate has a prominent hook-like process connected to its palmar element. The hamate articulates medially and proximally with the triquetral bone, and laterally with the capitate. The apex might articulate with the lunate bone. Distally the hamate articulates with the 4th and 5th metacarpal bones.
Recognition
- The hamate, to the distal and medial part of its palmar element, is easy to recognize, as it has a prominent hook-like procedure attached.
- The apex of the triangle being directed proximally, the hamate is triangular fit, when seen from the palmar aspect.
- Proximally, the tip of the bone might articulate with the lunate bone.
- Distally, the hamate articulates with the fourth and fifth metacarpal bones.
- Medially, and proximally the hamate articulates with the triquetral bone.
- Laterally, the hamate bone articulates with the capitate bone.
Sides
The hamate bone has six sides:
- The superior: The apex of the wedge, is narrow, convex, smooth, and articulates with the lunate.
- The inferior: By concave aspects which are separated by a ridge, articulates with the fourth and fifth metacarpal bones.
- The dorsal: Is triangular and rough for ligamentous attachment.
- The palmar: Presents, at its lower and ulnar side, a curved, hook-like process, the hamulus, directed forward and laterally.
- The medial: By an oblong facet, articulates with the triangular bone, cut sideways from above, downward and medialward.
- The lateral: By its upper and posterior articulates with the capitate part, the staying portion being rough, for the connection of ligaments.
Articulations
- The hamate bone articulates with five bones: the lunate, triquetral, capitate, fourth metacarpal, and fifth metacarpal.
- A small articular aspect takes place for the lunate bone. The proximal most point of the bone forms the tip of the wedge, at this point.
- The medial surface is convex proximally and concave distally for articulation along with the triquetral bone.
- The lateral surface forms a broad, marked articular facet for reception of the capitate bone.
- A lateral aspect for the fourth metacarpal and medial aspect for the fifth metacarpal, its distal side forms a minor ridge that divides this aspect of the bone into two articular facets.
Ossification
It is the second carpal bone to ossify. The hamate ossifies from a single center that arises during the third postnatal month.
Clinical Significance
Hamate Fracture
Causes
A fracture can take place from swinging a golf club, tennis racket or baseball bat particularly if it unexpectedly hits an immoveable object for instance a golf club striking the floor. A stress fracture can likewise occur and if it goes unnoticed it can progress and develop into a full fracture.
Treatment
If the injury is noticed late then it is likely not to heal where case the most popular option is to eliminate the piece of bone totally followed by immobilization in a cast for 3 weeks. Treatment normally involves immobilization in a cast for 4 weeks. Go back to sports specific training may take 6 weeks or more.
Putty exercises and using hand medicine ball are excellent for achieving repair of full movement, mobility strengthening workouts must be done to bring back complete movement and when the wrist comes out of the cast.

 (48 votes, average: 4.75 out of 5)
(48 votes, average: 4.75 out of 5)