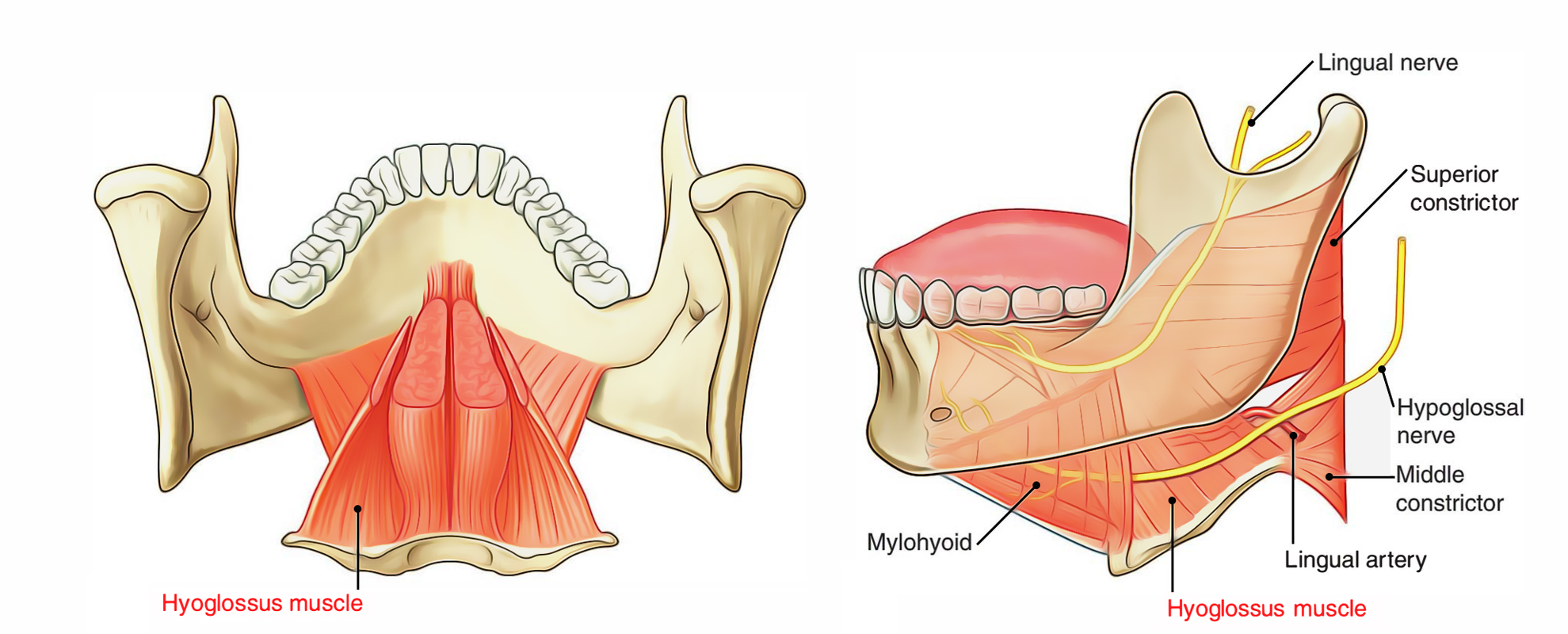
The hyoglossus muscles are slim quadrangular muscles and are located lateral towards the genioglossus muscles.
Hyoglossus Muscle
Origin
Hyoglossus muscles begin from upper surface of the total length of the greater cornu along with neighboring portion of the body of hyoid bone.
Insertion
Hyoglossus attaches into the side of tongue in the middle of styloglossus muscle laterally as well as inferior longitudinal muscle medially. The fibres of hyoglossus from hyoid bone travel upwards and a little forward and afterwards cross each other together with the fibres of styloglossus.
- The hyoglossus muscle at its source from the hyoid bone is located lateral towards the connection of the middle constrictor muscle of the pharynx.
- The muscle travels superiorly as well as anteriorly via the oropharyngeal triangle in the middle of the superior constrictor, middle constrictor, along with mylohyoid in order to insert within the tongue lateral towards the genioglossus and medial towards the styloglossus.
A part of hyoglossus may be connected to the lesser cornu of the hyoid bone and create a separate muscle referred to as chondroglossus.
Nerve Supply
The hyoglossus muscle is innervated by the hypoglossal nerve [XII].
Relations
The hyoglossus, a quadrilateral sheet of muscle, is the key muscle of the suprahyoid region because it serves as a landmark for neighboring structures in the region. Therefore, its relations are very important to surgeons.
Superficial
- Hypoglossal nerve traverses the lower portion of muscle from behind forwards.
- Lingual nerve goes across the upper portion of muscle from behind forwards.
- Deep section of the submandibular gland and submandibular duct. The gland is located in the middle of hyoglossus muscle and the duct is located in the middle of the gland and the muscle.
- Submandibular ganglion is located in the middle of the lingual nerve and deep portion of the submandibular gland.
- Styloglossus muscle interlocks with hyoglossus.
- Mylohyoid muscle anterosuperiorly covers the hyoglossus.
Deep
- Glossopharyngeal nerve.
- Stylohyoid ligament.
- Lingual artery.
- Inferior longitudinal muscle of tongue.
- Genioglossus muscle anteriorly.
- Middle constrictor of pharynx posteriorly.
Structures travelling deep towards posterior margin of hyoglossus
- Glossopharyngeal nerve.
- Stylohyoid ligament.
- Lingual artery.
Clinical Significance
The hyoglossus muscle is a vital marker in the floor of the oral cavity:
- The lingual artery from the external carotid artery in the neck goes inside the tongue deep in the direction of the hyoglossus, among the hyoglossus and genioglossus.
- The hypoglossal nerve along with lingual nerve, on the external side of the hyoglossus move inside the tongue correspondingly, from the neck and infratemporal fossa of the head.

 (53 votes, average: 4.72 out of 5)
(53 votes, average: 4.72 out of 5)