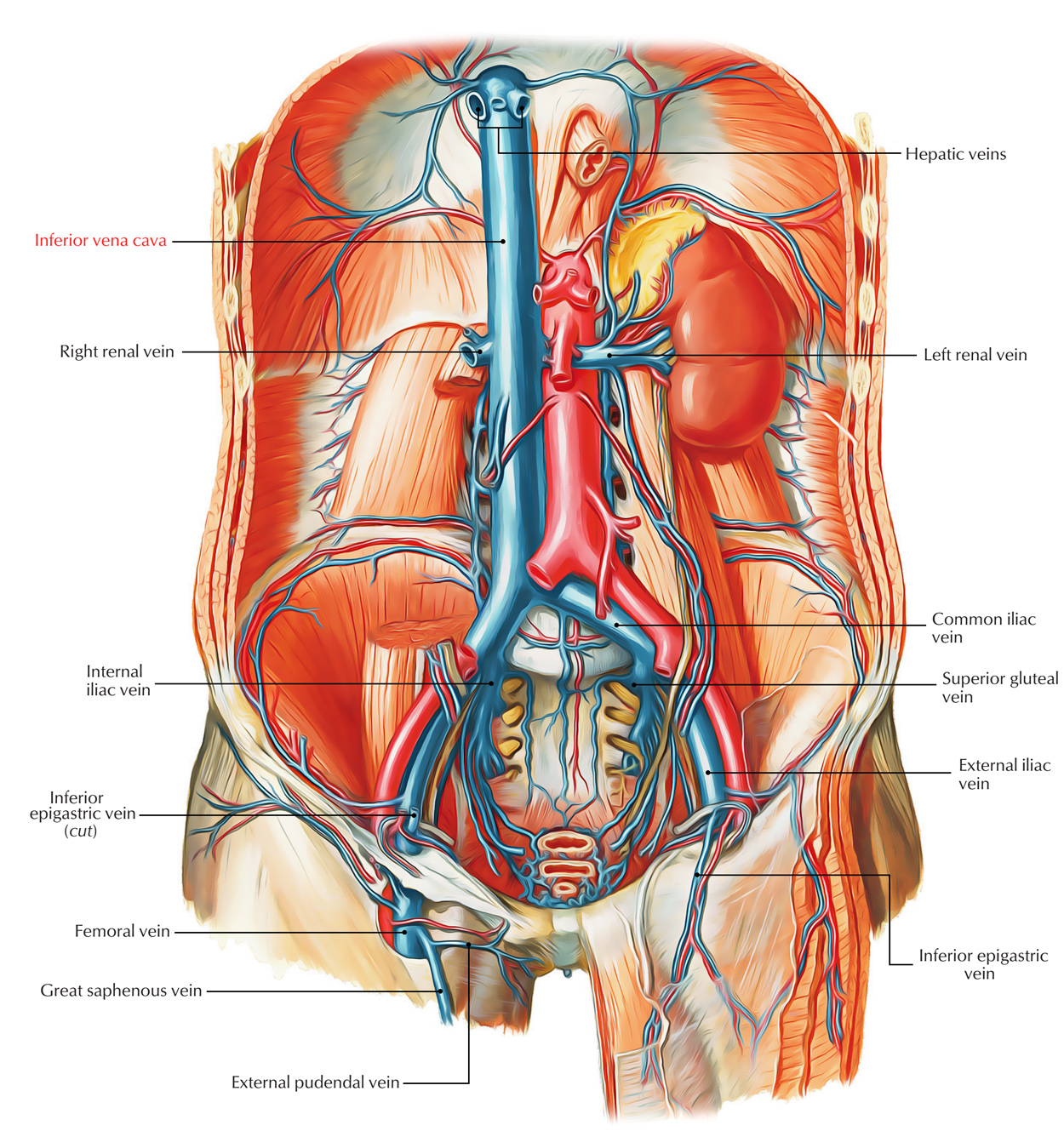
Inferior Vena Cava (IVC) is the largest and the broadest vein of the body. Its function is to empty the majority of the blood from the body below the diaphragm into the right atrium of the heart.
Inferior Vena Cava
Formation, Course and Conclusion
The union of left and right common iliac veins in front of the body of L5 vertebra, below the aortic bifurcation, and behind the right common iliac artery form the IVC. The IVC ascends from the front of the vertebral column on the right side of the aorta. It subsequently arches forward on the right crus of the diaphragm to get to the groove on the posterior outermost layer of the liver between the right and caudate lobes, just above the groove it pierces the central tendon of the diaphragm in the level of T8 vertebra and ends by going into the right atrium of the heart.
Stretching across 8 vertebrae (L4 to T8), it is about twice the length of the abdominal aorta.
Relations
Anterior: From below upward, the structures anterior to the IVC as it ascends are:
- The root of the mesentery.
- Right testicular/ovarian artery.
- The third part of the duodenum.
- Head of the pancreas and bile duct.
- Portal vein (posterior to first of duodenum and in the right free margin of lesser omentum).
- The posterior outermost layer of the liver between the right and caudate lobes.
Posterior: From below upward, the structures posterior to the IVC as it ascends are:
- Right sympathetic chain and psoas major.
- Right renal artery.
- Right coeliac ganglion.
- Right suprarenal gland (medial part).
- Right middle suprarenal vein.
- Right inferior phrenic artery.
Tributaries
The IVC gets the following tributaries:
- 3 formative veins: 2 common iliac veins and the median sacral vein. The latter may join the left common iliac vein. Every common iliac vein gets an iliolumbar vein.
- 3 abdominal wall tributaries: inferior phrenic vein and third and fourth lumbar veins. The very first and 2nd lumbar veins finish in the ascending lumbar vein.
- 3 Lateral visceral tributaries: right suprarenal vein, renal veins, and right testicular/ovarian vein. The left suprarenal vein and left gonadal veins drain into the left renal vein.
- 3 anterior visceral tributaries: right, middle, and left hepatic veins.
Clinical Significance
Compression of the Inferior Vena Cava (IVC)
The IVC is commonly compressed by an enlarged uterus during the past trimester of the pregnancy. This causes edema of the ankle and feet, and varicose veins in the lower limb.
The compaction and blockage of the IVC by the malignant retroperitoneal tumors result in dilatation of the anastomotic channel between IVC and superior vena cava (caval-caval shunt) so the blood might be returned to the right atrium. Medically, it presents as the notable sandwich cutaneous vein named thoraco-abdominal vein created because of dilatation of anastomotic venous channel between the lateral thoracic vein, a tributary of the axillary vein, and the superficial epigastric vein, a tributary of the femoral vein.

 (52 votes, average: 4.79 out of 5)
(52 votes, average: 4.79 out of 5)