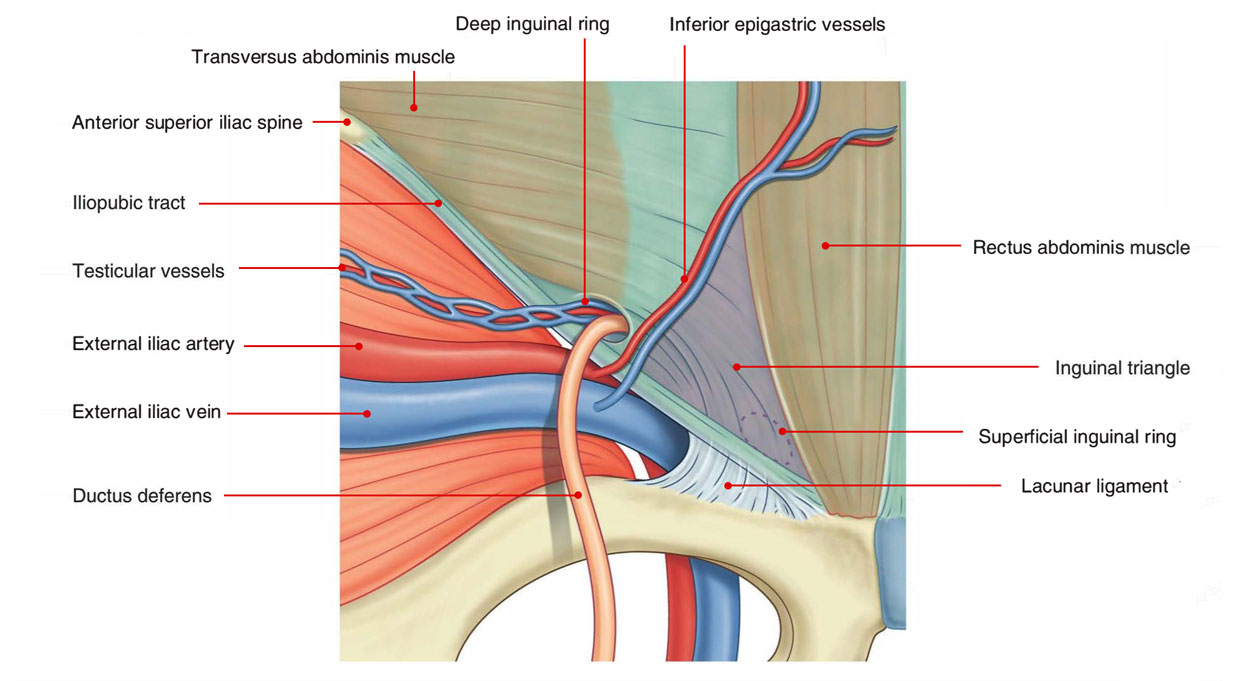
The location of the the inguinal triangle is found deep to the posterior wall of the inguinal canal. This is why the inguinal triangle is observed on the inner aspect of the lower part of the anterior abdominal wall.
Inguinal Triangle
Continue The Rest of The Article Below…
Boundaries of Inguinal Triangle
The Boundaries of the inguinal triangle are as follows:
- Medial: Lower 5 cm of the lateral border of the rectus abdominis muscle.
- Lateral: Inferior epigastric artery.
- Inferior: Medial half of the inguinal ligament.
Peritoneum covers the floor of the inguinal triangle, extraperitoneal tissue, and fascia transversalis.
The medial umbilical ligament (obliterated umbilical artery) crosses the inguinal triangle and splits it into medial and lateral parts. The medial part of the floor of the inguinal triangle is reinforced by the conjoint tendon.
The lateral part of the floor of the inguinal triangle is poor, therefore direct inguinal hernia generally takes place via this part.

Inguinal Triangle
Clinical Significance of Inguinal Triangle
Inguinal Hernias
A protrusion of abdominal viscera (example, loops of intestine) into the inguinal canal is named inguinal hernia. Medically it presents as a pear shaped swelling above and medial to pubic tubercle, above the inguinal ligament. There are just two types of inguinal hernias, direct and indirect.
Indirect Inguinal Hernia
- The indirect inguinal hernias happen if the hernial sac enters the inguinal canal via the deep inguinal ring, lateral to the inferior epigastric artery.
- It’s common in kids and young adults. The predisposing factor for this particular type of hernia is the whole or partial patency of the processus vaginalis.
- The indirect inguinal hernias are much more common than the direct inguinal hernias and take place more commonly in men than females. The indirect inguinal hernia could possibly be congenital or acquired.
Congenital Indirect Inguinal Hernia
It happens because of patent processus vaginalis (an outpouching of the peritoneum), linking peritoneal cavity with all the tunica vaginalis.
Got Indirect Inguinal Hernia
It happens because of increased intra-abdominal pressure as during strength training. When intra-abdominal pressure is increased hugely, the abdominal contents are pushed via the deep inguinal ring into the inguinal canal.
Direct Inguinal Hernia
The direct inguinal hernia happens if the hernial sac enters the inguinal canal directly by shoving the posterior wall of the inguinal canal forwards, medial to inferior epigastric artery via the Hesselbach’s triangle. The neck of hernial sac is wide. The direct inguinal hernias are typical in aged because of poor abdominal muscles. The direct hernia leaves the triangle via its lateral part or medial part, and consequently it’s of 2 types: (a) lateral direct inguinal hernia, and (b) medial direct inguinal hernia.
The term entire inguinal hernia is utilized if hernial contents get to the tunica vaginalis. If the hernial contents stay confined to inguinal canal and donot go through superficial inguinal ring it’s referred to as incomplete inguinal hernia/bubonocele.
The inguinal hernias happen only in men and not in other mammals. This is because of evolutionary changes that have taken place in inguinal region because of erect position.
Differences Between Inguinal and Femoral Hernias
Inguinal hernia | Femoral hernia | |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | More common in males | More common in females |
| Protrusion of hernial sac | Into inguinal canal | Into femoral canal |
| Neck of protrusion of hernia | Lies above and medial to pubic tubercle | Lies below and lateral to the pubic tubercle |
Differences Between the Indirect and Direct Inguinal Hernia
Indirect inguinal hernia | Direct inguinal hernia | |
|---|---|---|
| Site of protrusion of hernial sac | Deep inguinal ring | Posterior wall of inguinal canal |
| Shape | Pear shaped | Globular |
| Extent | Generally scrotal | Rarely scrotal |
Test Your Knowledge
INGUINAL TRIANGLE

 (50 votes, average: 4.52 out of 5)
(50 votes, average: 4.52 out of 5)