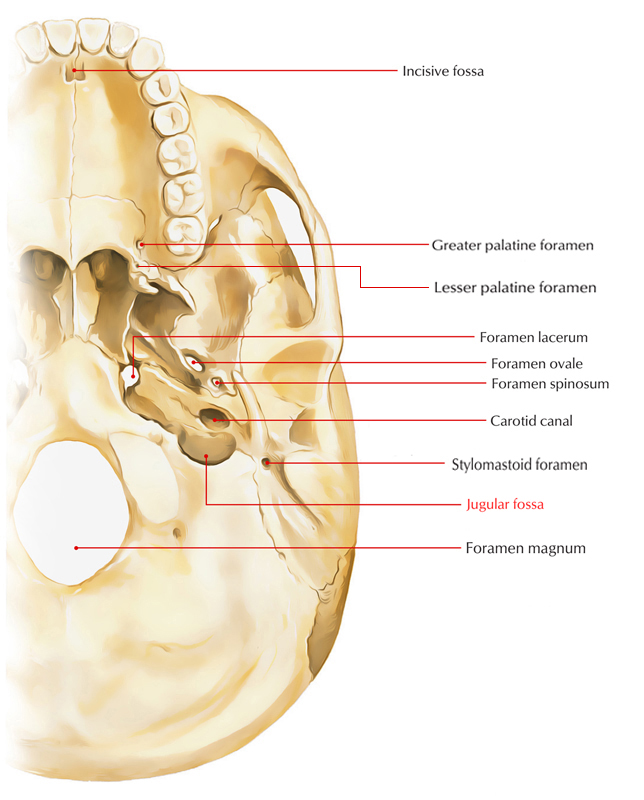
The jugular fossa refers to a recession which is located at the inferior side of petrous temporal bone posterior towards the inferior aperture of carotid canal.
Jugular Fossa
Relations
- The carotid sheath spreads out from the base of the skull superiorly towards the arch of the aorta inferiorly. It is attached towards the margins of carotid canal along with the jugular fossa at its upper end.
- Internal jugular vein lies in the jugular fossa of the temporal bone at its origin. It is associated to the base of the middle ear and is referred to as the superior bulb.
- It accommodates the jugular bulb.
- The jugular foramen is located anterior towards it.
- The tympanic branch of glossopharyngeal nerve along with lower aperture of the carotid canal penetrates the floor in the middle of the jugular fossa as well as inserts inside the tympanic cavity in order to participate in the creation of tympanic plexus.
- Auricular branch of vagus nerve a.k.a. Arnold’s nerve or Alderman’s nerve originates from the superior ganglion, travels inside the mastoid canaliculus at the lateral wall of the jugular fossa, and arises via the tympanomastoid fissure just posterior towards the external auditory meatus in order to innervate the skin posterior to the meatus along with neighboring portion of the auricle.
x

 (56 votes, average: 4.84 out of 5)
(56 votes, average: 4.84 out of 5)