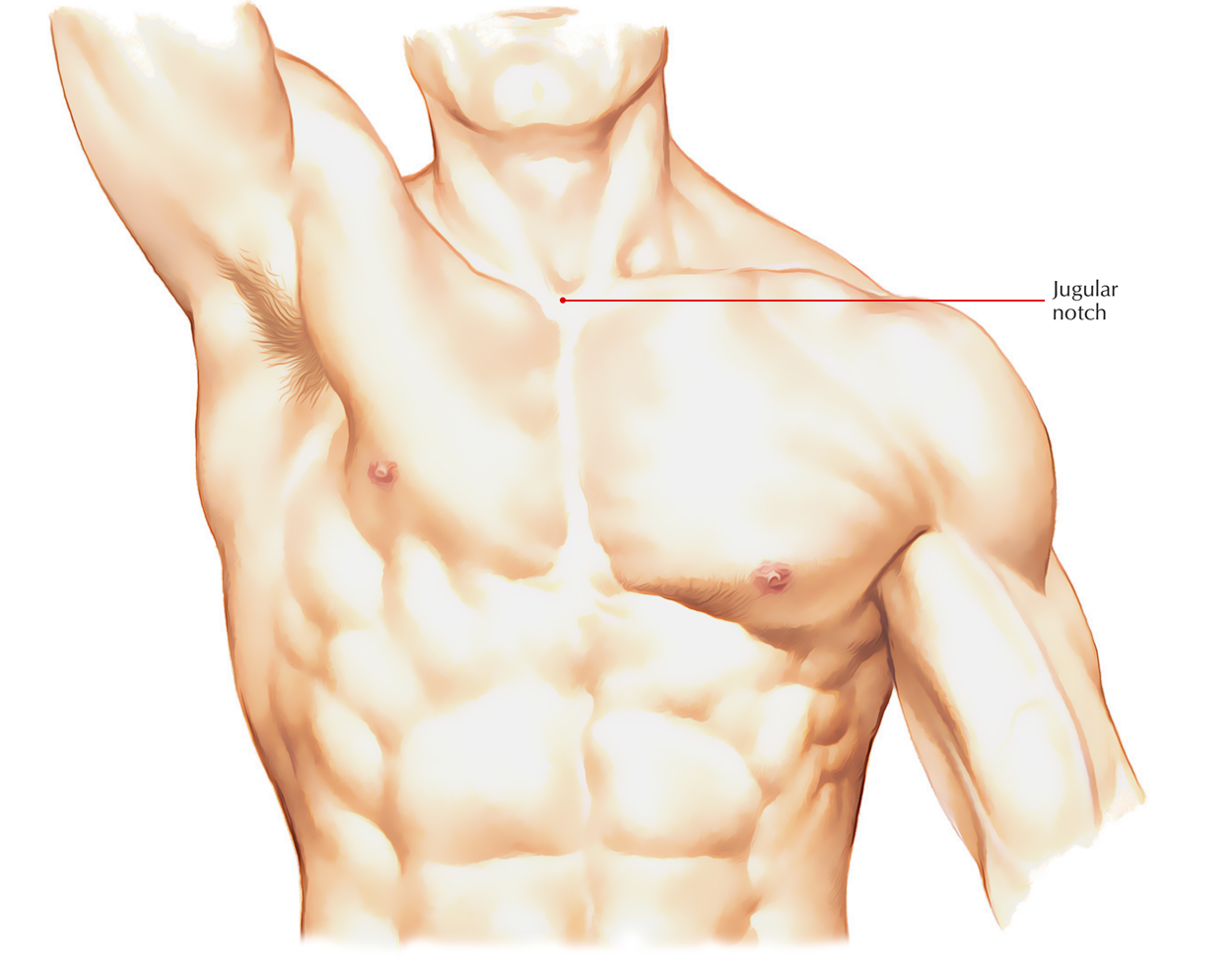
Jugular Notch
Jugular Notch/Suprasternal Notch is a large depression on the top of the sternum between the articulations and two clavicles. In adults, the notch is mainly present because of an aortic arch aneurysm. In a child, it is present due to coarctation of the aorta. It is an important part of the human anatomy. The jugular notch is effortlessly palpated and can be generally seen as an impression on the surface.
Relations
- The jugular notch shows the anterior intersection of the superior mediastinum along with the root of the neck.
- It posteriorly is located at the plane of the T2 vertebra.
- The body of the sternum intersects with the manubrium about 4 cm inferior towards the jugular notch; the joint is called manubriosternal joint. It forms the sternal angle detectible at the surface of the thorax.
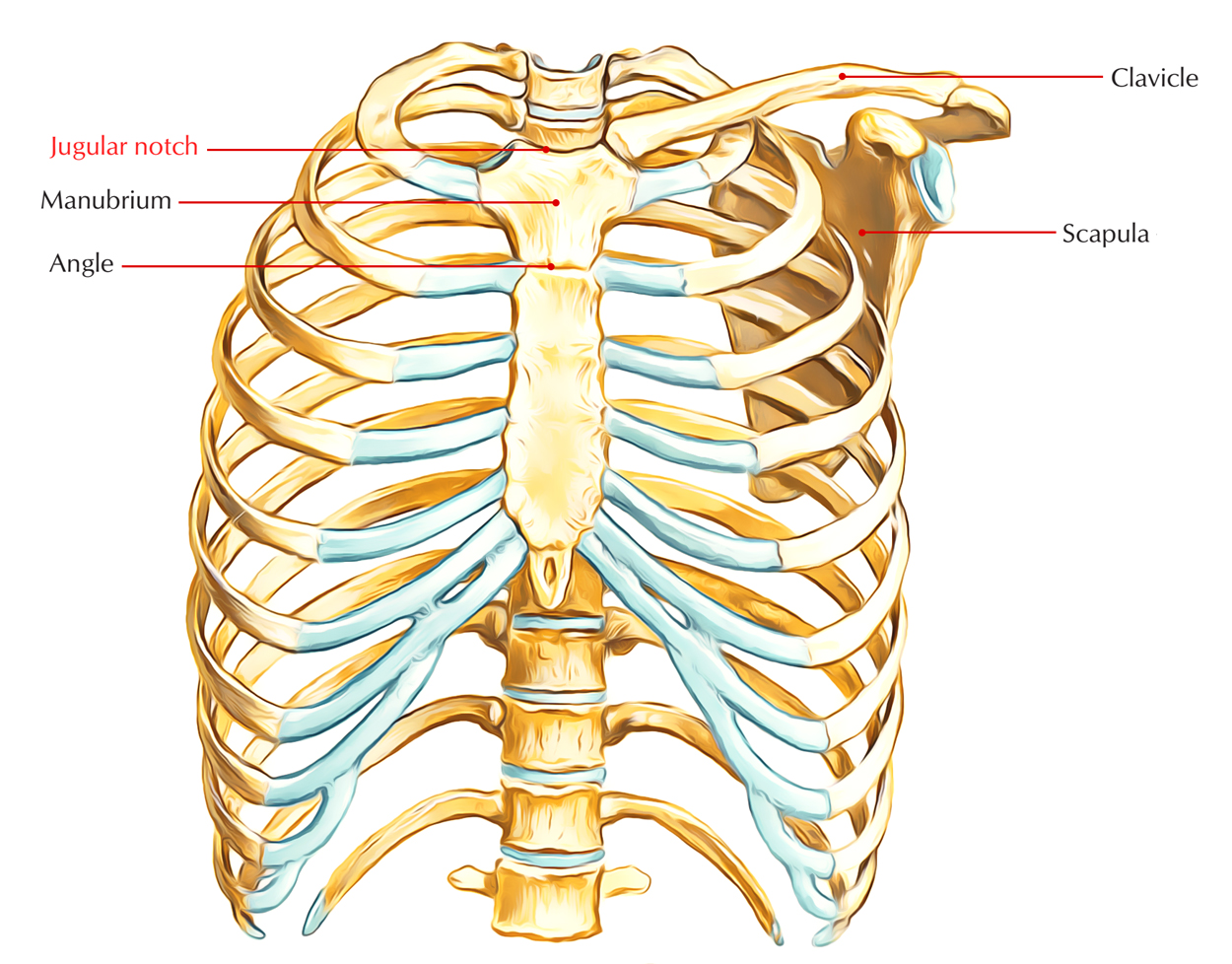
Jugular Notch: Relations
Clinical Significance
Palpation
The jugular notch (a.k.a. suprasternal notch) is palpated in the middle of the prominent medial end points of the clavicles.
Cervical Bronchial Cysts
- Most cervical bronchial cysts exist in the skin along with the subcutaneous tissue of the Jugular Notch/Suprasternal Notch. They are rarely ever located in the lower anterior neck, chin, or shoulder.
- With the ratio 3:1, they are more common in males as compared to females.
- Generally, the cysts appear as asymptomatic nodules which gradually increase in size and turn out to be clinically evident at or soon after birth. In approximately one third of cases, draining sinuses that show mucoid material are found.
- When the patient performs the Valsalva movement, the cyst becomes more noticeable.
Drug Diffusion for Treatment of Epilepsy
After anesthesia, through a 2–3 cm vertical incision is made inferior to the chin, via the Jugular Notch/Suprasternal Notch. After exposure of the sternothyroid muscle, the common carotid artery and separation from the posteriorly placed vagal nerve; the drug is diffused or administered through catheterization. The drug is primarily administered in solution form.

 (50 votes, average: 4.80 out of 5)
(50 votes, average: 4.80 out of 5)