The left atrium is among the four compartments of the heart, found on the left posterior side. Its primary functions are to perform as a stock chamber for blood recurring from the lungs as well as in order to function as a pump in order to transport blood towards other areas of the heart.
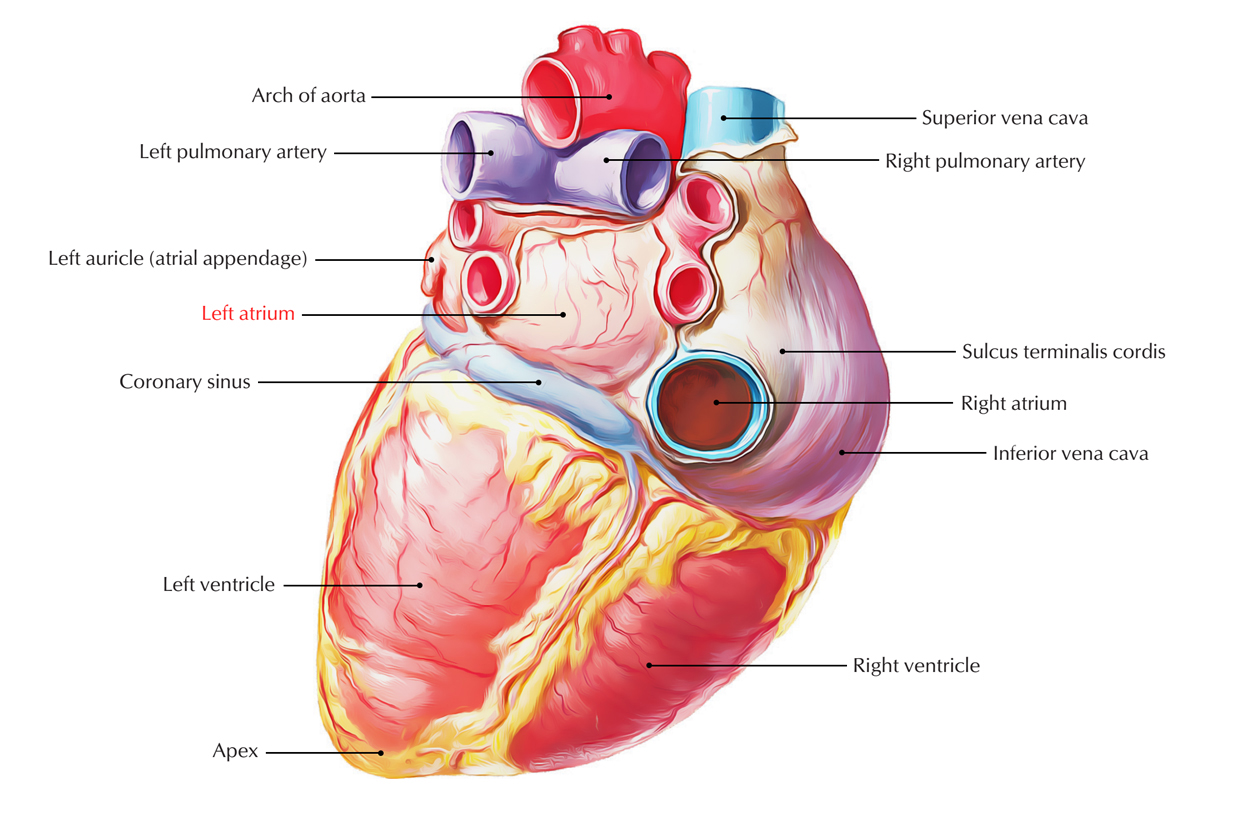
Left Atrium
Internal Features
- The interior of left atrium is smooth; however in the form of reticulum, the left auricle possesses muscular ridges.
- The anterior wall of left atrial cavity has fossa lunata, which corresponds to the fossa ovalis of the right atrium.
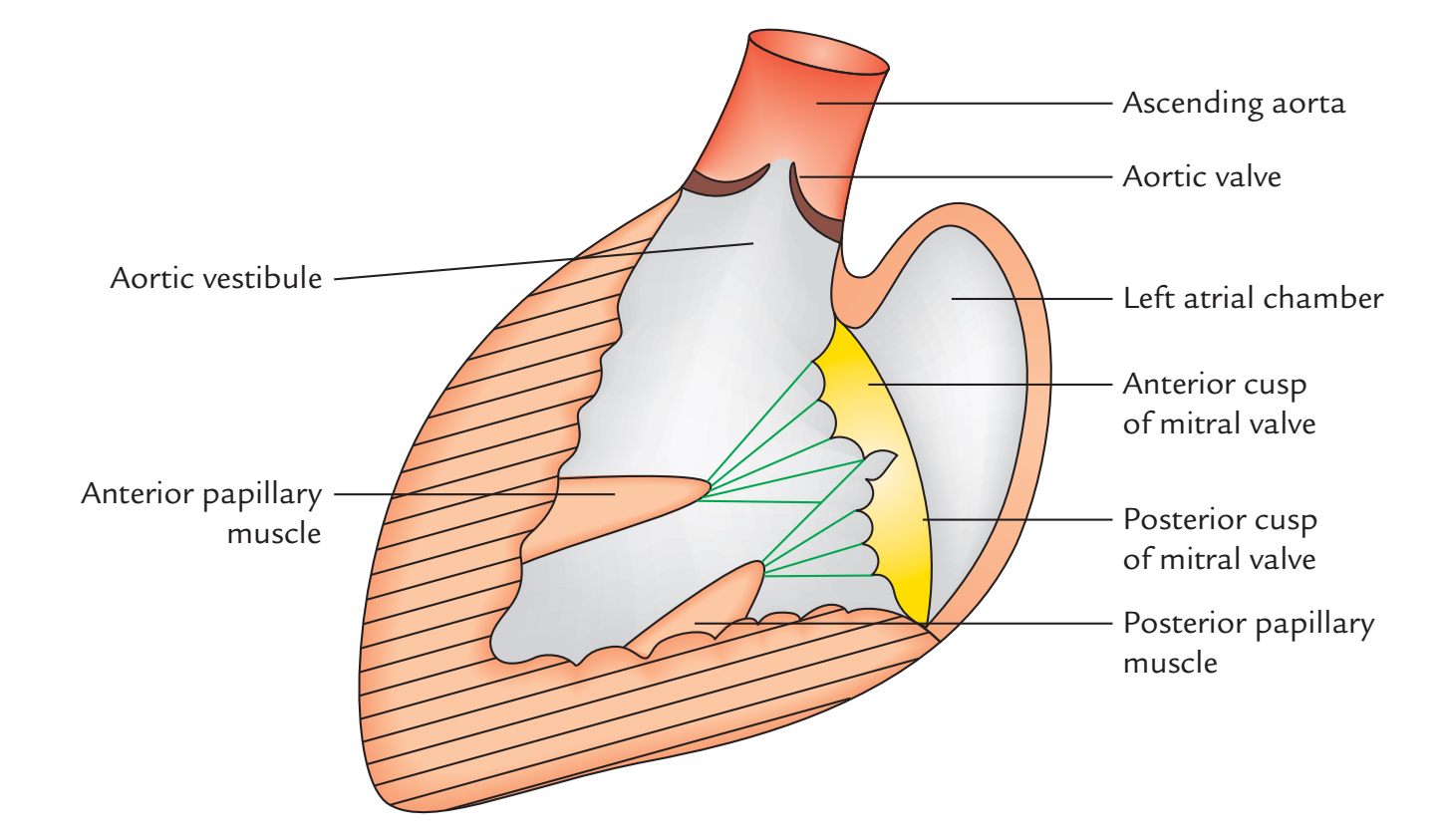
Left Atrium: Internal Features
External Features
- It is a thin-walled quadrangular chamber found posteriorly at the back and towards the left side of right atrium. It creates greater part of the base of the heart (left 2/3rd).
- In order to create the left auricle, which overlaps the infundibulum of right ventricle Its upper end is prolonged anteriorly.
- Structures behind the left atrium:
- Oblique sinus of serous pericardium.
- Fibrous pericardium.
Openings
Openings in the left atrium are as follows:
- Openings of four pulmonary veins in its posterior wall, two on each side, having no valves.
- Numerous small openings of venae cordis minimae.
- Left atrioventricular orifice. It is covered via the mitral valve.
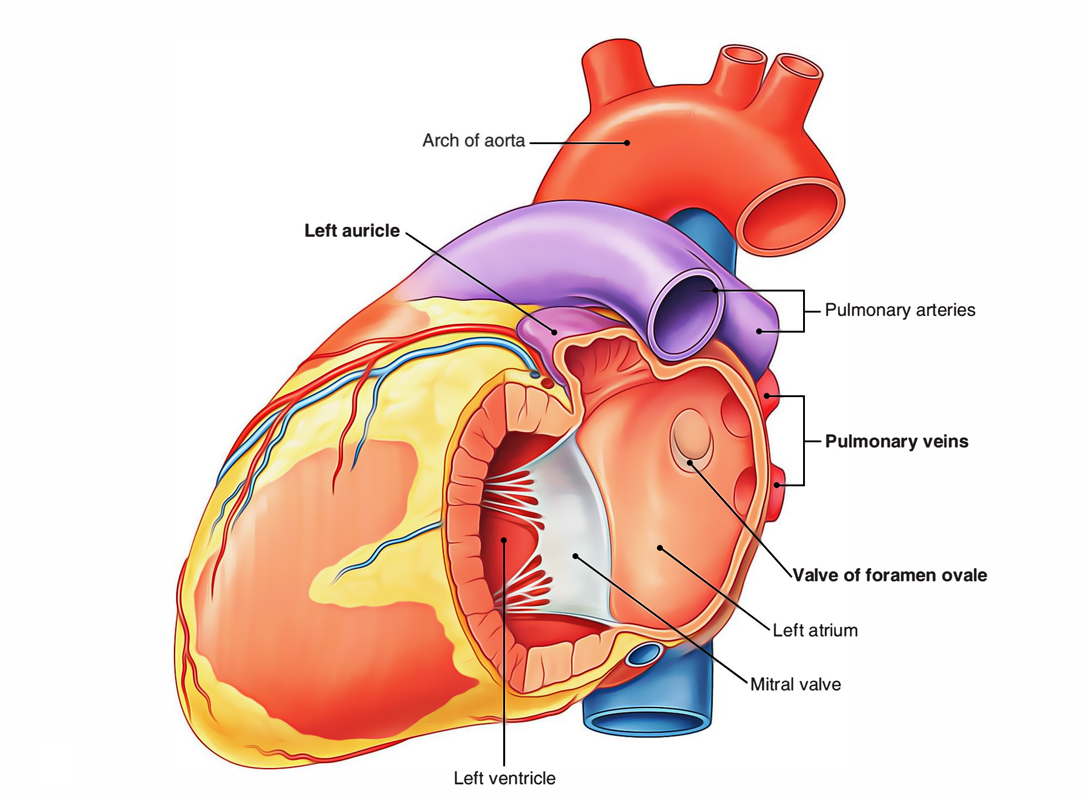
Left Atrium: Openings
Actions
- Blood goes inside via four pulmonary veins, the left and right superior and inferior on both sides.
- Afterwards the blood goes outside via the left atrioventricular opening through the mitral valve, inside the left ventricle.
- The mitral valve is bicuspid and the left atrium holds its anterior and posterior leaflets.
Development
As with the right atrium, the left atrium originates from two structures embryologically.
- The posterior half or inflow portion is the portion that gets the four pulmonary veins. It has smooth walls and originates via the proximal portions of the pulmonary veins at the time of development that are merged into the left atrium.
- The anterior half and the left auricle are constant with each other. It comprises of musculi pectinati and emerges from the embryonic primitive atrium. The two constituents of the left atrium are not divided by any specific structure, contradictory to the crista terminalis in the right atrium.
The interatrial septum is part of the anterior wall of the left atrium. The thin area or depression in the septum is the valve of the foramen ovale and is opposite the floor of the fossa ovalis in the right atrium.
During development, the valve of the foramen ovale prevents blood from passing from the left atrium to the right atrium. This valve may not be completely fused in some adults, leaving a “probe patent” passage between the right atrium and the left atrium.

 (49 votes, average: 4.85 out of 5)
(49 votes, average: 4.85 out of 5)