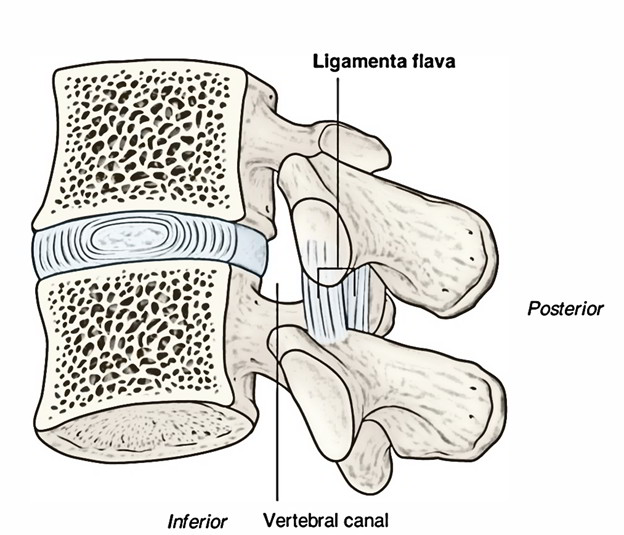
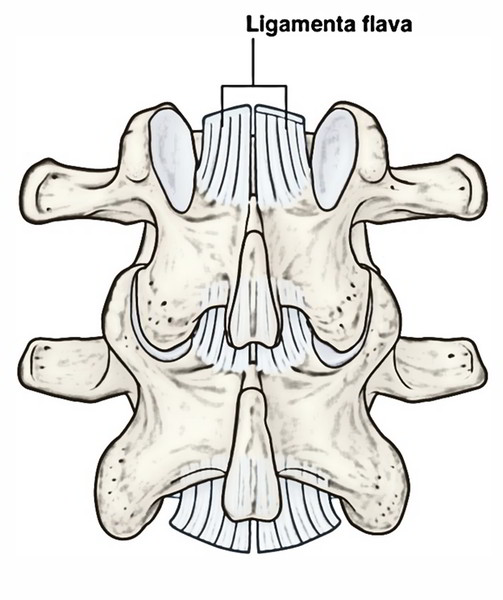
The posterior margins of the two portions touch and to a specific degree combined, small periods being left for the passage of small vessels. Each ligament includes two lateral portions which begin one on either side of the roots of the articular processes, and expand backwards to the point where the laminae connect to create the spinous process.
Structure
Each includes yellow elastic tissue, the fibers which, nearly perpendicular in instructions, are connected to the anterior side of the lamina above, some distance via its inferior margin, and to the posterior side and upper margin of the lamina underneath.
Insertion
The ligament flava, on each side, pass in between the laminae of surrounding vertebrae. These thin, wide ligaments are made primarily of elastic tissue and create part of the posterior side of the vertebral canal. Each ligamentum flavum runs in between the posterior sides of the lamina on the vertebra underneath to the anterior side of the lamina of the vertebra above
Relations
- Anterolateral: intervertebral foramen and contents (spinal nerve roots, segmental arteries, recurrent mengingeal nerves, communicating veins in between internal and external venous plexus).
- Anteromedial: spinal cord and meninges
- Posterolateral: lamina, facet joints.
- Posteromedial: spinous process, interspinous ligament, venous connection in between internal and external vertebral venous plexuses.
Innervation
- Superficial: medial branch of dorsal roots of spinal nerves.
- Deep: sinuvertebral nerves (recurrent meningeal nerves.
Attachments
- Emerges via the lower half of the anterior side of the lamina above and connects to the posterior side and upper margin of the lamina underneath.
- The lateral portion passes in front of the fact joint where it connects to the anterior element of the inferior and superior articular processes and creates the anterior capsule.
- On every side the ligament splits into a medial and lateral portion. The medial portion passes to the back of the next lower lamina. The most lateral fibers expand beyond the superior articular process to the pedicle underneath.
Functions
The ligamenta flava help to bring back the erect posture after flexion therefore guarding the disc via the injury and avoid the splitting up of laminae in spinal flexion.

 (53 votes, average: 4.84 out of 5)
(53 votes, average: 4.84 out of 5)