The Medial collateral ligament (also known as Tibial collateral ligament) is a strong, flat band on the medial element of the knee joint. The tibial collateral ligament expands slowly towards its inferior connection to the medial border of the tibia via its superior attachment to the medial femoral epicondyle and rather anteriorly on the surrounding medial surface of the tibia.
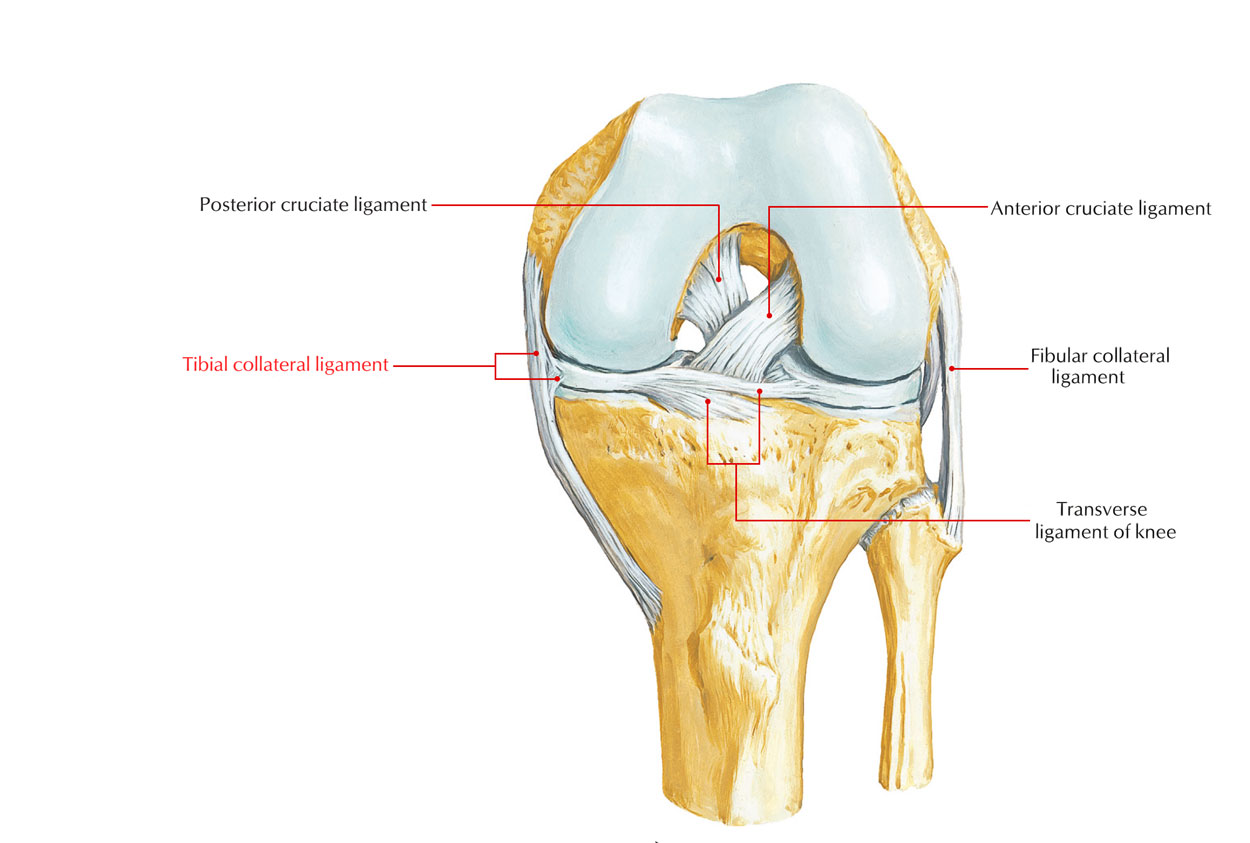
Medial Collateral Ligament
Attachments
The lower end of the ligament is crossed superficially by the pes anserinus; a bursa (the bursa anserinus) typically is located in the middle of these two. The inferior attachment of the tibial collateral ligament is almost a hand’s breadth below the knee joint line. The tibial collateral ligament is considered to be including two parts, an anterior band and a posterior band.
The posterior part of the tibial collateral ligament turns posteromedially, mixing with the capsule of the knee joint and in part, merging with the medial edge of the medial meniscus. The two parts are, naturally, not physically different. Sometimes, a bursa or more will lie deep to the anterior band, separating the ligament via the underlying joint capsule and medial meniscus; although still more distally, the medial inferior genicular neurovascular structures will be located in the middle of the medial collateral ligament and the tibia of the posterior part of the medial collateral ligament also connects to the medial tibial condyle.
Clinical Significance
Injury
- Medial ligament injuries prevail in contact sports such as football and rugby, in addition to martial arts.
- A medial ligament sprain or MCL injury is a tear of the ligament on the within the knee, normally an outcome of twisting or direct effect.
Treatment
Treatment can be divided into instant emergency treatment throughout the severe phase and longer term rehab.
Immediate Emergency Treatment
- Apply R.I.C.E. concept (Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation) to the hurt knee.
- Rest via training or any activities or movements which hurt to permit recovery to happen.
- Apply ice or cold treatment wrap for 10 to 15 minutes every hour at first decreasing frequency as symptoms enable. Ice must not be applied straight to the skin however utilize a damp tea towel or comparable. Professional cold treatment knee covers are convenient to utilize and will use compression too.
- Use a compression plaster or knee support to assist minimizes any swelling and proect the joint. A hinged knee brace is best especially for grade 2 and 3 injuries.
Hinged Knee Brace
A hinged knee brace is a strong knee support which has solid metal supports down the sides to prevent sideways movement of the joint and secure the knee ligaments while recovery.
More extreme grade 2 and complete grade 3 injuries might need a restricted motion hinged knee brace which limits the quantity of movement or knee bend in the joint whilst recovery.
Electrotherapy
- Interferential or tens includes using electrical currents to the tissue around the injury which can also aid with pain and swelling.
- Ultrasound treatment includes using high frequency acoustic wave to the hurt tissues.
- An expert therapist might do this in the early more intense phases to assist manage swelling and pain.
Taping
- An excellent taping method can offer outstanding support and frequently more support than a few of the less expensive hinged knee splints, however the efficiency of tape will minimize with time as the tape extends slightly.
- Taping the knee joint can also offer a high level of support and protection.
- It can be performed in the early stages along with later when going back to complete training.
- It will have to be re-applied to keep excellent support for the joint, especially throughout competitive sport.
Workouts
- In the early stages isometric reinforcing workouts or fixed muscle contractions can be done to assist keep muscle strength and avoid muscle squandering whilst the ligament heals.
- At first variety of motion mobility workouts are done to bring back complete pain totally free variety of movement.
- A complete rehab program including mobility and reinforcing workouts must start as quickly as pain permits.
- As the ligament heals reinforcing workouts such as mini crouches, leg press and step ups could be done however movements including switch or sideways pressures must be prevented till much later on in the rehab regimen.
- A hinged knee brace must be used to secure the ligament whilst working out.
Massage
Later on as the ligament begins to heel then light cross friction massage might be utilized and in particular if there is constant pain in the later phases of rehab then cross friction massage might be useful.
Manual treatment methods consisting of massage might be utilized as part of a rehab program.
Massage therapy to the hurt tissues must be prevented in the early severe phases.

 (60 votes, average: 4.82 out of 5)
(60 votes, average: 4.82 out of 5)