Scalene muscles are constituents of the lateral vertebral group of muscles.
The scalene muscles are:
- Posterior scalene or Scalenus posterior.
- Medial scalene or Scalenus medius.
- Anterior scalene or Scalenus anterior.
Medial scalene muscle is longest and biggest among all the scalene muscles.
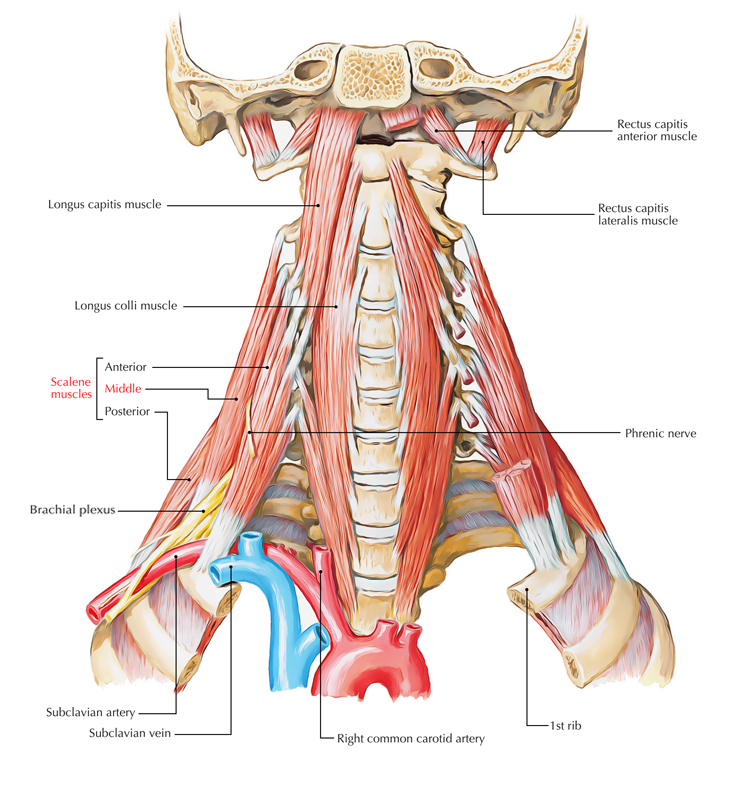
Medial Scalene Muscle
Origin
It originates via posterior tubercles of the transverse processes of C2-C6 cervical vertebrae.
Insertion
It inserts on the upper side of the first rib in the middle of the tubercle of the rib and groove for subclavian artery.
Nerve supply
Medial scalene muscle is innervated by ventral rami of C3-C8 spinal nerves.
Actions
- It turns the neck to the same side whenever first rib is stable.
- It raises the first rib when upper end is fixed.
Clinical Significance
Scalene syndrome
It includes complications that are created in the scalene triangle because of constriction of lower trunk of brachial plexus (C8 and T1) and subclavian artery:
- Lifting its base by the cervical rib.
- Due to spasm of scalene muscles.
Symptoms
- Tingling sensation and numbness along the inner border of forearm and hand.
- Gradual paresis and wasting of intrinsic muscles of the hand.
- Due to constriction of subclavian artery ischemic pain and deficiency of radial pulse.

 (55 votes, average: 4.78 out of 5)
(55 votes, average: 4.78 out of 5)