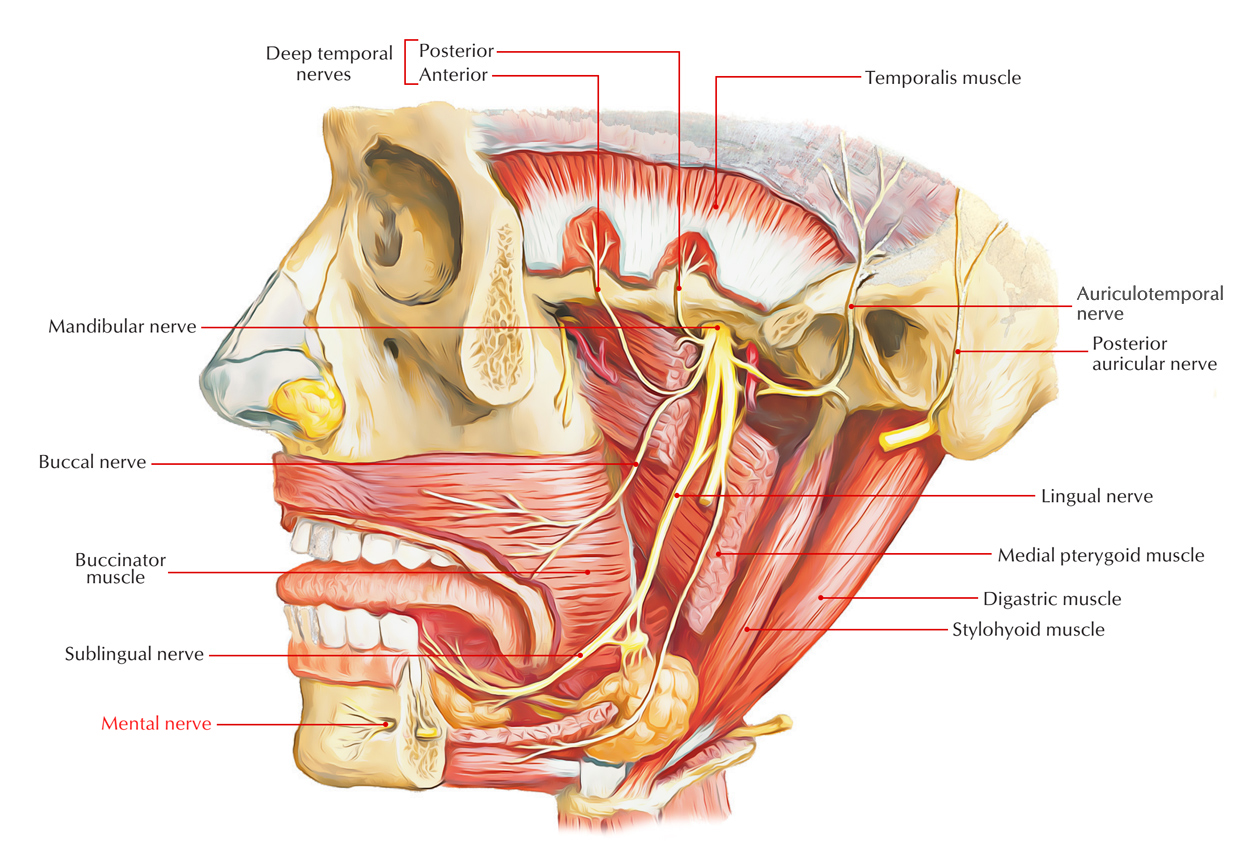
The mental nerve exits via the mental foramen and splits in 3 branches under the depressor anguli oris muscle. It arises from the inferior alveolar nerve.
Mental Nerve
Insertion
The mental foramen is located in the zone of the second premolar, at the midpoint among the alveolar crest along with the inferior mandibular border. In order to supply the lower lip and chin, the mental nerve leaves the mandible from the mental foramen.
Function
The mental nerve sends branches to supply:
- Skin and mucous membrane of the lower lip.
- Skin of the chin.
- Vestibular gingiva of the mandibular incisors.
Clinical Significance
Palpation
Through the oral mucosa adjacent to the roots of the premolar teeth, the mental nerve is detectible and visible oftentimes.
Mental Nerve Block
- The mental nerve block is a simple technique for giving anesthesia in this zone.
- It must be noted that this nerve block does not gives anesthesia for the teeth or mandibular soft tissue.
- When compared with other intraoral nerve blocks, the pain related to the mental nerve block is considerably lesser.
Mental Nerve Neuralgia
Mental nerve neuralgia is a painful disorder which can arise due to damage or improper function of the mental nerve.
Causes
- Mental nerve neuralgia appear due to variety of reasons.
- Complication of dental treatment is the most common cause.
- It may be the first sign of a systemic or general malignancy, if it’s not the cause.
Signs and Symptoms
Along with neuropathic pain, patients complain of numbness of their cheek and lower lip.
Diagnosis
- First, a neurological assessment of the cheek and lips must be done.
- A careful examination will be given by a dentist.
- If the problems are not caused by dental treatment, and if necessary, more examinations are done.

 (54 votes, average: 4.74 out of 5)
(54 votes, average: 4.74 out of 5)