The point of origin and insertion of Muscles of the foot as follows:
- The extensor digitorum brevis and extensor halluces brevis on the dorsal aspect of the foot or Dosrum of the foot;
- All the other muscles viz -the dorsal and plantar interossei, flexor digiti minimi brevis, flexor halluces brevis, flexor digitorum brevis, quadratus plantae (flexor accessorius), abductor digiti minimi, abductor hallucis, and lumbricals are on the plantar side of the foot in the sole where they are arranged in 4 layers.
The muscles mainly customize and improve the actions of the long tendons and help fine movements of the toes.
Except for the extensor muscle that is nervous supply by deep fibular nerve, all muscles of the foot have nervous supply by medial and plantar branches of tibial nerve. The deep fibular nerve may also partly supply nerves to the first two dorsal inerrosei.
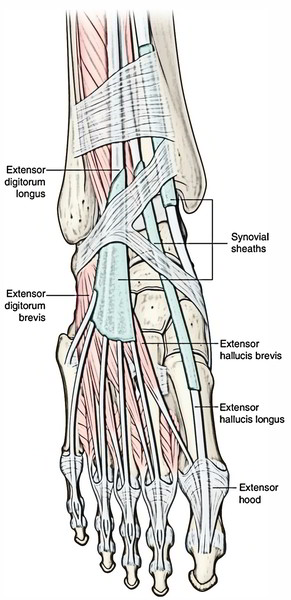
Muscles of The Dorsum of The Foot or Dorsal of the foot
Extensor Digitorum Brevis
It’s a small muscle situated on the lateral part of the dorsum of the foot, deep to the tendons of extensor digitorum longus. It’s the only muscle on the dorsum of the foot and creates a fleshy swelling anterior to the lateral malleolus. The youthful beginner physicians sometimes diagnose it as a contusion.
Origin
It originates from the anterior part of the superior surface of calcaneum, medial to the connection of the stalk of inferior extensor retinaculum.
Insertion
- The muscle splits into 4 tendons for the medial 4 toes. The tendon to the big toe crosses in front of dorsalis pedis artery and inserts on the dorsal surface of the proximal phalanx of the big toe. The Lateral 3 tendons join the lateral side of the tendons of the extensor digitorum longus to the 2nd, third, and fourth toes.
- Medial most part of the extensor digitorum brevis, which creates the tendon for the big toe, splits or becomes different early. It’s called extensor hallucis brevis.
Nerve Supply
It’s by the lateral terminal branch of the deep peroneal nerve.
Actions
- Extensor hallucis brevis (EHB) stretches the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe.
- The other 3 tendons stretch the metatarsophalangeal and interphalangeal joints of 2nd, third, and fourth toes, especially when the foot is dorsiflexed.
Extensor Hallucis Brevis
The extensor hallucis brevis originates in conjunction with the extensor digitorum brevis. Its tendon attaches to the base of the proximal phalanx of the great toes. The muscle extends the metatarsophalangeal joint of the great toe and is innervated by the deep fibular nerve.
Attachments
It arises from the calcaneus, the interosseous talocalcaneal ligament and the inferior extensor retinaculum and it connects to the base of the proximal phalanx of the great toe.
Actions
It helps the extensor hallucis longus in extending the great toe at the metatarsophalangeal joint.
Innervation
It is innervated by Deep fibular nerve.
Plantar Side of The Foot (Muscles of The Sole of The Foot)
There are 18 intrinsic muscles and 4 extrinsic tendons in the sole of the foot. The muscles of the sole are described in 4 layers from superficial to deep.
Muscle Layers of The Sole of The Foot
| Layer | Muscles | Features |
|---|---|---|
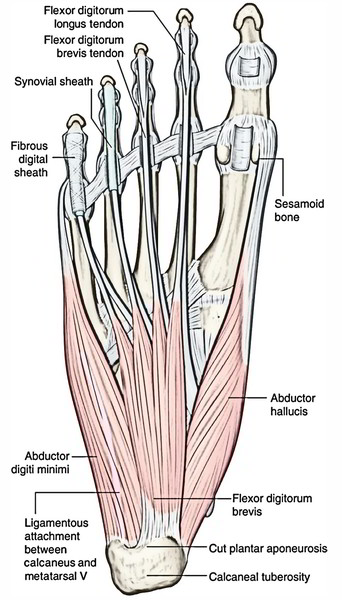
| First layer | 1. Flexor digitorum brevis. 2. Abductor hallucis. 3. Abductor digiti minimi | They cover whole of the sole |
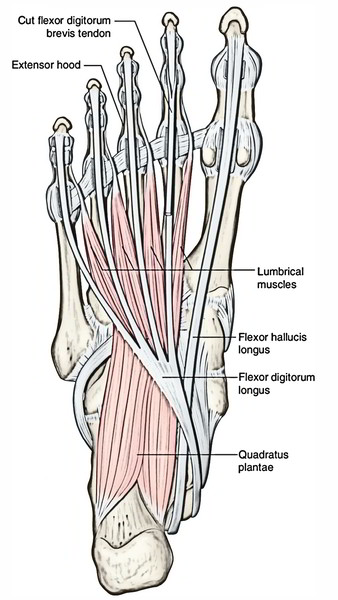
| Second layer | 1. Flexor digitorum accessories Four lumbricals. 2. Two tendons (tendon of flexor digitorum longus and tendon of flexor hallucis longus) | Flexor digitorum accessorius and lumbricals are attached to the tendon of flexor digitorum longus |
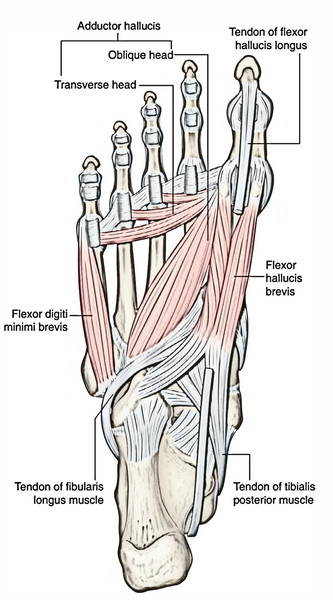
| Third layer | 1. Flexor hallucis brevis. 2. Flexor digiti minimi brevis. 3. Adductor hallucis | 1. They are confined to the metatarsal region of the sole. 2. Two of these muscles act on the big toe and one on the little toe |
| Fourth layer | 1. Interossei (3 plantar interossei and 4 dorsal interossei). 2. Tendon of tibialis posterior. 3. Tendon of peroneus longus | They fill up the intermetatarsal spaces |
First layer
Second Layer
Third Layer
Fourth Layer
The muscles of the sole are primarily concerned with supporting the arches of the foot. The short and long muscles of the foot serve as synergists.
Neurovascular planes of the sole: There are 2 neurovascular planes between the muscle layers of the sole:
- Superficial neurovascular plane between the first and 2nd layers.
- Deep neurovascular plane between the 3rd and fourth layers.
In the superficial neurovascular plane is located the trunks of medial and lateral plantar nerves, and the arteries.
In the deep neurovascular plane is located the deep branches of the lateral plantar nerve and artery.
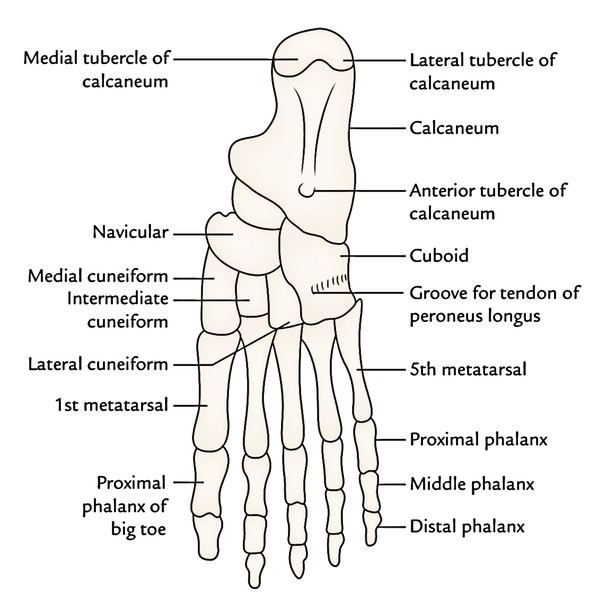
To understand the origin and insertion of the muscles of the foot the student must study the layout of the various bones on the plantar aspect of the skeleton of the foot.
Origin, Insertion, Nerve Supply, and Actions of The Muscles of The Sole
| Muscles | Origin | Belly/Tendon | Insertion | Nerve supply | Actions |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| • Flexor digitorum brevis (resembles flexor digitorum superficialis of the hand) | Medial tubercle of the calcaneum | 1.It forms 4 tendons for the lateral 4 toes. 2.Each tendon splits into two slips opposite the bases of proximal phalanges to allow passage of the long flexor tendon | Margins of the middle phalanges of lateral 4 toes | Medial plantar nerve (S2, S3) | Flexor of the lateral toes |
| • Abductor hallucis (lies along the medial border of the foot) | 1. Medial tubercle of the calcaneum. 2. Flexor retinaculum. | Its tendon fuses with medial portion of the tendon of flexor hallucis brevis for a common insertion | Medial side of the base of proximal phalanx of the big toe | Medial plantar nerve (S2, S3) | Flexion and abduction of the big toe |
| • Abductor digiti minimi (lies along the lateral border of the foot) | Medial and lateral tubercles of the calcaneum in a continuous line | Its tendon fuses with the tendon of flexor digiti minimi brevis for a common insertion | Lateral side of the base of proximal phalanx of the little toe | Lateral plantar nerve (S2, S3) | Flexion and abduction of the little toe |
| • Flexor digitorum accessorius | By two heads: 1. Medial head from the medial concave surface of the calcaneum and adjoining part of the medial tubercle. 2. Lateral head from the calcaneum in front of the lateral tubercle | The two heads unite at an acute angle | Tendon of the flexor digitorum longus (FDL) | Lateral plantar nerve (S2, S3) | 1. Straightens the pull of the long flexor tendons. 2. Assists the flexor digitorum longus in flexing the lateral 4 toes |
| • Lumbricals (4 in number and numbered from medial to lateral side) Tendon of flexor digitorum longus Tendon of flexor hallucis longus | From the tendons of the flexor digitorum longus | Tendons pass forwards on the medial sides of the metatarso-phalangeal joints of the lateral four toes | Into the extensor expansions and bases of proximal phalanges of lateral 4 toes | 1st by the medial plantar nerve, and 2nd, 3rd, and 4th by the lateral plantar nerve (S2, S3) | Extension of toes at the interphalangeal joints |
| Third Layer | |||||
| • Flexor hallucis brevis | It arises by a Y-shaped tendon: 1.Lateral limb from the medial part of the plantar surface of the cuboid bone. 2.Medial limb from the lateral cuneiform | Muscle belly splits in two parts. Each part gives rise to a tendon which contains a sesamoid bone near its insertion. The medial tendon blends with the abductor hallucis, and the lateral tendon blends with the adductor hallucis | Each side of the base of proximal phalanx of the big toe (1st digit) | Medial plantar nerve (S2, S3) | Flexion of the proximal phalanx of big toe |
| • Flexor digiti minimi brevis | Base of the 5th metatarsal bone | Forms narrow tendon which blends with the abductor digiti minimi | By a narrow tendon into the lateral side of the base of proximal phalanx of the little toe | Superficial branch of the lateral plantar nerve (S2, S3) | Flexes the proximal phalanx of the little toe |
| • Adductor hallucis | It arises by two heads: 1.Large oblique head from bases of the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th metatarsals. 2.Small transverse head from the plantar ligaments of the metatarso-phalangeal joints of 3rd, 4th, and 5th toes | The common tendon of both heads fuses with the lateral tendon of the flexor hallucis brevis | By the composite tendon on the lateral side of the base of proximal phalanx of the big toe | Deep branch of the lateral plantar nerve (S2, S3) | 1.Adduction of the big toe .2Maintains transverse arches of the foot. |
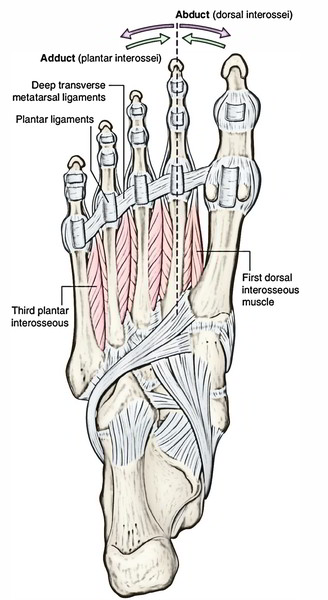
| • Dorsal interossei * (4 in number, and lies between the metatarsal bones) | They are bipennate and arises from the adjacent sides of the metatarsal bones (1-5) | Tendons are arranged on the abductor sides of the toes | 1.1st on the medial side of the proximal phalanx of 2nd digit. 2nd-4th on the lateral sides of 2nd-4th digits | Lateral plantar nerve (S2, S3) | 1.Abducts digits (2nd-4th). 2. Flexes the metatarso-phalangeal joints. |
| Plantar interossei * (3 in number and lies rather below the metatarsals) | They are unipennate and arises from the medial sides of the metatarsal bones (3rd-5th) | Tendons are arranged on the adductor sides of the toes | Medial sides of bases of the phalanges of 3rd-5th digits | Lateral plantar nerve (S2, S3) | 1.Adducts the digits (2nd-4th). 2.Flexes the metatarso-phalangeal joints |

 (46 votes, average: 4.87 out of 5)
(46 votes, average: 4.87 out of 5)