The muscles of the posterior of the forearm are categorized into two classes:
- superficial
- deep
The muscles that form the back of the forearm are commonly known as Extensor Muscles. These are provided by the radial nerve.
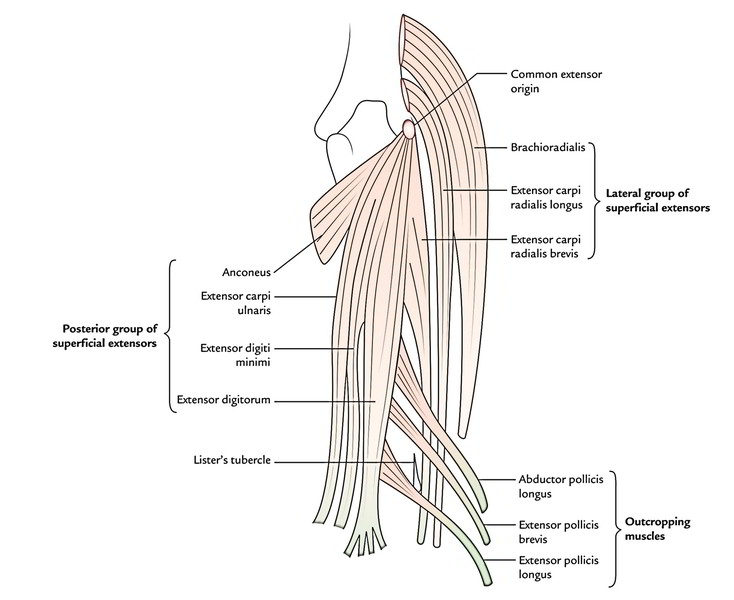
Superficial Muscles of the back of Forearm
The superficial muscles of the back of forearm are seven in number. From lateral to medial these are:
- Brachioradialis.
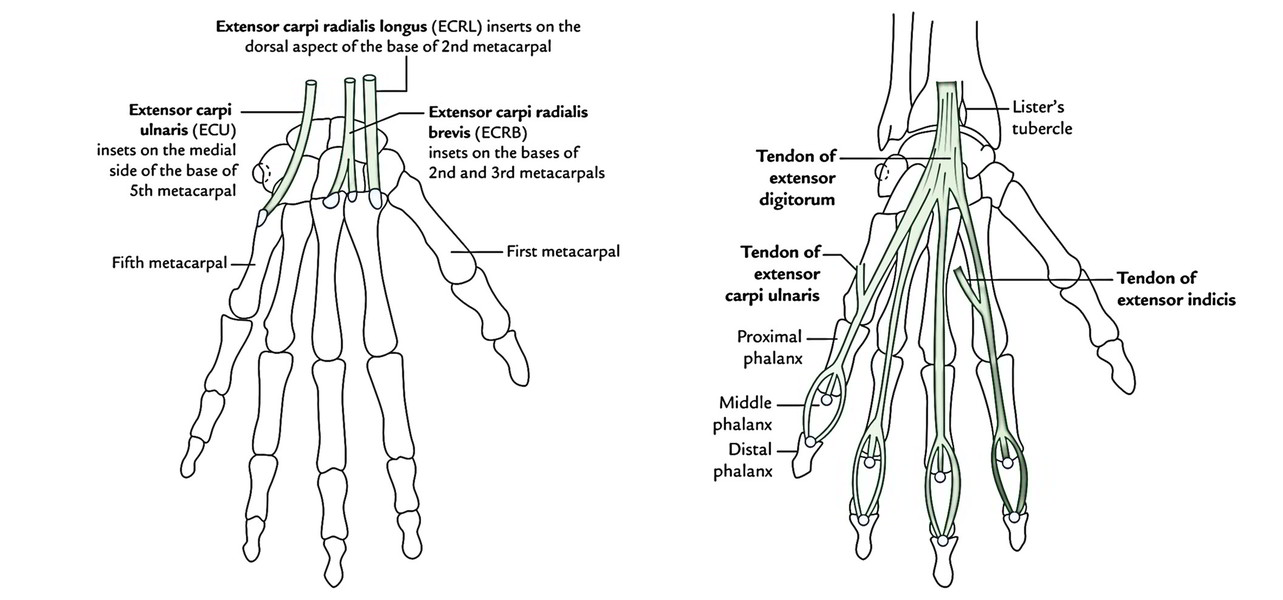
- Extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL).
- Extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB).
- Extensor digitorum (ED).
- Extensor digiti minimi (EDM).
- Extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU).
- Anconeus.
The superficial muscles of the back of the forearm are further categorized into two groups: lateral and posterior. Each group consists of three muscles:
Lateral group of superficial extensors
- Brachioradialis.
- Extensor carpi radialis longus.
- Extensor carpi radialis brevis.
Posterior group of superficial extensors
- Extensor digitorum.
- Extensor digiti minimi.
- Extensor carpi ulnaris.
- Anconeus.
Clinical Significance
Lateral epicondylitis is the overuse syndrome in the elbow. It’s an injury involving the extensor muscles of the forearm. There is degeneration of the attachment of the tendon, placing stress and weakening the site.
It’s also referred to as lateral epicondylitis but this is a misnomer because, in general evaluation of the tendons doesn’t show signs of inflammation, but rather degeneration and collagen disarray.
Tennis elbow is the most common reason that people see their doctors for elbow pain. It is most common at about any age, although it can come up in people of the age of 40, on an average.
Origin, insertion, nerve supply, and actions of the superficial muscles of the back of the forearm (superficial extensors)
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve supply | Actions |
| Lateral group | ||||
| Brachioradialis | Upper two-third of the lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus | Lateral surface of the distal end of radius just above the styloid process | Radial nerve |
|
| Extensor carpi radialis longus (ECRL) | Lower one-third of the lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus | Lateral side of the dorsal surface of the base of second metacarpal bone | Radial nerve |
|
| Extensor carpi radialis brevis (ECRB) | By a common tendon from the lateral epicondyle of the humerus and lateral ligament of the elbow joint | Lateral side of the dorsal surface of the base of third metacarpal bone | Posterior interosseous nerve before piercing the supinator | -do- |
| Posterior group | ||||
| Extensor digitorum | By a common tendon from the lateral epicondyle |
| Posterior interosseous nerve | Extends the medial four digits. Can also extend the wrist |
| Extensor digiti minimi | By the common tendon from the lateral epicondyle |
| Posterior interosseous nerve |
|
| Extensor carpi ulnaris (ECU) | By the common tendon from the lateral epicondyle and by an aponeurosis from the upper two-third of the posterior border of ulna along with flexor carpi ulnaris and flexor digitorum profundus | Into a tubercle on the medial side of the dorsal surface of the base of the fifth metacarpal | Posterior interosseous nerve |
|
| Anconeus | From the back of the lateral epicondyle | Lateral side of the olecranon process and upper one- fourth of the posterior surface of the ulna | Nerve to anconeus, which arises from radial nerve in spiral groove and descends through medial head of the triceps brachii | Weak extensor of the elbow joint |
Deep Muscles of the Back of Forearm
- Supinator.
- Abductor pollicis longus(APL).
- Extensor pollicis brevis (EPB).
- Extensor pollicis longus (EPL).
- Extensor indicis.
The three deep extensors of the forearm, which function on thumb (abductor pollicis longus, extensor pollicis brevis, and extensor pollicis longus) are located deep to the superficial extensors and in order to acquire insertion on the three short long bones of thumb ‘crop out’ (emerge) from the furrow in the lateral element of the forearm between lateral and posterior groups of superficial extensor. These three muscles are therefore called outcropping muscles.
Clinical Significance
Wrist drop, also known as radial nerve palsy, is a condition where a person cannot extend their wrist and it hangs flaccidly. The individual may experience many symptoms including numbness in the wrist and forearm when there’s an injury to this nerve. The individual may find it hard to work with the hand in day to day tasks like objects. There may be weakness. The individual may find it tough to bend the wrist back.
Symptoms may include a burning or sharp pain sensations in fingers and the thumb. It is common to experience numbness, tingling, and trouble straightening your arm. You may realize that you straighten or cannot extend fingers and your wrist. This is called “wrist drop” or “finger drop,” and it does not happen in all circumstances.
Treatment
Initial management includes splinting of the wrist for support together with Osteopathic medicine, Physiotherapy and Occupational Therapy. In some instances, operative removal of bone spurs or other anatomical defects that may be impinging on the nerve may be warranted. If injury was caused by pressure from use of other mechanisms of injury or fitted crutches, then the symptoms of wrist fall will resolve within 8 – 12 weeks.
Origin, insertion, nerve supply, and actions of the deep muscles of the back of the forearm (deep extensors of forearm)
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Nerve supply | Action |
| Supinator |
| Upper one-third of the posterior, lateral, and anterior surfaces of the radius | Posterior interosseous nerve before piercing the supinator | Supination of the forearm |
| Abductor pollicis longus (APL) |
| Lateral side of the base of first metacarpal | Posterior interosseous nerve | Abducts the thumb |
| Extensor pollicis brevis (EPB) | From a small area on the posterior surface of radius below the origin of abductor pollicis longus and from adjoining interosseous membrane | Dorsal surface of the base of proximal phalanx of thumb | Posterior interosseous nerve | Extends the thumb at metacarpophalangeal joint and extends the carpometacarpal joint |
| Extensor pollicis longus | From lateral part of middle one-third of the posterior surface of ulna and adjoining interosseous membrane | Dorsal surface of the base of distal phalanx of thumb | Posterior interosseous nerve |
|
| Extensor indicis | From the posterior surface of ulna below the origin of extensor pollicis longus and also from the adjoining interosseous membrane |
| Posterior interosseous nerve |
|

 (61 votes, average: 4.85 out of 5)
(61 votes, average: 4.85 out of 5)