Main innervation of foot is done by the:
- Tibial Nerve
- Deep Fibular Nerve
- Superficial fibular Nerve
- Sural Nerve
- Saphenous Nerves
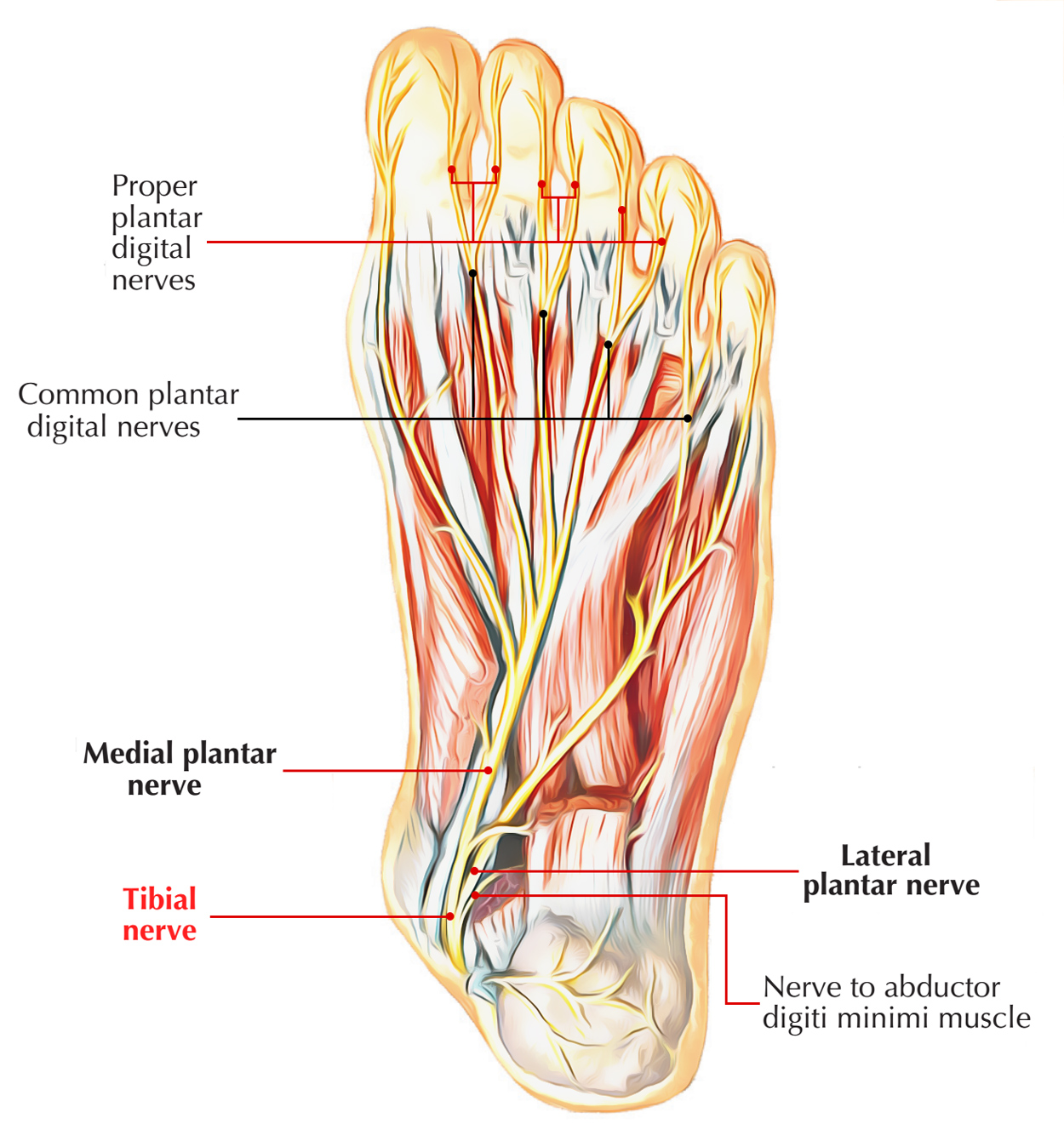
Tibial Nerve
The tibial nerve travels inside the foot via the tarsal tunnel, posterior towards the medial malleolus. The nerve lies lateral towards the posterior tibial artery inside the tunnel and also produces medial calcaneal branches, in order to innervate the heel while penetrating the flexor retinaculum. The tibial nerve bifurcates with the posterior tibial artery, in the middle of the medial malleolus and the heel, into:
- A large medial plantar nerve.
- A smaller lateral plantar nerve.
Nerves of Foot: Tibial Nerve
Medial Plantar Nerve
In the sole of the foot, the medial plantar nerve is the main sensory nerve.
It innervates:
1. Skin on large part of the anterior two-thirds of the sole.
2. Surrounding surfaces of the medial three along with one-half toes, which comprises the great toe.
3. Along with large area of plantar skin, the nerve also supplies four core muscles:
- Abductor hallucis.
- Flexor digitorum brevis.
- Flexor hallucis brevis.
- First lumbrical.
Lateral Plantar Nerve
The lateral plantar nerve is an important motor nerve in the foot because it innervates:
- All intrinsic muscles in the sole, except for the muscles supplied by the medial plantar nerve.
- It also innervates a strip of skin on the lateral side of the anterior two-thirds of the sole.
- The adjacent plantar surfaces of the lateral one and one-half digits.
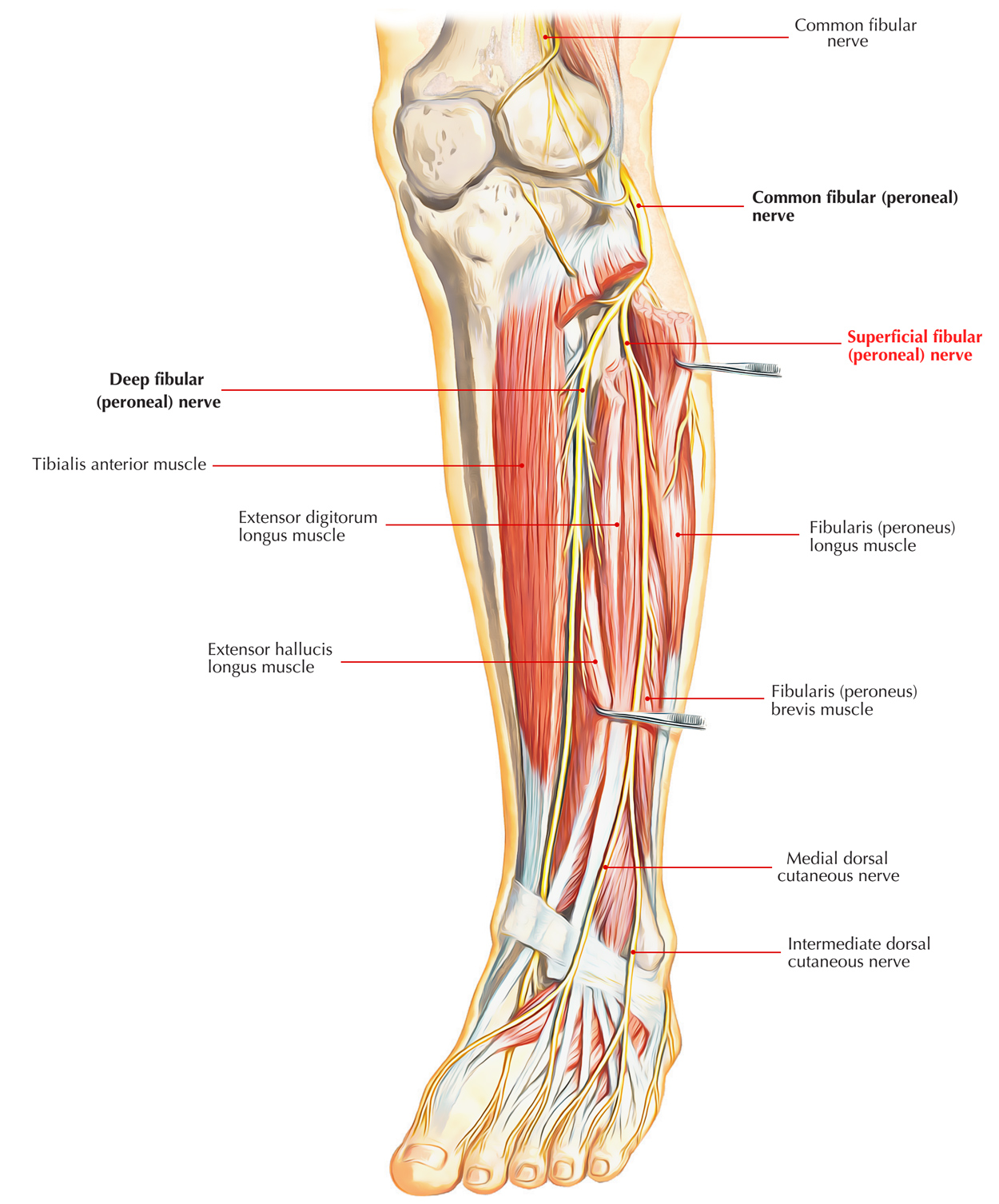
Deep fibular nerve
The deep fibular nerve is parallel and lateral to the tendon of the extensor hallucis longus muscle and goes inside the dorsal aspect of the foot on the lateral aspect of the dorsalis pedis artery. The nerve produces a lateral branch just distal towards the ankle joint, which stimulates the extensor digitorum brevis from its deep surface. The deep fibular nerve innervates:
- Extensor digitorum brevis.
- First two dorsal interossei muscles.
- Supplies general sensory branches towards the skin on the neighboring dorsal aspects of the first and second toes and also towards the web space among them.
Superficial Fibular Nerve
Nerves of Foot: Superficial Fibular Nerve
The superficial fibular nerve, on the anterolateral aspect of the lower leg, pierces deep fascia and move within superficial fascia on the dorsal aspect of the foot. Along its course, it produces
- Cutaneous branches.
- Dorsal digital nerves.
The superficial fibular nerve:
- Gives sensory innervation to most skin on the dorsal aspect of the foot and toes.
- With the exception of for skin on neighboring sides of toes I and II (innervated by the deep fibular nerve) and skin on the lateral side of the foot and little toe (innervated by the sural nerve).
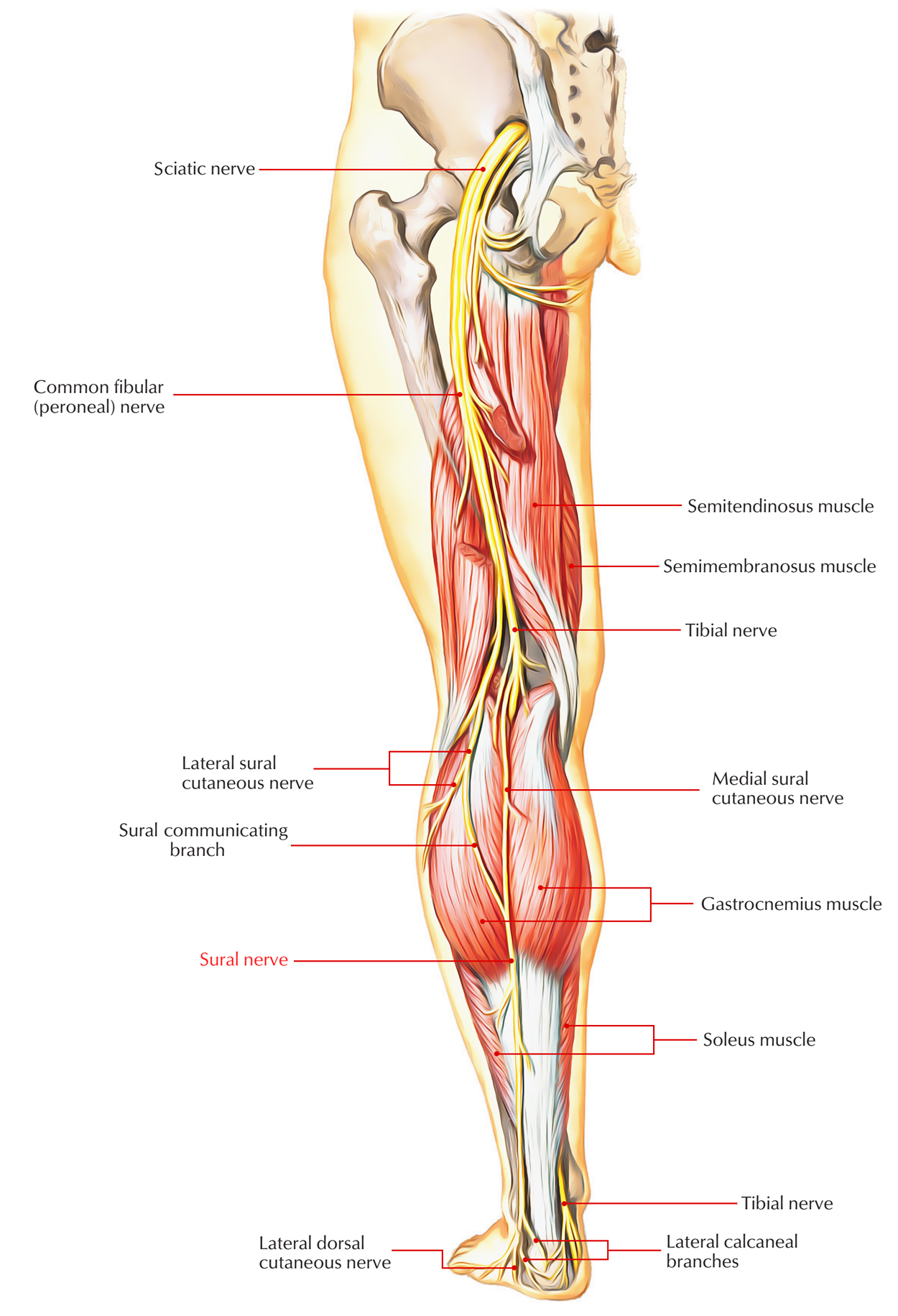
Sural Nerve
Nerves of Foot: Sural Nerve
The sural nerve is a cutaneous branch of the tibial nerve that emerges higher in the leg. Nearby the short saphenous vein, it goes inside the foot within superficial fascia posterior towards the lateral malleolus. Terminal branches innervate:
- Skin on the lateral aspect of the foot.
- Dorsolateral surface of the little toe.
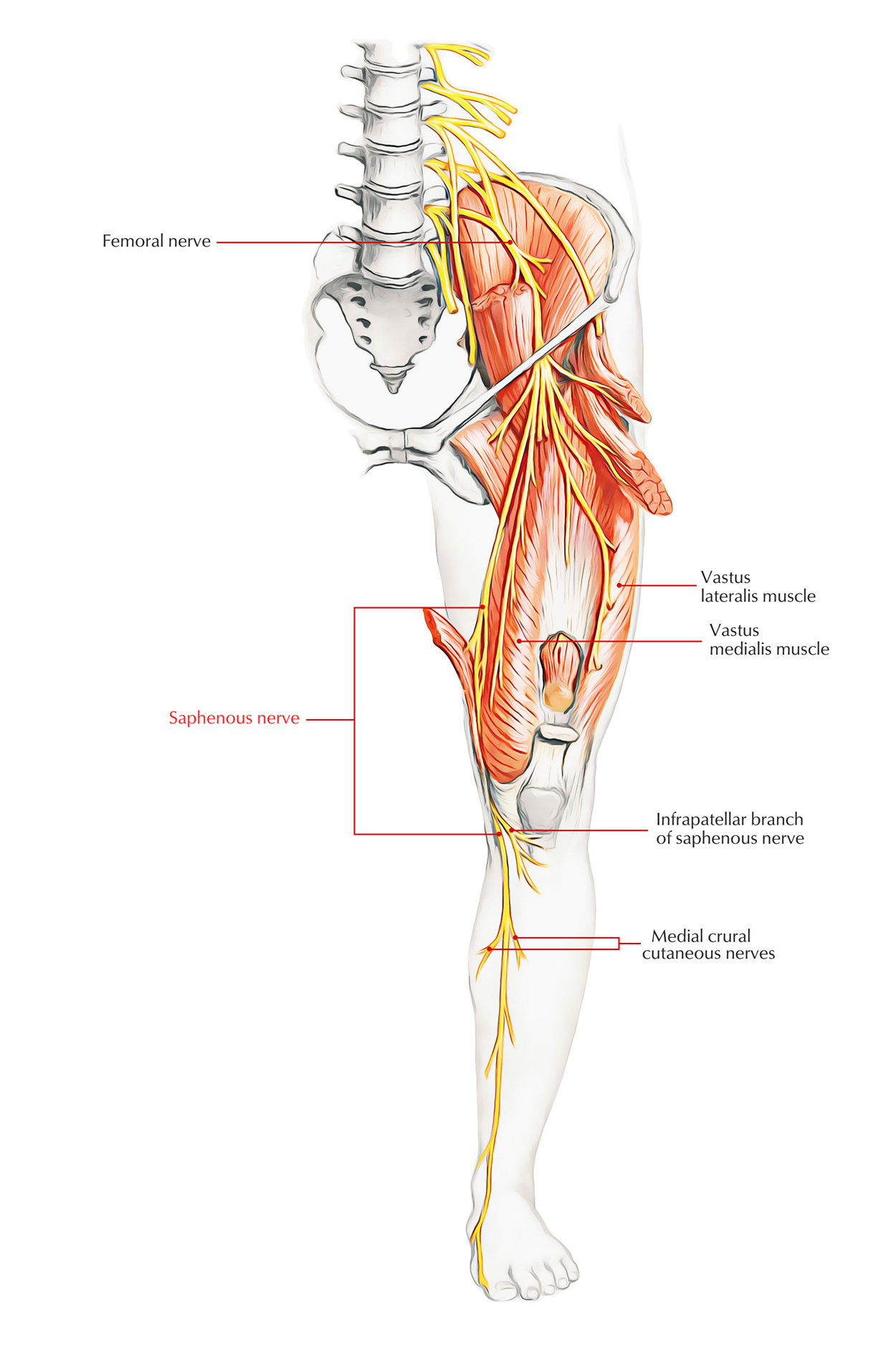
Saphenous nerve
Nerves of Foot: Saphenous Nerve
The saphenous nerve is a cutaneous branch of the femoral nerve that originates in the thigh. Terminal branches supply skin on the medial side of the proximal foot and enter the foot in superficial fascia on the medial part of the ankle.

 (59 votes, average: 4.64 out of 5)
(59 votes, average: 4.64 out of 5)