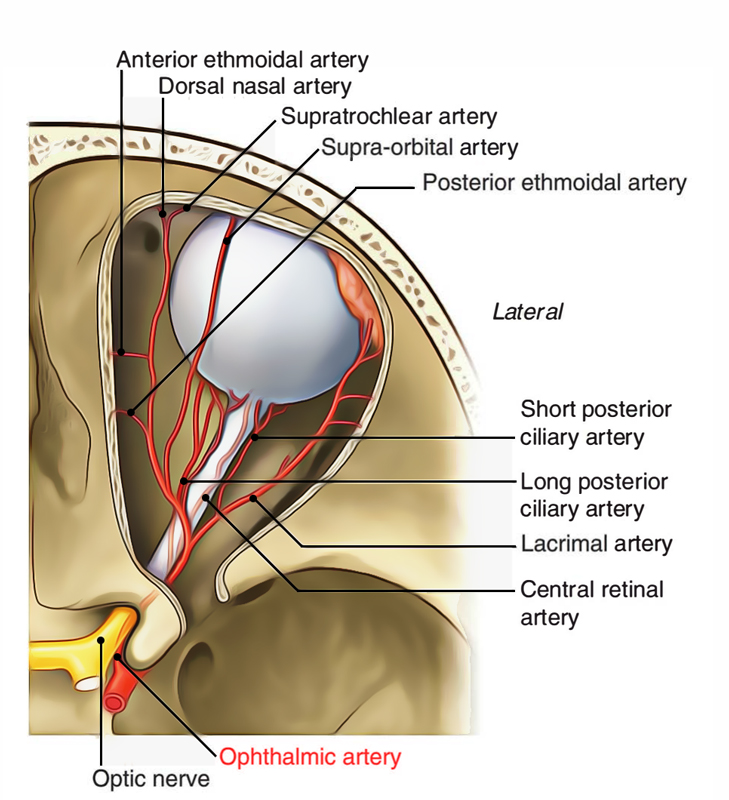
It appears from internal carotid artery as it appears medial to anterior clinoid process near the optic canal from the roof of the cavernous sinus. It’s branch of the internal carotid artery. Via optic canal inferolateral to the optic nerve the artery enters the orbit, both being located in a standard dural sheath.
The artery, ascends over the lateral side of the optic nerve to cross it superiorly from lateral to medial side together with the nasociliary nerve, pierces the dura mater. To enable the movements of the eyeball, it then runs forwards along the medial wall of the orbit tortuously. It ends by dividing into 2 branches: supra trochlear and dorsal nasal, near the medial angle of the eye.
Ophthalmic Artery
Branches
The branches of the ophthalmic artery are as follows:
Central artery of the retina (first and most essential) appears from ophthalmic artery (still in dural sheath) below the optic nerve, runs forwards in the dural sheath and pierces the optic nerve inferomedially about 1.25 cm behind the eyeball. The central artery reaches the optic disc via the central part of the nerve. It supplies the optic nerve and inner 6/7 layers of the retina.
Lacrimal artery originates from ophthalmic artery just before it crosses the optic nerve. It enters forwards along the upper border of lateral rectus and supplies the lacrimal gland, eyelids and conjunctiva. The lacrimal artery produces the following branches:
⦁ Glandular branches to lacrimal gland.
⦁ 2 lateral palpebral arteries-1 to every eyelid.
⦁ 2 zygomatic branches: zygomaticofacial and zygomaticotemporal.
⦁Recurrent meningeal branch runs backwards to goes into the middle cranial fossa via the superior orbital fissure.
⦁ Muscular branches.
- Posterior ciliary arteries contain 2 sets: long and short, each of which pierce the sclera of the eyeball around the optic nerve and mainly supply the choroid and sclera. Long ciliary arteries are typically 2 and short ciliary arteries are normally 7 in number. (Remember that anterior ciliary arteries originate from muscular arteries.).
- Supraorbital artery accompanies the supraorbital nerve. It goes through supraorbital notch to go into the scalp and breaks up into medial and lateral branches.
- Posterior ethmoidal artery enters the posterior ethmoidal foramen in the medial wall of the orbit and supplies the ethmoidal air sinuses, nasal cavity and dura mater.
- Anterior ethmoidal artery enters the anterior ethmoid foramen in the medial wall of the orbit and supplies the ethmoidal air sinuses, medial and lateral wall of nasal cavity and dura mater.
- Dorsal (external) nasal artery supplies the lower part of the dorsum of nose.
- Supratrochlear artery accompanies the supratrochlear nerve to furnish the brow.
- Medial palpebral branches, 1 to every eyelid, anastomose with the corresponding lateral palpebral branches of the lacrimal artery.
- Branches of ophthalmic artery accompany all the branches of nasociliary frontal and lacrimal nerves (originated from ophthalmic nerve) and inside the orbit supply all the extraocular muscles, lacrimal gland and the eyeball.
Clinical Significance
The central artery of retina is an instance of an average end artery. Its damage creates unanticipated complete blindness on the side of the lesion.

 (52 votes, average: 4.85 out of 5)
(52 votes, average: 4.85 out of 5)