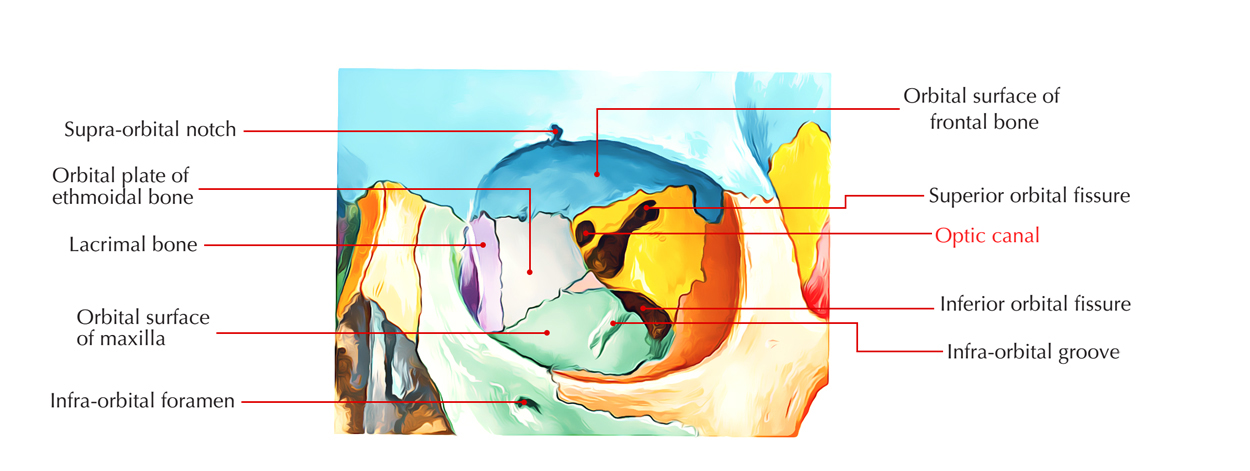
The optic canal is the rounded gap at the tip of the pyramid shaped. It opens into the middle cranial fossa and is surrounded medially via the body of the sphenoid as well as laterally via the lesser wing of the sphenoid.
Optic Canal
Structure
Approximately the optic canal is 0.4 to 1 cm in length. The canal is created medially via the body of the sphenoid and laterally via the lesser wing. Around the optic nerve, the bony optic canal creates a rigid covering.
Relations
- Sulcus chiasmaticus is a shallow oblique groove that goes on both sides into the optic canal travels into the orbit.
- Ophthalmic artery goes inside the orbit via optic canal in order to supply structures of the orbit together with eyeball.
- Both lesser wing of sphenoid arises via the anterior part of the body of sphenoid through two roots. The optic canal is located in the middle of these two roots.
- At the optic canal and base forward, represented by the orbital margin each orbit is a four-sided pyramid with apex going behind.
- Optic foramen, the optic canal opens within the skull base.
- Optic nerves exit the cranial end of the optic canal and travel medially, backwards and slightly upwards within the subarachnoid space of the middle cranial fossa.
- Superior Orbital Fissure is a triangular-shaped gap in the middle of the roof and lateral wall of the bony orbit which is located just lateral to the optic canal.
Clinical Significance
Inflammation associated with fractures has a tendency in order to compress the vascularity of the nerve in the canal. In the case of skull fractures and sinus infections, the closeness of the optic nerve towards the walls of the optic canal through in the middle of the meninges associates the nerve.

 (46 votes, average: 4.86 out of 5)
(46 votes, average: 4.86 out of 5)