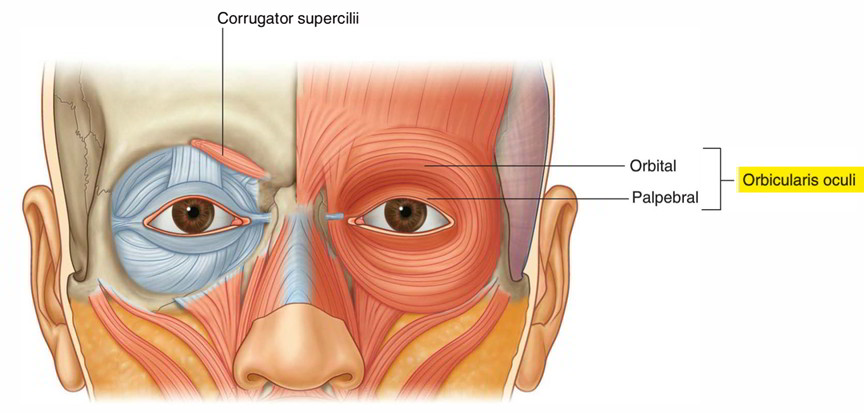
The orbicularis oculi is a large muscle that completely surrounds each orbital orifice and extends into each eyelid. It closes the eyelids. It has two major parts:
- The outer orbital part is a broad ring that encircles the orbital orifice and extends outward beyond the orbital rim.
- The inner palpebral part is in the eyelids and consists of muscle fibers originating in the medial corner of the eye that arch across each lid to attach laterally.
The orbital and palpebral parts have specific roles to play during eyelid closure. The palpebral part closes the eye gently, whereas the orbital part closes the eye more forcefully and produces some wrinkling on the forehead.
An additional small lacrimal part of the orbicularis oculi muscle is deep, medial in position, and attaches to bone posterior to the lacrimal sac of the lacrimal apparatus in the orbit
Parts
- Orbital part
- Palpebral part
- Lacrimal part
Orbital Part
Origin
- Medial palpebral ligament.
- Frontal process of the maxilla.
- Nasal process of the frontal bone.
Insertion
It encircles around the orbital margin. The upper and lower fibres are continuous with each other at the lateral orbital margin. Some fibres are inserted on the skin over the eyebrow. Upper fibres meet and fuse with the frontal belly of occipitofrontalis muscle. It opposes the action of the frontalis.
Palpebral Part
Origin
- Medial palpebral ligament.
- Medial border of the orbit above and below the medial palpebral ligament.
Insertion
Lateral palpebral raphe.
Lacrimal Part
Origin
- Lacrimal fascia
- Lacrimal crest and lateral surface of the lacrimal bone.
Insertion
It divides into upper and lower portions. They enter the eyelids. They are attached to the tarsal plate and lacrimal canalicull Most fibres of this muscle extend laterally and decussate at lateral palpebral raphe.
Nerve supply
Temporal and zygomatic branches of the facial nerve.
Actions
Orbital part: It locks the eyelids. Thus it acts as a strong sphinctre of the orbit. It opposes the action of the frontalis muscle.
Palpebral part: Shuts the eyelids tightly during blinking and sleeping.
Lacrimal part: Pulls the eyelids medially. Dilates the lacrimal sac.
Applied Anatomy
Supranuclear lesions of the facial nerve does not affect the functions of this muscle. Infranuclear lesion of facial nerve paralyses the orbicularis oculi. So the eyelids are wide open.
Blinking of the eye is not possible, lacrimal circulation is impaired and tears overflow on the cheek.
Test Your Knowledge
Orbicularis Oculi

 (62 votes, average: 4.60 out of 5)
(62 votes, average: 4.60 out of 5)