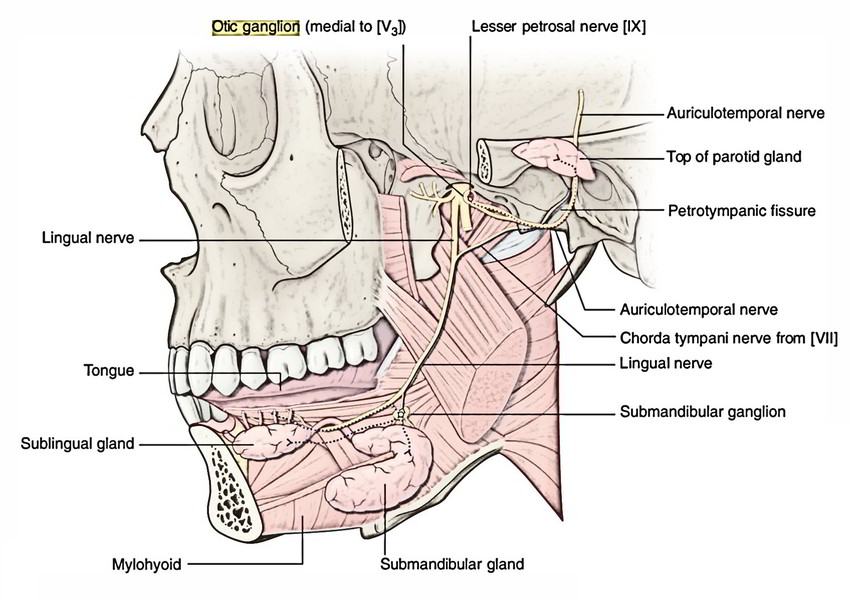
It’s joined to the mandibular division of trigeminal nerve and gives a relay station to the secretomotor fibres to the parotid gland and is a small parasympathetic ganglion. It’s closely associated with the mandibular nerve but functionally it’s related to glossopharyngeal nerve, topographically.
Size: Pinhead (2-3 millimeters in size).
Location: Temple fossa, just below the foramen ovale.
Connections
- Lateral: Mandibular nerve.
- Medial: Tensor palati muscle.
- Posterior: Middle meningeal artery.
- Anterior: Medial pterygoid muscle.
Roots or Links
Parasympathetic motor (secretomotor): From lesser petrosal nerve.
Preganglionic parasympathetic fibres originate from inferior salivatory nucleus; pass successively via glossopharyngeal nerve, tympanic branch of glossopharyngeal nerve (Jacobson’s nerve), tympanic plexus and lesser petrosal nerve to relay in the ganglion. Postganglionic parasympathetic fibres from ganglion cells go through auriculo-temporal nerve to supply parotid gland
Sympathetic: From sympathetic plexus around the middle meningeal artery.
Preganglionic sympathetic fibres originate from T1 and T2 spinal sections, goes into the cervical sympathetic chain in the level of its inferior ganglion and after that ascend to relay in the superior cervical sympathetic ganglion. The postganglionic fibres originate from this ganglion and create plexus around the middle meningeal artery. They then go through the ganglion without relay to make it to the parotid gland via auriculotemporal nerve. They’re vasomotor in nature and responsible for thick salivary secretion.
Sensory: From auriculotemporal nerve.
Somatic motor: Nerve to medial pterygoid. It goes through ganglion to supply medial pterygoid, tensor palati and tensor tympani muscles.
Branches
- Postganglionic parasympathetic.
- Postganglionic sympathetic.
- Sensory.
All these branches supply parotid gland through auriculotemporal nerve.
Key Points
In individuals, the chorda tympani nerve is joined to the otic ganglion and nerve to pterygoid canal. These links offer an alternative pathway of taste sensations from anterior two-third of the tongue.
Clinical evidence indicates that in people the parotid gland also gets secretomotor fibres via chorda tympani nerve.

 (56 votes, average: 4.79 out of 5)
(56 votes, average: 4.79 out of 5)