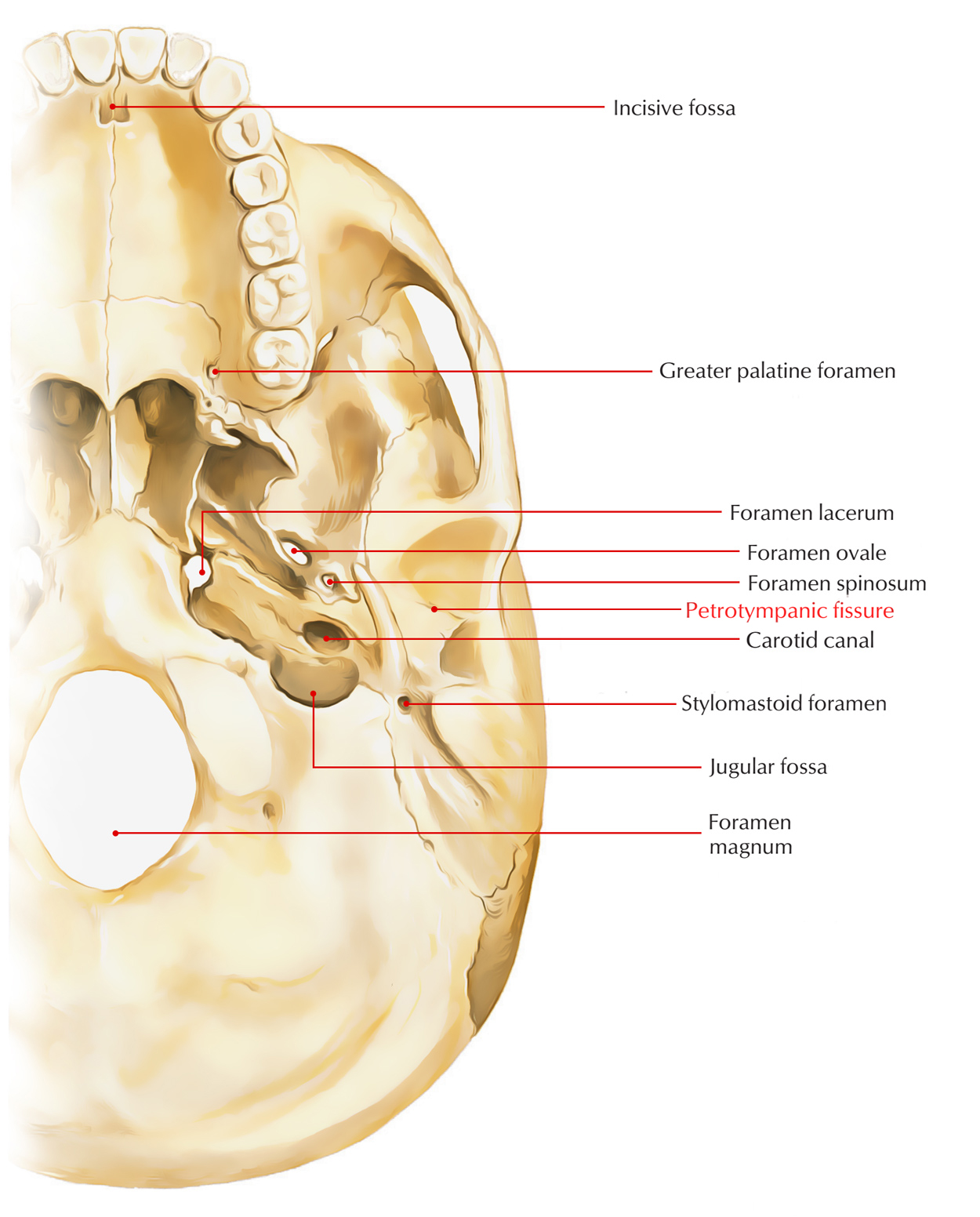
The petrotympanic fissure refers to a small crevice located in the temporal bone. It splits the mandibular fossa anteriorly via the articular tubercle as well as posteriorly via the tympanic portion of the temporal bone. Via this fissure, the chorda tympani travel inside the infratemporal fossa.
Petrotypanic Fissure
Structure
The tissue is found in the middle of the temporomandibular joint as well as the middle ear.
- The mandibular fossa a.k.a. glenoid fossa is circumscribed via the articular tubercle anteriorly and via the tympanic part of the bone posteriorly.
- While the tympanic bone section splits it up from the external acoustic meatus, the petrotympanic fissure splits the mandibular fossa into two parts as well as develops as a contracted slit.
- The tissue opens where the tympanic membrane is inserted, just anteriorly and above the bony ring. In this position, it appears as a 2 mm. long tiny slit.
It holds the anterior malleus ligament as well as the anterior protuberance. It also allows passage to the anterior tympanic branch in the internal maxillary artery.
Function
The fissure performs various functions:
- It enables interaction of the middle ear along with the temporomandibular joint.
- It gives the tongue with special sensory innervation for taste.
- It transmits:
- Chorda tympani.
- Anterior ligament of malleus.
- Anterior tympanic branch of the maxillary artery.
Relations
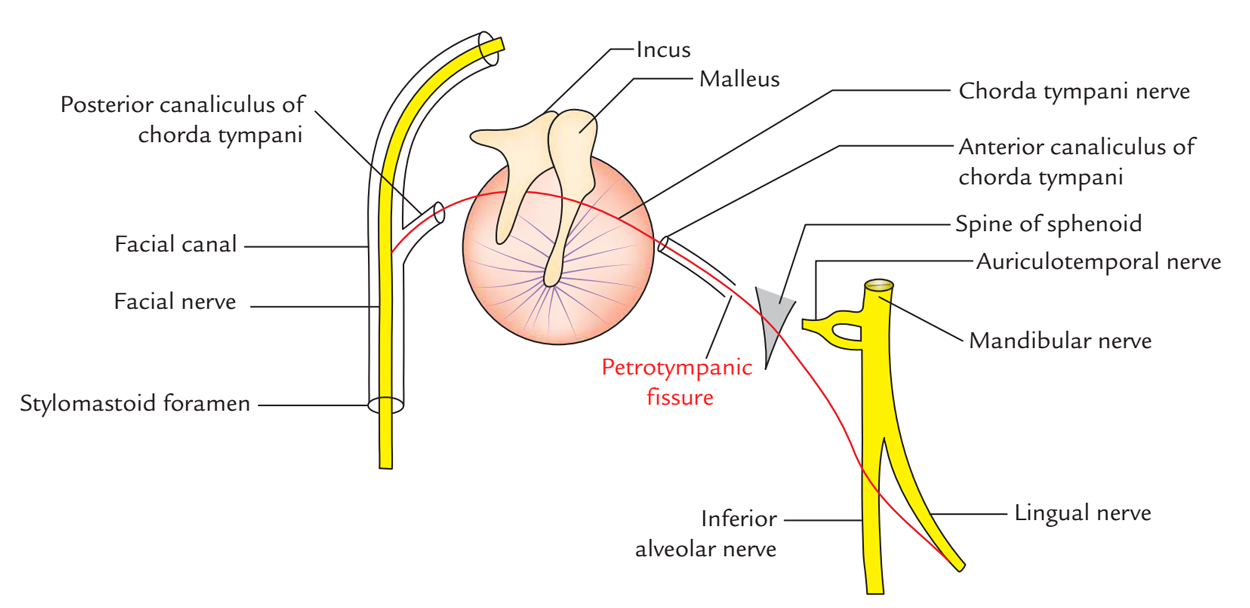
The constituents of the petrotympanic fissure comprise of connections of cranial nerve VII towards the infratemporal fossa. The chorda tympani is a branch of cranial nerve VII, travels via the fissure in order to connect with the lingual nerve towards the anterior two-third of the tongue supplying sensory innervation for taste.
Petrotympanic Fissure: Relations
Middle
The petrotympanic fissure also contains the discomalleolar ligament that gives a little stability to the posterior connection of the disc, as well as the anterior malleolar part of the sphenomandibular ligament.
Bottom
The connection of the petrotympanic fissure towards the middle ear cavity along with the ossicles is seen distinctly on cross section. It is assumed that the tension on the anterior malleolar ligament and to a lesser extent, the discomalleolar ligament is accountable for some of the ear-related problems of tympanic membrane damage and hearing damage. Petrotympanic fissure conveys:
- Chorda tympani nerve which is a branch of facial nerve.
- Anterior tympanic artery which is a branch of the first part of the maxillary artery.
- Anterior ligament of the malleus.

 (51 votes, average: 4.84 out of 5)
(51 votes, average: 4.84 out of 5)