Plantar Arteries are of two types- medial and lateral.
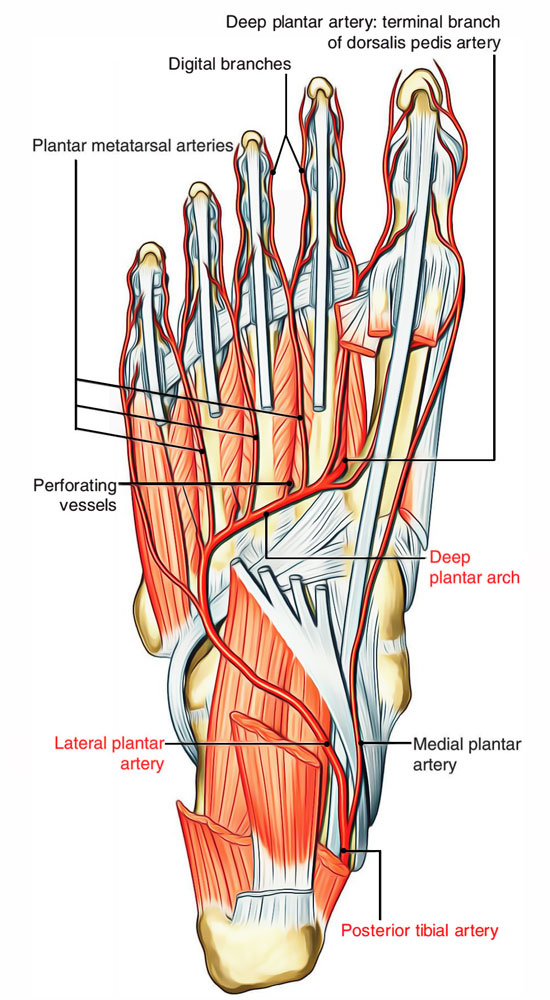
Plantar Arteries
Medial Plantar Artery
The medial plantar artery is the smaller terminal branch of the posterior tibial artery. It originates below the flexor retinaculum and appears in the sole deep to abductor hallucis escorted by the medial plantar nerve on its lateral side. It ends on the medial side of big toe by splitting into subsequent 2 branches:
- A small branch, which enters distally along the medial side of the big toe and anastomoses with the electronic branch of first plantar metatarsal artery, on the lateral side of the big toe.
- A large branch, which divides into 3 superficial digital branches and anastomoses with the first to third plantar metatarsal arteries.
Distribution
It supplies rise to these branches:
- Muscular branches to the adjoining muscles.
- Cutaneous branches to the medial side of the sole.
- Digital arteries (vide supra).
Lateral Plantar Artery
The lateral plantar artery is the bigger terminal branch of the posterior tibial artery. It originates below the flexor retinaculum and runs forwards in the direction of the base of the fifth metatarsal. The lateral plantar nerve is located on its medial side. At the base of the fifth metatarsal bone, it curves medially with concavity facing proximally and runs in the direction of the very first inter-digital space to join the dorsalis pedis artery and so creates the plantar arch. It provides rise to these branches:
- Muscular branches to provide the adjoining muscles.
- Superficial branches to provide skin and fasciae laterally.
- Anastomotic branch to anastomose at the lateral border of foot together with the lateral tarsal and arcuate arteries.
- Calcaneal branch is occasional to the heel.
Plantar arch
It’s an arterial arch created by the direct continuation of the lateral plantar artery from the base of the fifth metatarsal bone to the first intermetatarsal space. It’s finished medially by anastomosing with the terminal part of the dorsalis pedis artery. It stretches from the base of the fifth metatarsal bone to the proximal part of the first intermetatarsal space. It is located between the 3rd and fourth layers of the sole. It’s convex distally across the bases of fourth, third, and 2nd metatarsals. It’s escorted by a deep branch of the lateral plantar nerve, which is located in its concavity.
Branches
It provides rise to these branches:
Four plantar metatarsal arteries: They pass forward in the intermetatarsal spaces and end by breaking up into a set of plantar digital arteries. Near their stage of division, every plantar metatarsal artery provides a distal perforating branch to join the corresponding dorsal metatarsal artery.
The very first plantar metatarsal artery sends a digital branch to the medial side of the big toe. The electronic branch to the lateral side of little toe originates from the lateral plantar artery.
3 proximal perforating arteries: They ascend via the proximal parts of the 2nd, third, and fourth intermetatarsal spaces, and anastomoses with the corresponding dorsal metatarsal arteries.
Key Points
- All the structures (example, chief neurovascular bundle and long flexor tendons) goes into the sole via a gap between the flexor retinaculum and the calcaneus referred to as porta pedis with the exception of the tendon of peroneus longus, which enters the sole via a groove underneath the cuboid named side gate of the sole.
- The passages for proximal and distal perforating arteries are named windows of the sole.

 (52 votes, average: 4.75 out of 5)
(52 votes, average: 4.75 out of 5)