Popliteal artery is the extension of femoral artery. The starting point is adductor hiatus (an opening of osseo-aponeurotic type located in adductor magnusat , the junction of middle one-third and lower one-third of thigh), it gets divided into anterior and posterior tibial arteries when it comes across the floor of popliteal fossa by the medial to lateral side to reach the border of the popliteus.
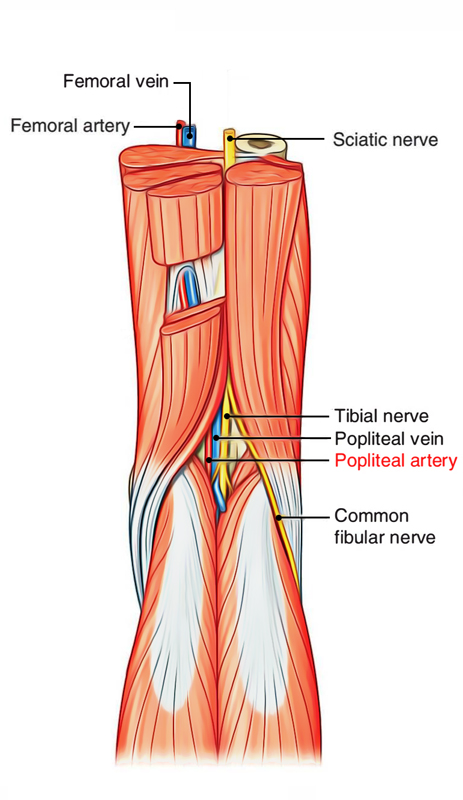
Popliteal Artery
Relations
All these are as follows:
- Anterior (deep): Floor of the popliteal fossa (i.e., popliteal surface of femur, posterior aspect of the knee joint, and fascia covering the popliteus muscle).
- Posterior (superficial): Popliteal vein, tibial nerve, fascial roof, superficial fascia, and skin (from deep to superficial).
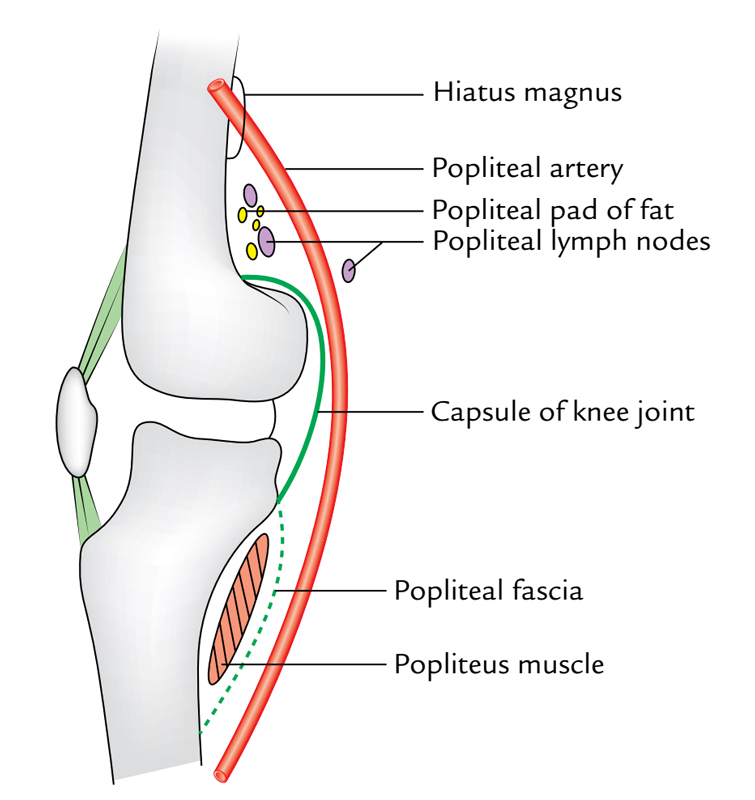
Popliteal Artery: Relations
Branches
All these are split into 3 groups- cutaneous, muscular, and articular (genicular).
- Cutaneous branches: They pierce the roof and supply the overlying skin.
- Muscular branches: They’re large and several in number. The upper branches (2 or 3 in number) supply adductor magnus and hamstring muscles. 1 or 2 of them anastomose with the fourth perforating artery.
The lower muscular branches supply the triceps surae muscles (i.e., 2 heads of gastrocnemius and soleus) and plantaris. - Genicular (articular) branches: They’re 5 in number and provide the knee joint.
1. Superior medial and lateral genicular arteries: They wind around the corresponding side of the femur immediately above the corresponding femoral condyles and take part in the formation of genicular anastomosis.
2. Inferior medial and lateral genicular arteries: They wind around the corresponding tibial condyles and pass deep to the corresponding collateral ligaments of the knee joint to take part in the formation of genicular anastomosis.
3. Middle genicular artery: It pierces the oblique popliteal ligament of the knee to supply the cruciate ligaments and synovial membrane of the knee joints.
Genicular anastomosis: It’s an arterial anastomosis around the knee joint created by the branches of popliteal, anterior tibial and posterior tibial, femoral, and profunda femoris arteries.
This anastomosis keeps sufficient blood supply to the knee joint and leg during flexion of the knee joint, when the popliteal artery is compressed (kinked) and blood circulation in it becomes dull. The anastomosis occurs as follows
- Superior medial genicular artery anastomosis together with the descending genicular branch of the femoral artery and inferior medial genicular artery.
- Inferior medial genicular artery anastomosis with the superior medial genicular artery and saphenous artery- a branch of the descending genicular artery (a branch of femoral artery).
- Superior lateral genicular artery anastomosis together with the descending branch of the lateral circumflex femoral artery and inferior lateral genicular artery.
- Inferior lateral genicular artery anastomosis with the superior lateral genicular artery, anterior and posterior recurrent branches of the anterior tibial artery, and circumflex fibular branch of the posterior tibial artery.

 (51 votes, average: 4.65 out of 5)
(51 votes, average: 4.65 out of 5)