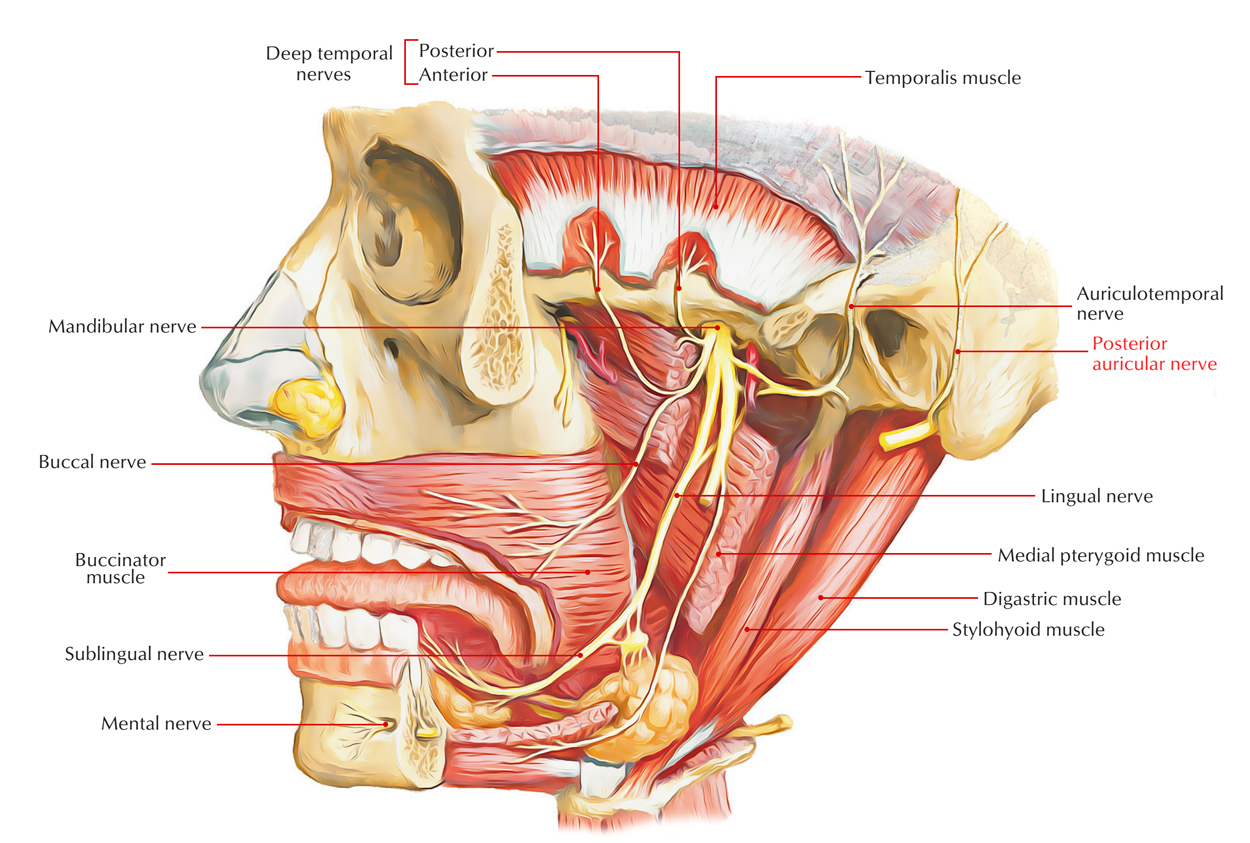
Near the stylomastoid foramen, the posterior auricular nerve arises from the facial nerve and travels upward facing the mastoid process.
Posterior Auricular Nerve
Insertion
- The posterior auricular nerve arises close to the stylomastoid foramen from the facial nerve and in front of the mastoid process runs upwards.
- Here from the auricular branch of the vagus, it is merged with a filament as well as connects with the posterior branch of the great auricular as well as by the lesser occipital.
- As it ascends among the external acoustic meatus along with mastoid process, it splits into auricular and occipital branches.
- On the cranial surface of the auricular, the auricular branch supplies the auricularis posterior along with the intrinsic muscles.
- The occipital branch, along the superior nuchal line of the occipital bone travel backwards as well as supplies the occipitalis.
Connections
The posterior auricular nerve, communicates with:
- Great auricular nerve
- Lesser occipital nerve
- Auricular branch of the vagus nerves.
Branches
The posterior auricular nerve divides into two branches:
- An auricular branch for the posterior auricular muscle along with the intrinsic muscles of the auricle.
- An occipital branch for the occipital belly of the epicranius muscle.
Function
- The posterior auricular nerve follows the posterior auricular artery and stimulates the muscles of the auricle alongside the occipitalis.
- The superior and anterior auricular muscles are however stimulated via the temporal branches of the facial nerve.
- The posterior auricular nerve also sends sensory fibers towards the auricle.
x

 (47 votes, average: 4.74 out of 5)
(47 votes, average: 4.74 out of 5)