Pterygoid process protrudes down from the junction in the middle of the body as well as greater wing of sphenoid posterior towards the last molar tooth. It splits within medial along with lateral pterygoid plates; the pterygoid fossa divides them from each other. A free posterior border is found in each plate.
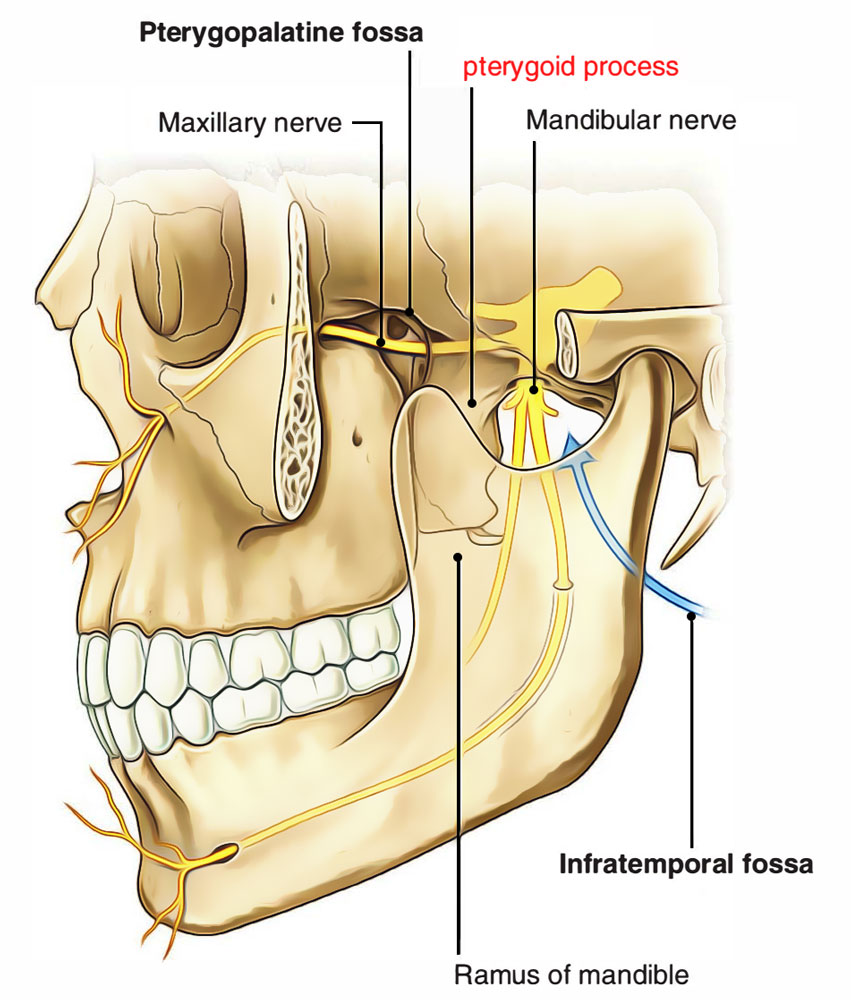
Pterygoid process
The upper end of posterior border of medial pterygoid plate encloses a triangular recession referred to as scaphoid fossa, and the lower end possesses a hook-like protuberance known as pterygoid hamulus.
Structure
- The pterygoid processes spread out downward via the interconnection of the body as well as the greater wings in the anterior part of base of skull.
- Each of these processes has a tapered medial plate and wider lateral plate, which are divided from each other by the pterygoid fossa.
- The pterygoid hamulus is a hook-like projection from which each medial plate of the pterygoid process inferiorly terminates with. Each medial plate of pterygoid process divides superiorly in order to create the small, shallow scaphoid fossa.
- The opening of the pterygoid canal, which travels forward near the anterior margin of the foramen lacerum, is located at the root of the medial plate of the pterygoid process, immediately superior towards the scaphoid fossa.
Parts
Each of these processes is made up of a constricted medial plate as well as a wider lateral plate divided by the pterygoid fossa.
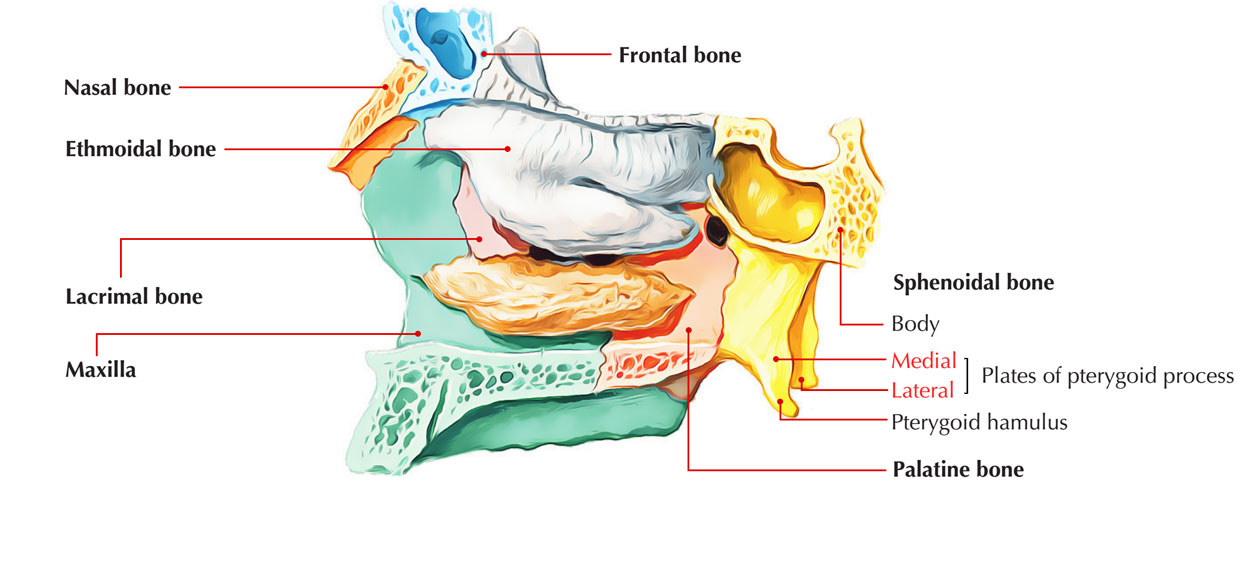
Plates of Pterygoid process
Medial pterygoid plate
The medial pterygoid plate a.k.a. medial pterygoid lamina of the sphenoid bone is a horse-shoe shaped process which emerges from its bottom.
It is narrower as well as longer compared to the lateral pterygoid plate and turns laterally at its lower edge into a hook-like protuberance, the pterygoid hamulus, about which travels the tendon of the tensor veli palatini.
- The lateral surface of this plate creates portion of the pterygoid fossa.
- The medial surface is made up of the lateral margin of the choana or posterior opening of the conforming nasal cavity.
Lateral Pterygoid Plate
- The lateral pterygoid plate of the sphenoid a.k.a. lateral lamina of pterygoid process is wide, slim, and outwards or inside out.
- It creates the lateral portion of a horseshoe like protuberance which spreads outwards from the inferior part of the sphenoid bone.
- It acts as the beginning of the lateral pterygoid muscle, which enables the mandible in order to move within a lateral as well as medial direction, or through side-to-side
Pterygoid Canal
It is found in pterygoid process of the sphenoid bone attaching anterior wall of foramen lacerum towards pterygopalatine fossa.
It conveys:
- Nerve of pterygoid canal a.k.a. Vidian’s nerve.
- Vessels of the pterygoid canal.
Relations
- The zones divided via the medial and lateral plate are
- Pterygoid fissure inferiorly.
- Pterygoid fossa posterosuperiorly.
- The medial boundary of the infratemporal fossa is created via the lateral part of the lateral pterygoid plate.
- The posterior wall of the pterygopalatine fossa created via the root of the pterygoid process.
- On the anterior part of the root of the pterygoid process, the anterior opening of the pterygoid canal is also located.
- The pterygoid hamulus has two significant associations, linked to its utility:
- Tensor veli palatini tendon travels directly at the back of it.
- Superior connection of the pterygomandibular raphe.
Attachments
- Lateral pterygoid muscle has it’s the lower part connect to the lateral part of the lateral pterygoid plate.
- Medial pterygoid muscle is attached towards medial part of the lateral pterygoid plate.
- Superior pharyngeal constrictor is attached towards inferior end of the medial pterygoid plate.

 (51 votes, average: 4.85 out of 5)
(51 votes, average: 4.85 out of 5)