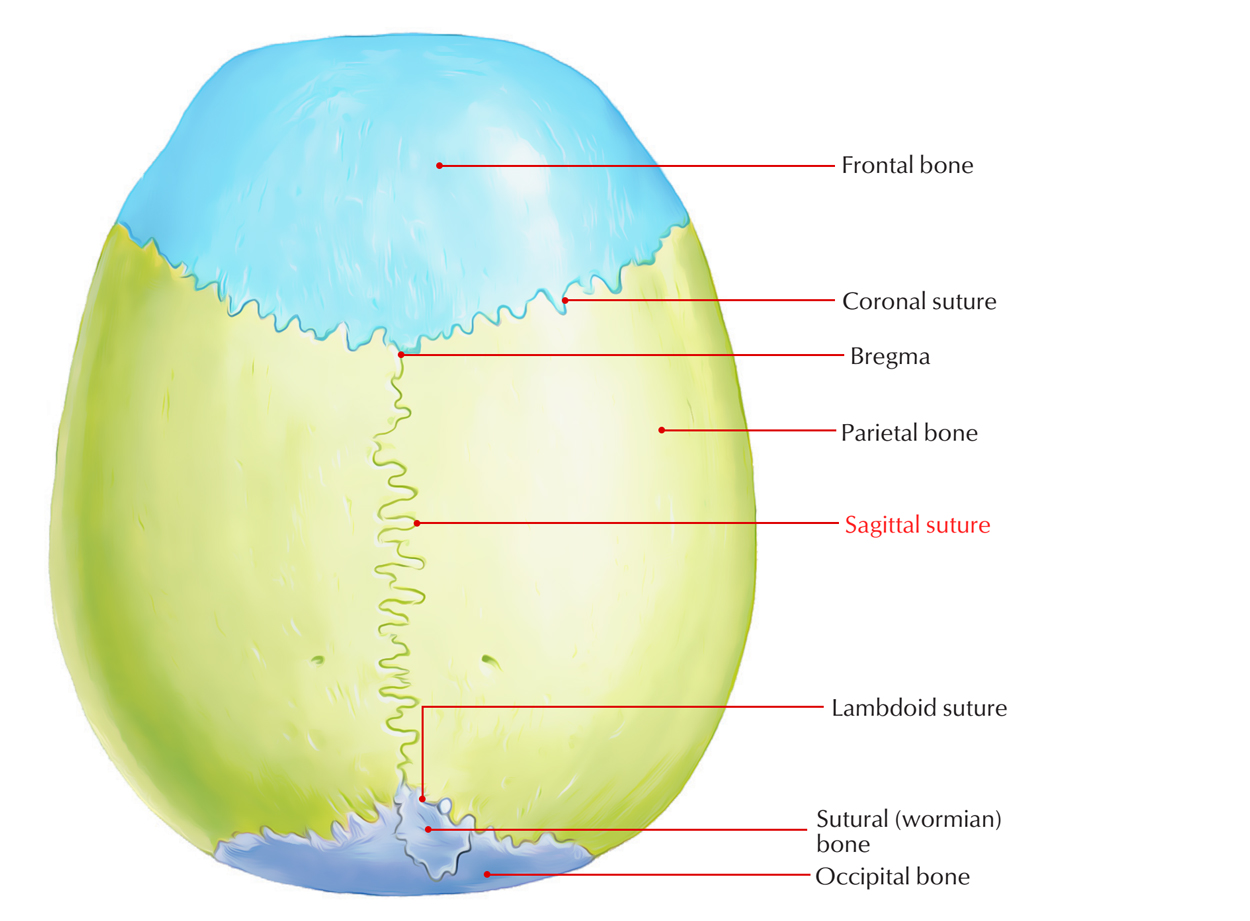
The sagittal suture is a fibrous connective tissue joint in the middle of the two parietal bones of the skull. The sagittal suture is also called Interparietal suture or Sutura interparietalis.
Sagittal Suture
The sagittal suture is located medially in the middle of the two parietal bones. This is finely denticulated, with the exception of the region of the obelion, though this will not be seen if elimination of the suture from the merging of the two parietal bones has been completed. Posteriorly the sagittal suture and lambdoid suture combine at the lambda, which indicates the position of the posterior fontanelle of the foetus, in the adult.
Related Features
- Bregma is a point on which coronal and sagittal sutures merge.
- Vertex is the highest spot on the skull. It is located on the sagittal suture near its middle and is located behind the bregma a few centimeters.
- Parietal foramen is a small foramen at parietal bone close to sagittal suture in front of lambda.
- Obelion is a spot on sagittal suture in the middle of the two parietal foramina.
Clinical Significance
Scaphocephaly
Scaphocephaly a.k.a. dolichocephaly is a type of craniosynostosis, in which early closure of the sagittal suture causes weak lateral growth of the skull but continues anteroposterior growth creating a contracted elongated shape of the skull.
- Sagittal craniosynostosis happens because of a disorder of the mesenchyme in which intramembranous ossification of the suture occurs, which causes premature fusion.
- This causes scaphocephaly, or “boat-shaped” skull, described by anterior-posterior elongation with contraction over the parietal bones along with a prominent occiput and forehead.
Single suture synostosis including the sagittal suture may be a part or symptom of a syndrome, like cranioectodcrmal dysplasia.

 (59 votes, average: 4.51 out of 5)
(59 votes, average: 4.51 out of 5)