There are three primary salivary glands sublingual, submandibular and parotid. Each has their own ducts. Salivary ducts are channels that bring saliva to the mouth right after it is produced in salivary glands. They open up in buccal cavity. The ducts of the salivary glands enable the movement of salivary juice via the glands to the oral cavity:
- Parotid duct (Stenson duct): links the parotid gland to the buccal mucosa, beside maxillary second molar.
- Submandibular duct (Wharton duct): links the submandibular gland to the floor of the mouth.
- Duct of Rivinus: the sublingual gland drains pipes via many small ducts all which open up into the floor of the mouth and are collectively called the duct of Rivinus; the biggest is the main duct of the sublingual salivary gland called Bartholin duct.
Parotid Ducts
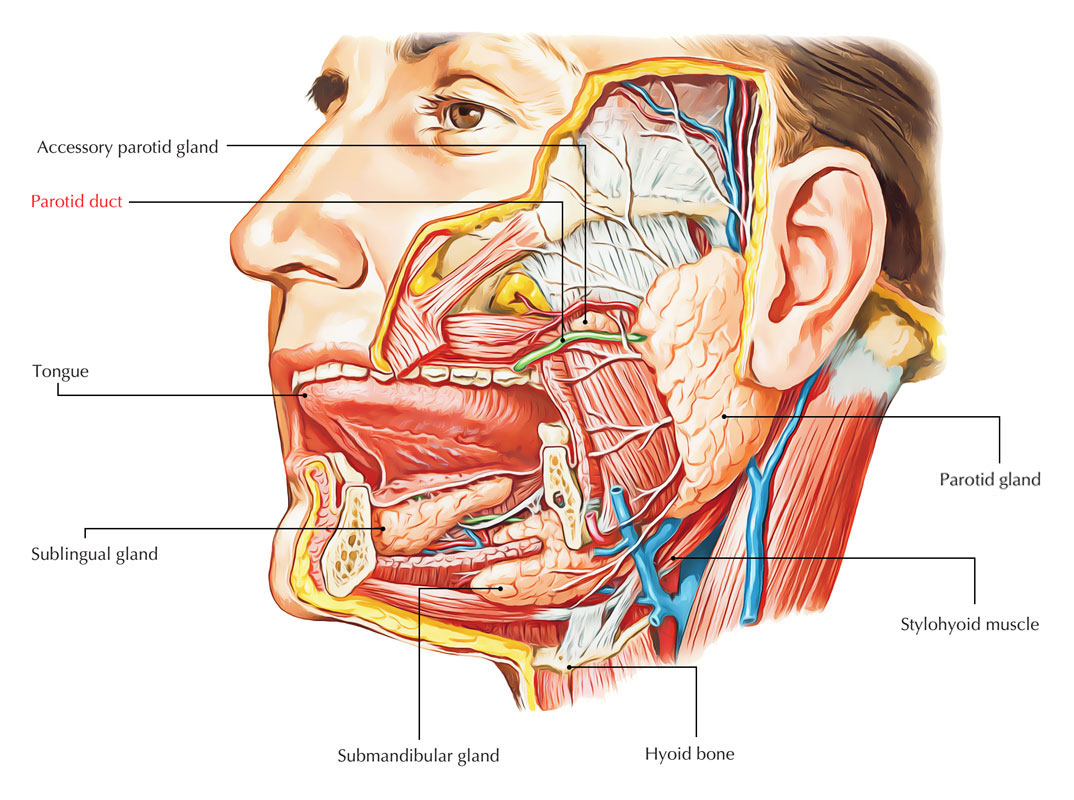
Parotid Ducts
- It is formed when numerous interlobular ducts the biggest ducts inside the parotid gland connect.
- It arises via the gland and runs forward along the lateral side of the masseter muscle.
- Throughout its route, the duct is neighbored by the buccal fat pad and after that it takes a high turn at the border of the masseter and goes through the buccinator muscle, opening into the vestibule of the mouth, the region of the mouth in between the cheek and the gums, at the parotid papilla, which lies throughout the second superior molar tooth.
- The buccinator serves as a valve that avoids air forcing into the duct, which would trigger pneumoparotitis. Going with the duct superiorly is the transverse facial artery and upper buccal nerve; going with the duct inferiorly is the lower buccal nerve.
The Submandibular Duct
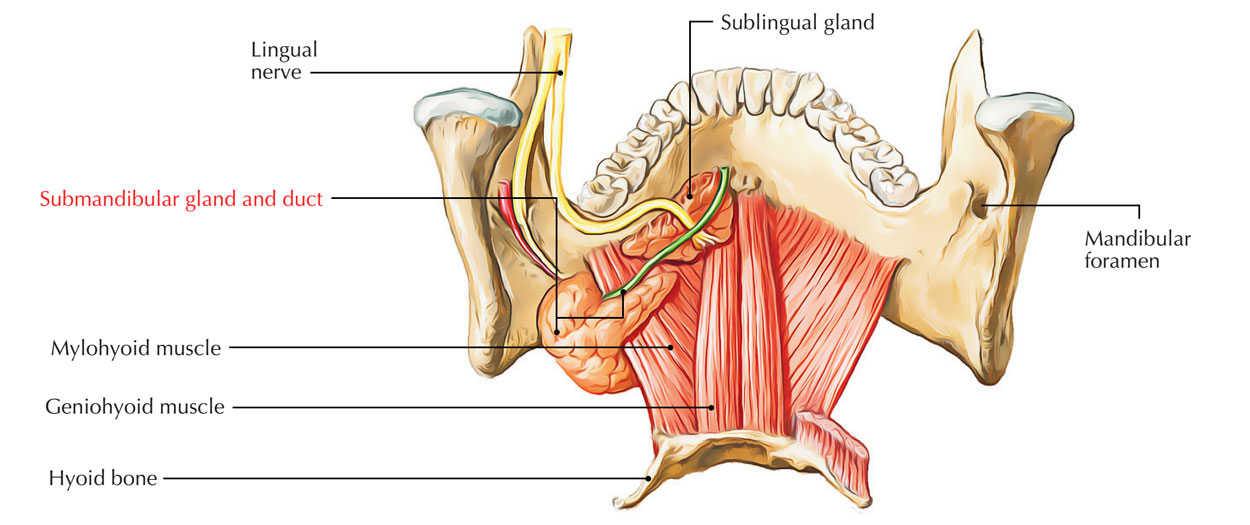
The Submandibular Duct
- The submandibular gland creates combined serous and mucous secretions.
- It actively produces iodine and reveals strong contrast improvement.
- The submandibular duct like the parotid duct has to do with 5 cm long and arises anteriorly via the deep section of the gland to run forward with the lingual nerve.
- On the floor of the buccal cavity, it opens on the sublingual papilla.
- It starts by many branches via the superficial surface of the gland, and runs forward in between the mylohyoid, hyoglossus, and genioglossus muscles.
- It then enter in between the sublingual gland and the genioglossus and opens by a narrow entrance on the top of a small papilla at the side of the frenulum of the tongue.
Sublingual Gland Ducts (Duct of Rivinus)
The sublingual gland drains through many small ducts, all which open into the floor of the mouth and are collectively called the duct of Rivinus. The biggest is the main duct of the sublingual salivary gland called Bartholin duct.

 (53 votes, average: 4.57 out of 5)
(53 votes, average: 4.57 out of 5)