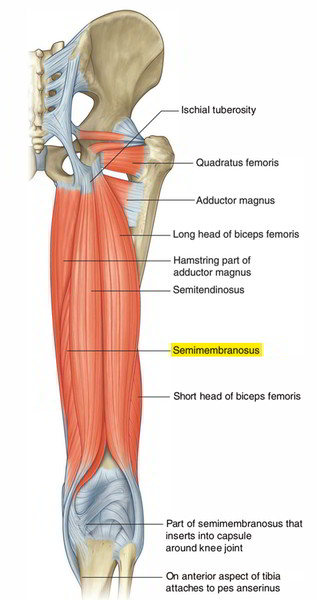
The semimembranosus muscle is located deep towards the semitendinosus muscle inside the posterior part of the thigh. Extensions via the tendon as well enter inside and support the creation of ligaments as well as fascia over the knee joint. It is connected superior to the superolateral indentation over the ischial protuberance as well as under primarily towards the hollow along with surrounding bone at the medial as well as posterior sides of the medial tibial condyle.
Origin
It emerges via the upper lateral portion of the quadrilateral region of the ischial protrusion. It is membranous within the upper half but fleshy inside the lower half. It is located deep towards semitendinosus.
Structure and Insertion
- The semimembranosus contains a fleshy muscle belly along with a tendon in each termination. It originates as a wide “membranous” tendon which is rounded side to side in order to create a longitudinal channel superiorly.
- The channel expands downward inside its fleshy muscle belly, as well as the belly of the semitendinosus is located in this channel. The semimembranosus terminates inside a strong, flattened tendon which emerges via the medial portion of its muscle belly
- This tendon is not detectable externally, but lies between the tendons of the semitendinosus and gracilis at the inner back corner of the knee.
- The muscle fibers of the fleshy belly expand down towards the layer of the middle of the medial condyle of the femur that carries these fleshy fibers onto the fleshy fibers of the medial head of the gastrocnemius.
Muscle Belly
The muscle belly of the semimembranosus is partially superficial at both parts of the semitendinosus, medial towards it like an elongated shape on nearly the complete length of the inner back corner of the thigh as well as lateral towards the lower portion of its belly along with tendon.
Lower Lateral Portion
- The lower lateral portion is located just over the backside of the knee, just where it occupies the majority of the popliteal space as well as push against the biceps femoris.
- The combined shape is located just medial to the midline of the hack of the thigh. This specific part may be considered a descending elongation of the extended shape of the semitendinosus belly located directly above it.
- The lower lateral part protrudes while full knee extension, though it is partly or fully encompassed by the popliteal fat pad.
- This section of the semimembranosus helps straight towards the popliteal protrusion which grows laterally towards the fold created by the semitendinosus tendon, primarily inside the extended knee whenever the fat is thin
Medial Portion
The medial part of the semimembranosus does not expand completely as much as the gluteus maximus, however terminates inside a point where the semitendinosus as well as adductor magnus bellies converge. It occasionally divides the section of the semimembranosus superior to it in an independent shape. An oblique tendinous intersection, pointed downward as well as medially and also alongside the medial edge of the adductor magnus, lies through the upper portion of this medial shape. Operating along with the semitendinosus muscle, it medially turns the thigh on the hip joint as well as the leg on the knee joint. The semimembranosus flexes the leg over at the knee joint and also expands the thigh on the hip joint.
Nerve supply
The semimembranosus muscle is stimulated by tibial section of the sciatic nerve.

 (56 votes, average: 4.82 out of 5)
(56 votes, average: 4.82 out of 5)