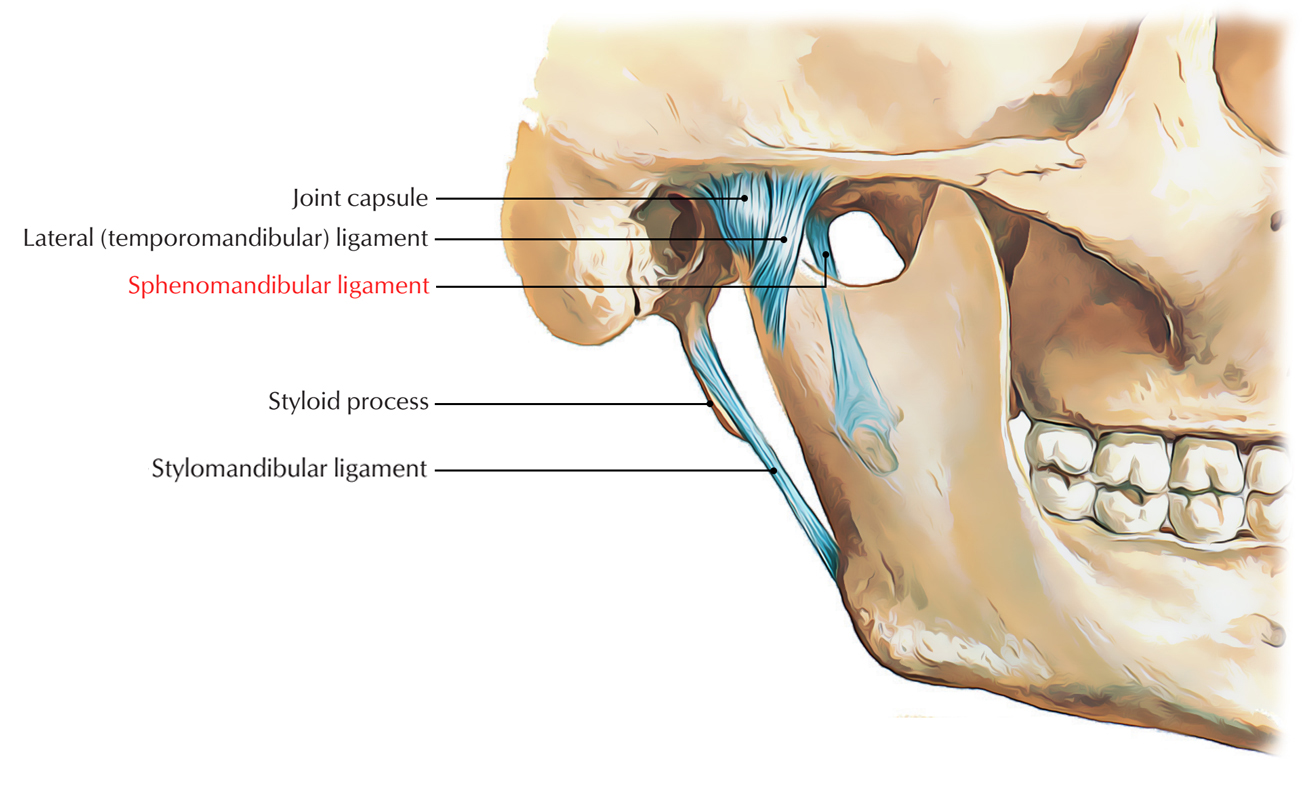
The sphenomandibular ligament is an extracapsular ligament which belongs to the temporomandibular joint.
Sphenomandibular Ligament
Structure
Sphenomandibular ligament is remnant of the unossified middle portion of the sheath belonging to the Meckel’s cartilage of the first pharyngeal arch. It gets highlighted and rigid whenever the mandible is protruded.
Sphenomandibular ligament is attached superior towards the spine of the sphenoid and inferior towards the lingula and lower margin of the mandibular foramen of the mandible. It is located out of the joint capsule at a deeper plane.
Relations
Relations of sphenomandibular ligament:
- Laterally:
- Lateral pterygoid muscle
- Auriculo-temporal nerve
- Maxillary artery
- Inferior alveolar nerve and vessels
- Medially:
- Medial pterygoid
- Chorda tympani nerve
- Wall of the pharynx.
The sphenomandibular ligament is perforated via mylohyoid nerve and vessels around its lower end.
Functions
The sphenomandibular ligament limits expansion of the mandible inferiorly. It is loose when the temporomandibular joint is closed. As the condyle of the mandible gets in front of the temporomandibular ligament, it becomes tightened.
Clinical Significance
For administration of local anesthetic during inferior alveolar nerve block, the sphenomandibular ligament is an important landmark.

 (53 votes, average: 4.57 out of 5)
(53 votes, average: 4.57 out of 5)