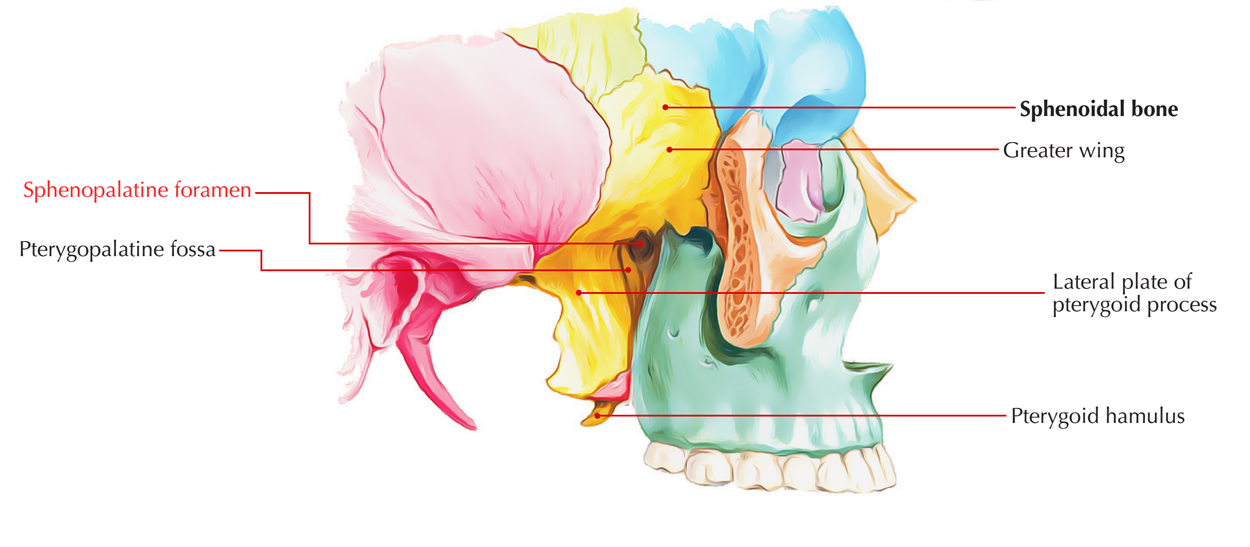
The sphenopalatine foramen is found inside the skull. It connects the nasal cavity and the pterygopalatine fossa.
Sphenopalatine Foramen
Structure
In the adult skull this foramen travels via the pterygopalatine fossa inside the posterior section of the superior meatus of the nose.
It afterwards sends out:
- Sphenopalatine artery
- Sphenopalatine vein
- Superior nasal nerves
- Nasopalatine nerves
The sphenopalatine notch divides the processes of the superior margin of the palatine bone, which is afterwards transformed into the sphenopalatine foramen via the inferior surface of the body of the sphenoid bone.
Function
1. It links the nasal cavity as well as the pterygopalatine fossa.
2. Sending outwards
- Nasopalatine nerve
- Posterior superior nasal nerves
- Sphenopalatine artery and vein
Clinical Significance
Prineural Tumor
Perineural tumour is a condition related to local incursion where primary tumor cells multiply along the tissues of the nerve sheath. It occurs commonly within head and neck cancers.
Perineural tumour spread symptoms:
- Nerve thickening
- Broadening of the neural foramen.
- Loss of the fat (lipid) near the nerve.
- Growth of the nerve following different administration.

 (47 votes, average: 4.71 out of 5)
(47 votes, average: 4.71 out of 5)