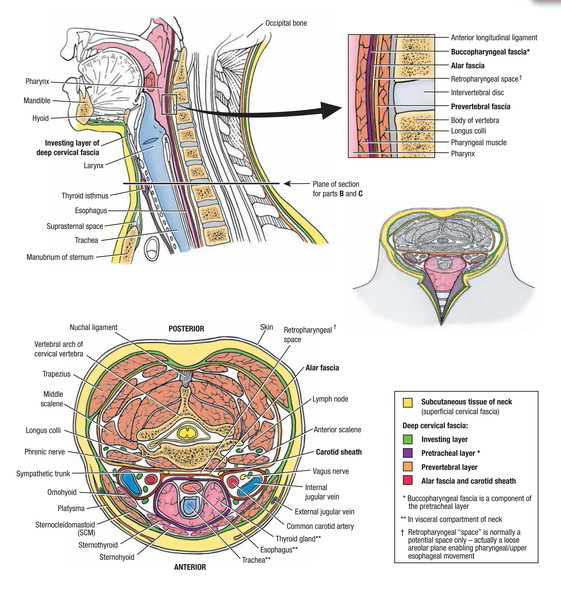
It is made up of thin layer of loose areolar tissue and includes a thin sheet of a muscle known as platysma.
It also includes cutaneous nerves, superficial veins, superficial lymph nodes and lymph vessels along with platysma. The location of cutaneous nerves and veins is deep to the platysma.
Compared to men, the amount of subcutaneous fat is more in kids and women.
Platysma
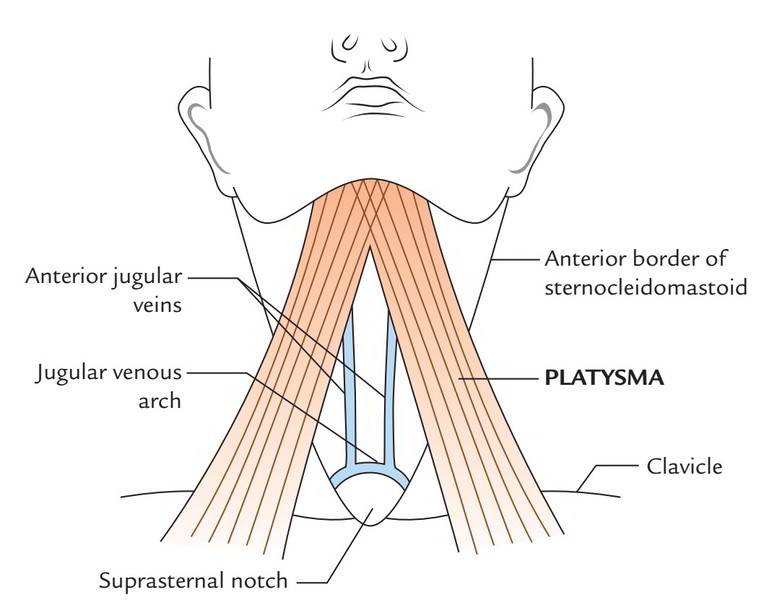
It’s located in the superficial fascia of the side of the neck and is a thin quadrilateral broad sheet of muscle. From the very front of the neck it ascends onto the face. Morphologically it signifies the remnant of panniculus carnosus of creatures. Second pharyngeal arch is the growing point. It covers superior part of the anterior triangle of the neck and the anteroinfeSecoior part of the posterior triangle.
Origin
The point of origin is from skin and deep fascia covering the upper parts of the pectoralis major and anterior part of the deltoid muscle.
Insertion
After origin, the fibres sail upwards and forwards superficial to the clavicle and sternocleidomastoid. It crosses over the lower part of the posterior triangle and upper part of the anterior triangle to reach the lower border of the mandible, where anterior fibres decussate with the corresponding fibres of the opposite side on the other side of the midline for about 2.5 cm below and behind the symphysis menti. Majority of the fibres (intermediate and posterior) are added into the lower border of the body of the mandible. Some posterior fibres pass superficial to the angle of the mandible and masseter muscle and after that turn medially to fit into the skin of angle of the mouth via risorius.
Nerve Supply
The platysma is supplied by the cervical branch of the facial nerve.
Actions
Acting from above, the platysma creates vertical ridges in the skin of the neck discharging the pressure of skin over the underlying veins and therefore helps in the venous return. It, for that reason, functions to facilitate the pressure of tight collar. Acting from below, it will help to depress the mandible and pulls the angle of the mouth downwards and laterally as in expression of terror/ dread.
Though the risorius seems to be a continuance of platysma, it’s another Nerve Supply, specifically, the buccal branch of facial nerve.
Clinical Significance
The surgeons while closing an incision in the neck, suture platysma meticulously as a different layer to stop adhesion of skin and subcutaneous tissue to deeper neck muscles because such adhesions cause the overlying skin to move as the deeper muscles contract or relax and the wound will heal with an awful scar that is cosmetically unacceptable.
Since the superficial veins of the neck is located below the cover of platysma, the retraction of split platysma keeps the cut veins open. These veins can not retract because of their connection to the deep cervical fascia. But if deep fascia is cut, the veins retract and the majority of the bleeding stops.

 (48 votes, average: 4.83 out of 5)
(48 votes, average: 4.83 out of 5)