The retinaculum is around 3 cm broad from top to bottom. It is strained through the anterior perimeter of the triangular subcutaneous region of the fibula going on medially and a little upwards to the lower portion of the anterior border of the tibia.
The extensor retinaculum describes the set of ligaments within the ankle that link the tibia as well as fibula, that are the bones of the lower leg.
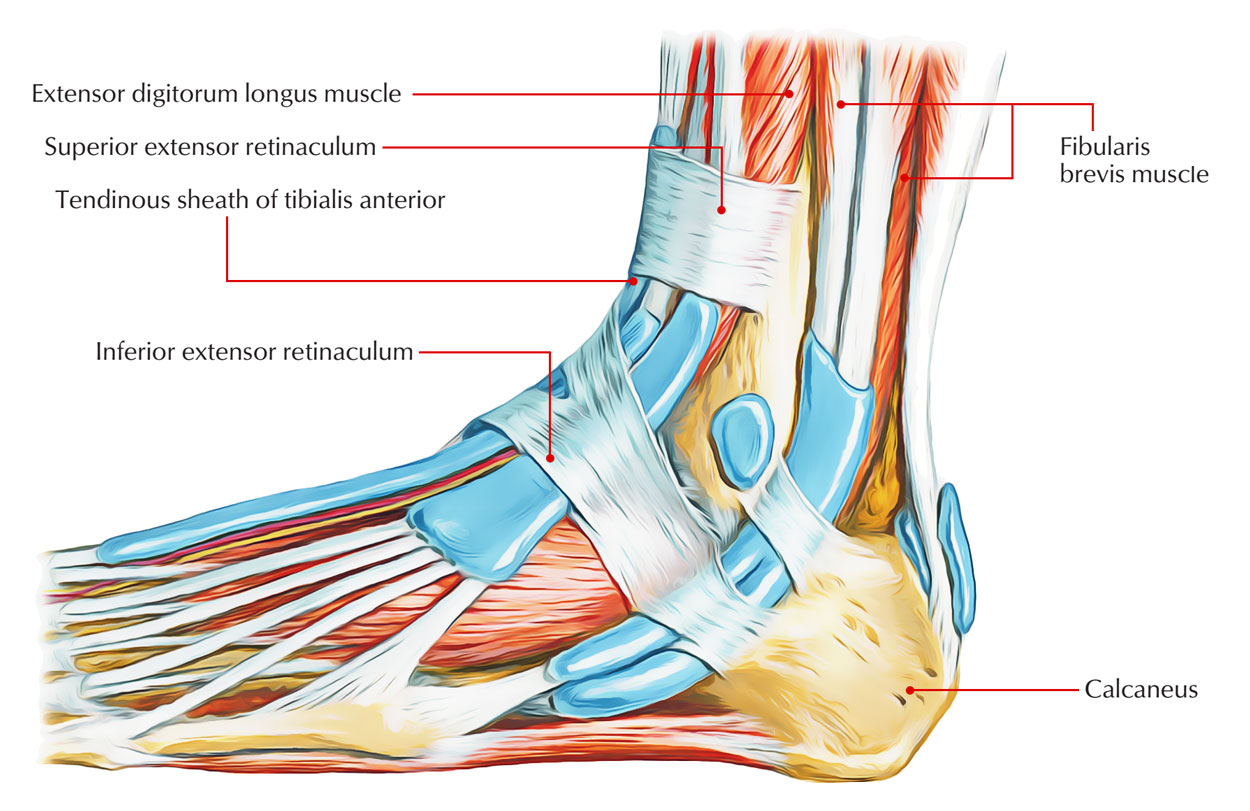
Superior Extensor Retinaculum
The Achilles tendon and tissue in the sole of the foot are also linked by the extensor retinaculum. The superior extensor retinaculum ligament expands throughout the back of the leg and is connected horizontally to the fibula and in the middle of the tibia.
Attachments
- Medially, forming the anterior limit of the extended triangular region simply above the lateral malleolus it is connected to the lower part of the anterior border of the tibia, and laterally to the lower part of the anterior border of the fibula.
- These ligaments are a group of fibrous bands inside the fascia of the leg that connect the extensor tendons to the joint of the ankle.
- The superior extensor retinaculum intercrosses over the front area of the ankle and connects the peroneus tertius, extensor hallucis longus, tibialis anterior, and also the extensor digitorum longus tendons to the joint of the ankle.
- The inferior extensor retinaculum is the lower band of extensor retinaculum which connects width wise to the calcaneus (heel bone) and overpasses and beneath the extensor muscle tendons in the ankle.
The following tendons pass beneath the superior extensor retinaculum:
- Extensor digitorum longus tendon
- Extensor hallucis longus tendon
- Peroneus tertius tendon
- Tibialis anterior tendon
Interactions
The superior extensor retinaculum also communicates with tendons in your lower body, so injury and pain to this ligament may have other impacts. Traumas to the superior extensor retinaculum were associated with injuries in the tibialis anterior tendon, which links to your shin muscles. As a result, if one ignores pain in superior extensor retinaculum and experience a ligament rupture or tear, you may deal with increased danger of injury to the tendons and muscles that go along your shins.
Clinical Significance
Indications of Injury and Impact on Muscles
The pain felt with a superior extensor retinaculum injury is generally localized accompanying the front of the foot and ankle. In many cases, damage to the ligament may impact muscle movement, avoiding a complete variety of activity at your ankle. Given that the superior extensor retinaculum engages with tendons linked to your shin muscles, you may also see irregular muscle working in your shins. If one continues to run even when one’s in pain, the ligaments’ result on muscle function may even more add to injury.
Treatment
- Limitations of the retinacula can be dealt with rather efficiently with Manual Treatment (Active Release Techniques, Graston Method, and Massage Treatment) and a series of restorative workouts.
- Treating with manual treatment includes breaking down limitations in between the retinaculum and the tendon. Basically the professional is bringing back relative motion in between the retinaculum and the tendons (and obviously the muscles that the tendons are connected to).
- The specialists must also concentrate on the fascial lines of tension. Lines of tension in fascia are typically developed throughout injury in numerous areas not simply at the site of pain. If these regions of fascial tension can be launched, then typical fascial stress can be brought back.
- Bring back total fascial stress, besides launching adhesions in between retinaculum and the soft tissues that pass under them, can have substantial results in fixing an injury.

 (58 votes, average: 4.52 out of 5)
(58 votes, average: 4.52 out of 5)