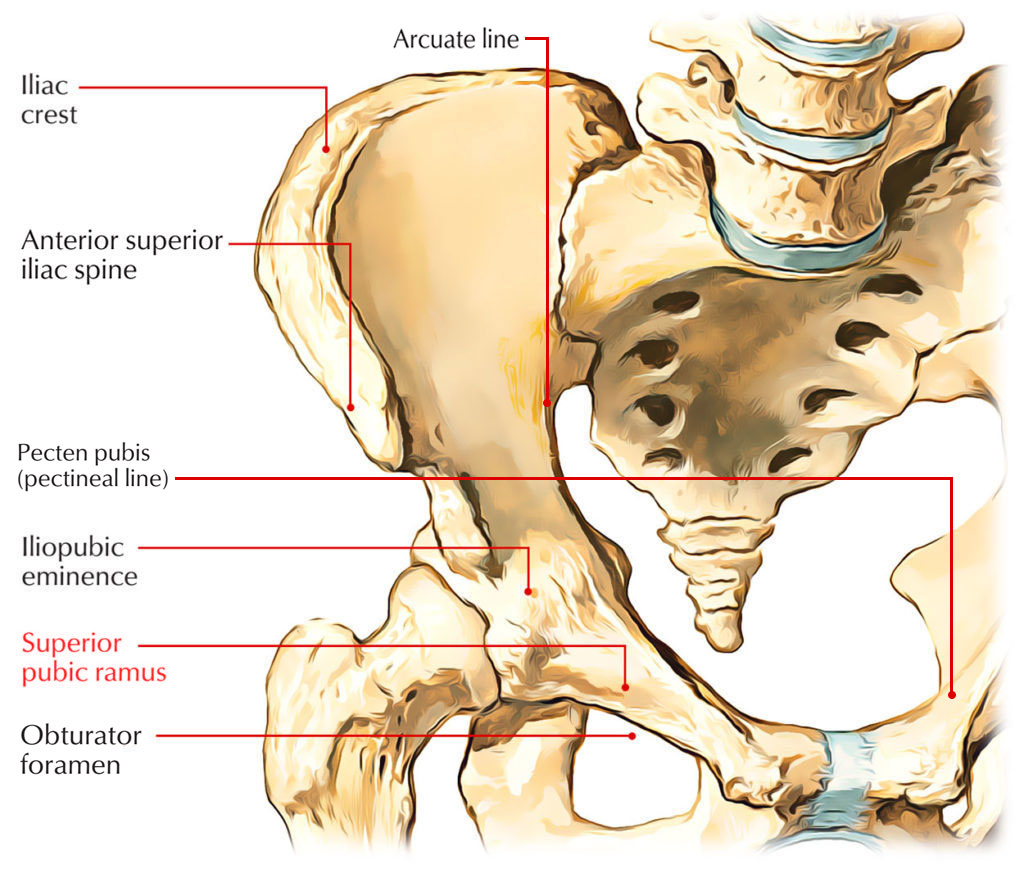
The superior pubic ramus connects with the ilium along with ischium at its base, which is located toward the acetabulum and protrudes posterolaterally from the body. The sharp superior border of triangular surface creates part of the linea terminalis of the pelvic bone as well as the pelvic inlet and is called the pectineal line a.k.a. pecten pubis. Anteriorly, the pubic crest is constant with pectineal line and is also a portion of the linea terminalis and pelvic inlet. The obturator groove exhibits the inferior surface of the superior pubic ramus, and also creates the upper border of the obturator canal.
Superior Pubic Ramus
Surface and Borders
It spreads out from the body of pubis towards the acetabulum over the obturator foramen.
Borders
It has three borders that are pectineal line, obturator crest, and inferior border.
Pectineal line
The pectineal line which is also called pecten pubis ranges from pubic tubercle towards the iliopubic eminence. A part of the pelvic brim is made by the pectineal line.
Fibers of the pectineal ligament and the proximal origin of the pectineus muscle are located across it. It makes the iliopectineal line together with the arcuate line.
Obturator crest
The obturator crest ranges from pubic tubercle to the acetabular notch. It creates a part of the border of the obturator foramen and also provides connection to the obturator membrane.
Inferior border
The inferior border makes the upper border of the obturator foramen.
Surfaces
It has three surfaces:
- Pectineal
- Pelvic
- Obturator
Pectineal Surface
The pectineal surface is located in the middle of the pectineal line and obturator crest. It ranges from pubic tubercle to the iliopubic eminence.
Pelvic Surface
The pelvic surface is located between the inferior border of the superior ramus and pectineal line.
Obturator Surface
The obturator surface is found among the obturator crest as well as inferior border.
Clinical Significance
Fractures
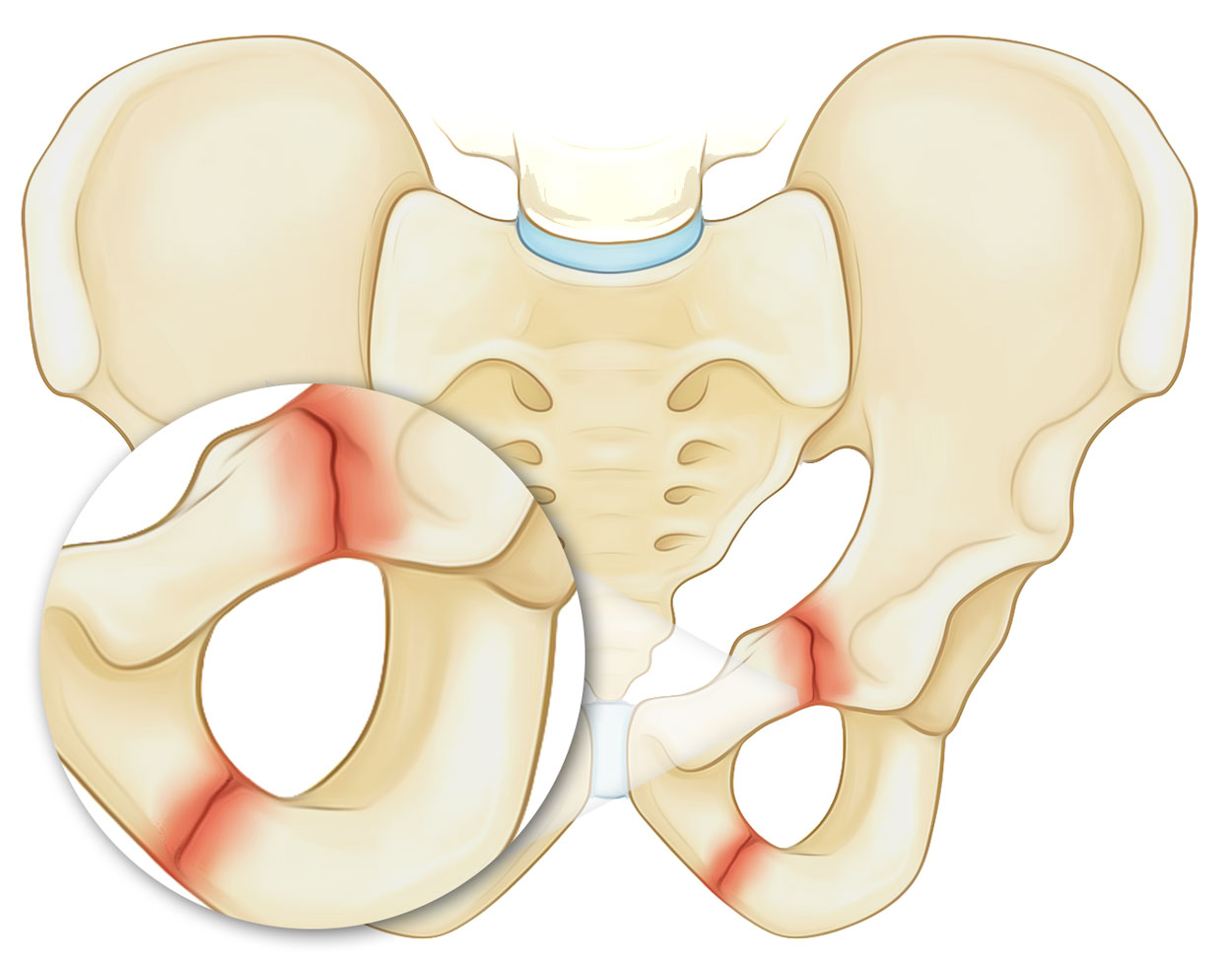
Pubic Ramus Fractures
In children, the most common osseous fracture of pelvic ring occurring in almost 50% cases is a ramus fracture, with most being one-sided and mainly including the superior pubic ramus. These are specifically the majority of childhood injuries. Though, avulsion fractures are not generally included statistically, which are hardly ever included in most events focused on substantial pediatric pelvic injuries.

 (55 votes, average: 4.89 out of 5)
(55 votes, average: 4.89 out of 5)