The suprapleural membrane, also known as Sibson fascia is a strong fascial connective tissue layer above the superior thoracic inlet on each side, placed on top of the tips of the lungs.
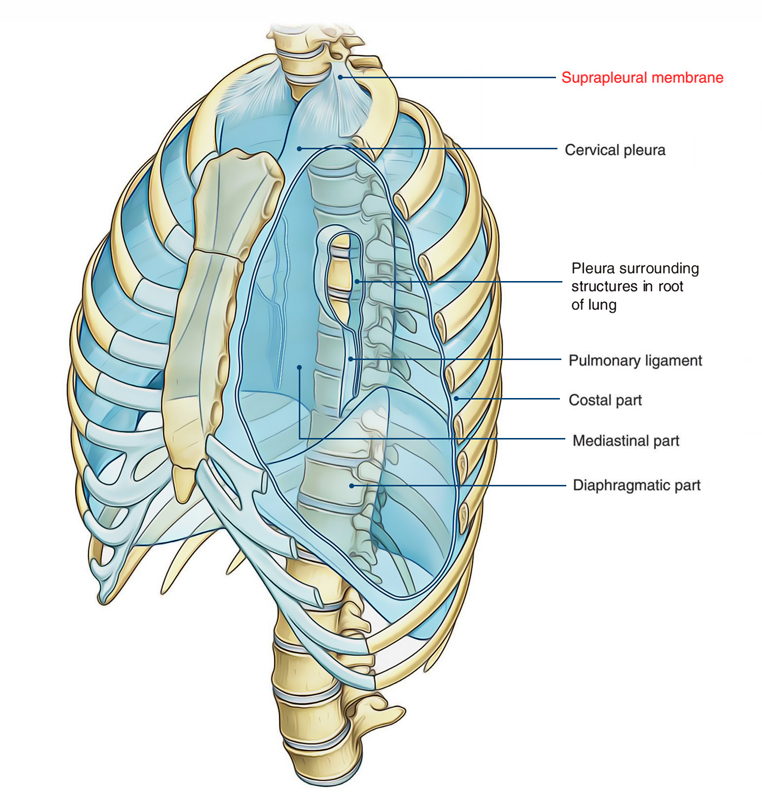
Suprapleural Membrane
It can be said to be an extension of the tendinous attachment of the scalenus minimus muscle. It slopes down towards the horizontal as the inlet on the identical oblique angle.
Structure
The structure fastens itself towards the internal margin of the first rib along with the transverse processes of vertebra C7. It spreads approximately 1 inch more superior towards the superior thoracic aperture.
- Laterally, it is attached to the medial margin of the first rib along with costal cartilage.
- It is attached at its apex towards the tip of the transverse process of the seventh cervical vertebra.
- Medially, it is attached to the fascia that covers the structures going from the thorax inside the neck.
- Its peripheral attachment range varies.
- Deep portion of the membrane can be quite strong and aponeurotic.
- The scalenus minimus occasionally swaps the deep or posterior portion of the membrane.
- In diameter, the muscle may be till 10 mm in its broadest portion, but generally it is much smaller.
The membrane envelops the apical pleura and interferes in the middle of it as well as the subclavian artery. The margin of the first rib, the foramen via which the first thoracic nerve escapes creates the posterior margin of the membrane.
Relations
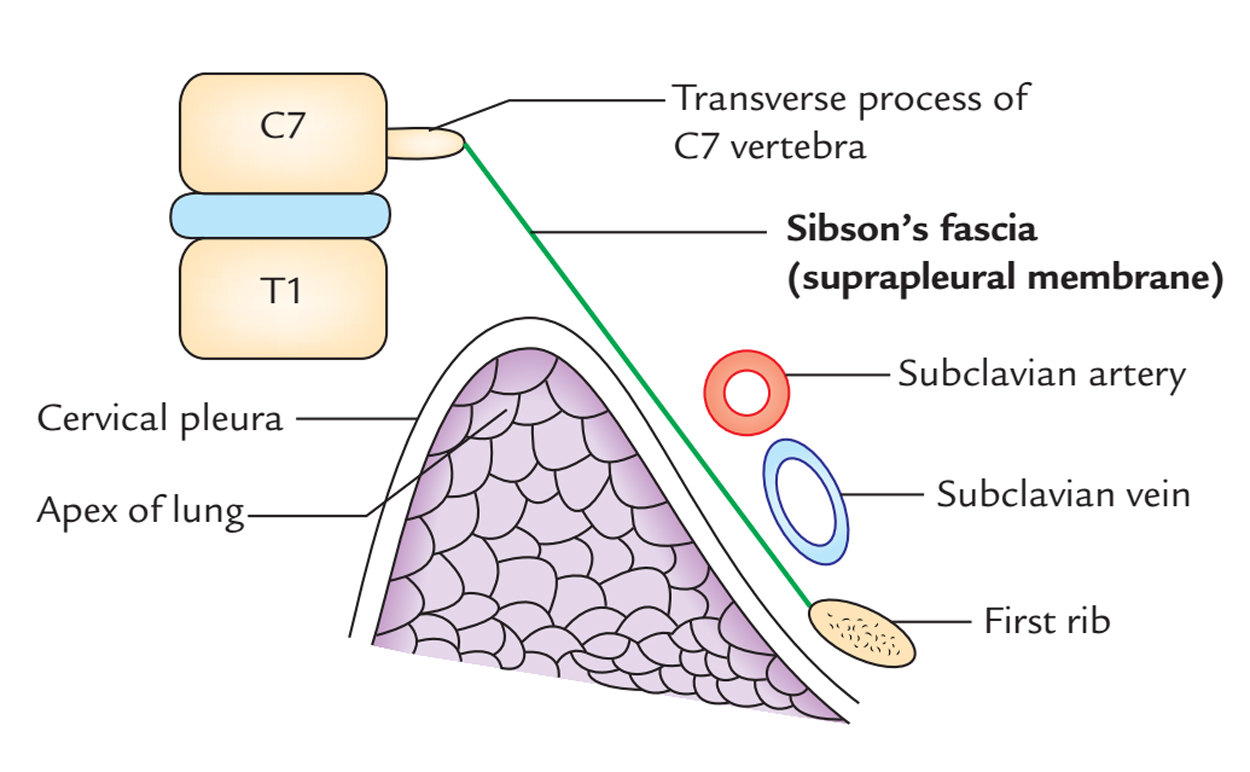
Suprapleural Membrane: Relation
Its superior surface is associated with the subclavian vessels and its inferior surface is related to cervical pleura, covering the apex of the lung.
Functions
The functions of Sibson’s fascia are as follows:
- It protects the underlying cervical pleura, beneath which is located the apex of the lung.
- It resists the intrathoracic pressure at the time of respiration. Consequently, the root of neck is not puffed up and down during respiration.
- Apical reinforces for the pleural cavity in the root of the neck are provided is provided by the suprapleural membrane.
Morphologically, Sibson’s fascia represents the spread out degenerated tendon of scalenus minimus (or pleuraiis) muscle.

 (61 votes, average: 4.72 out of 5)
(61 votes, average: 4.72 out of 5)